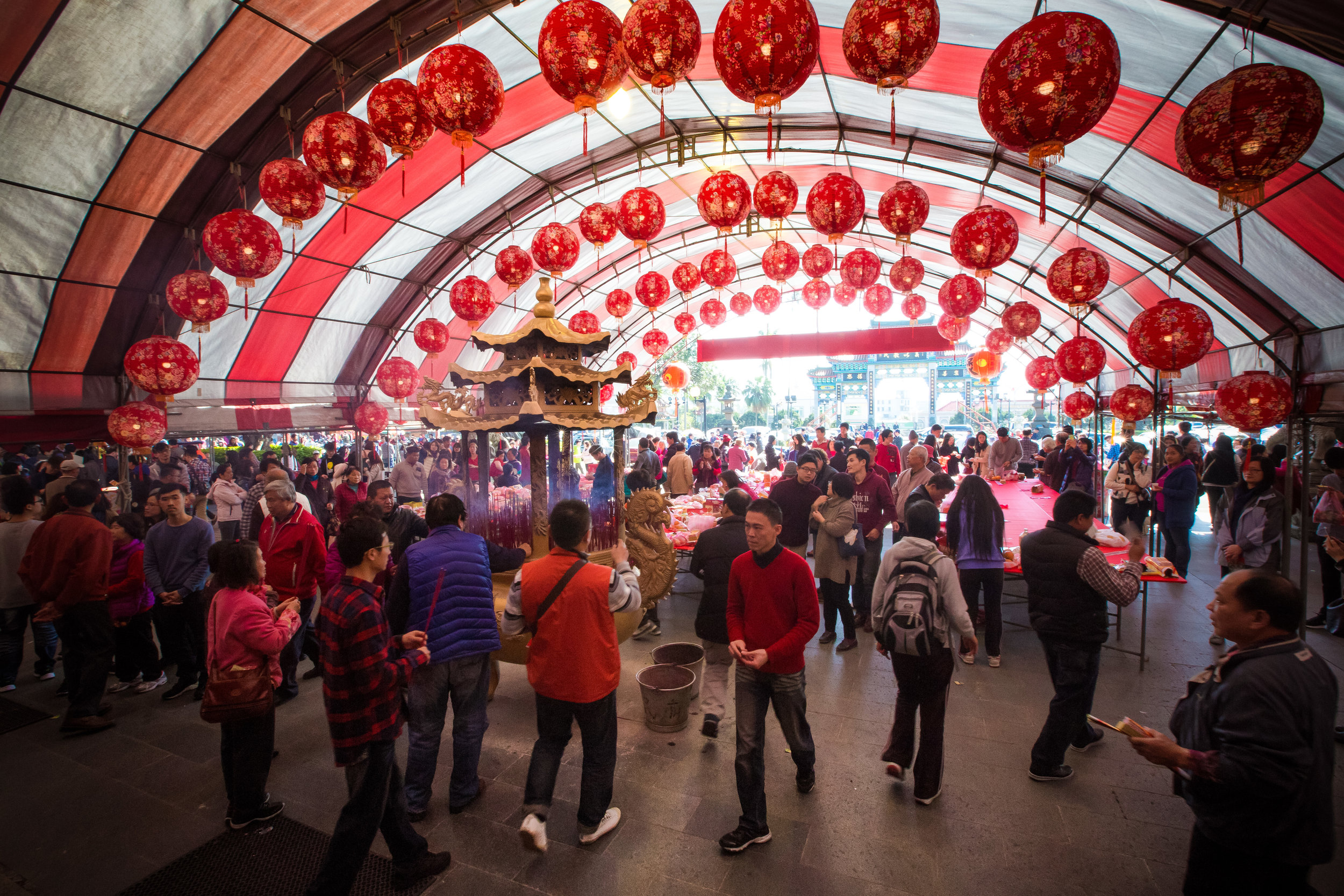
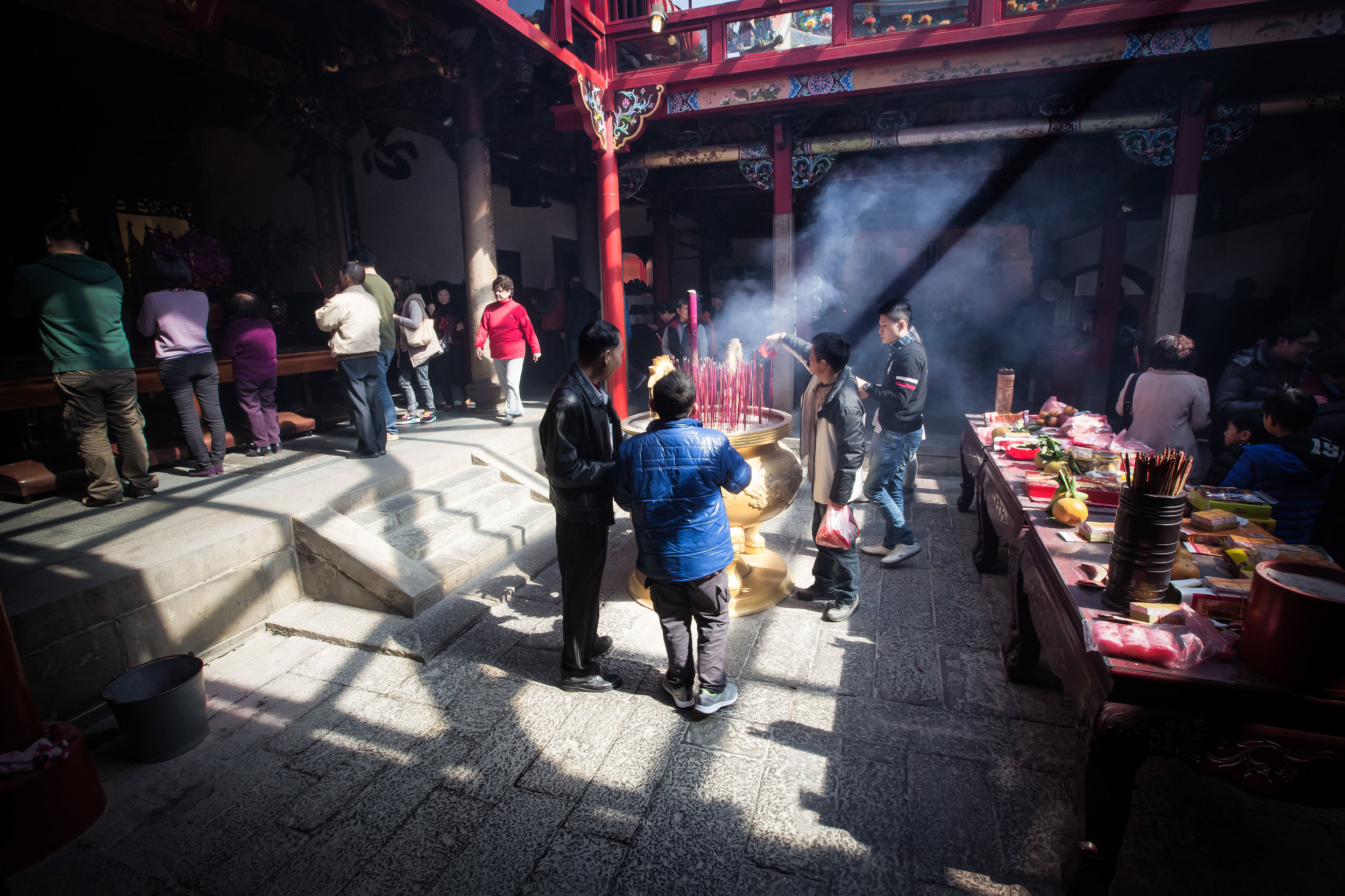
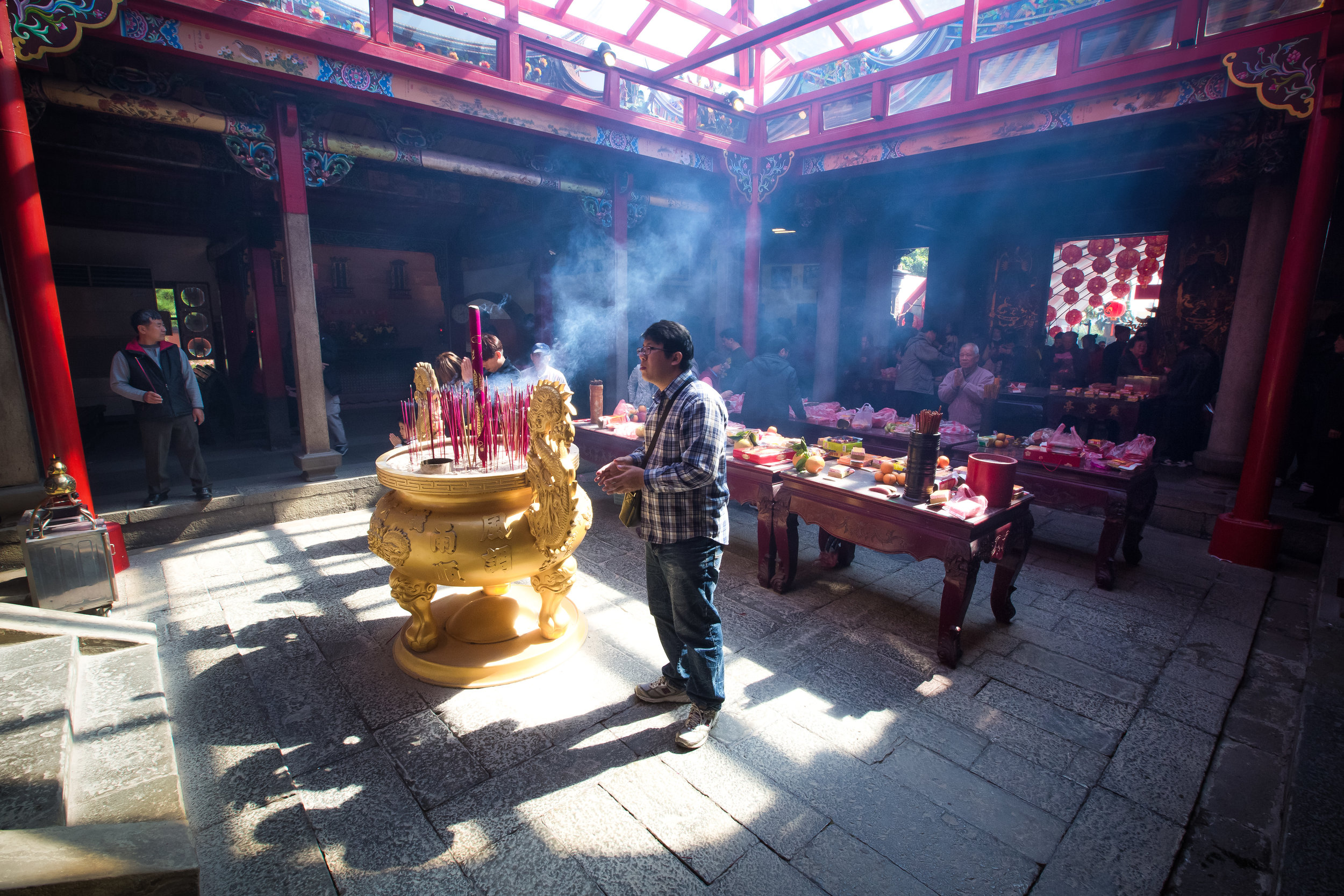
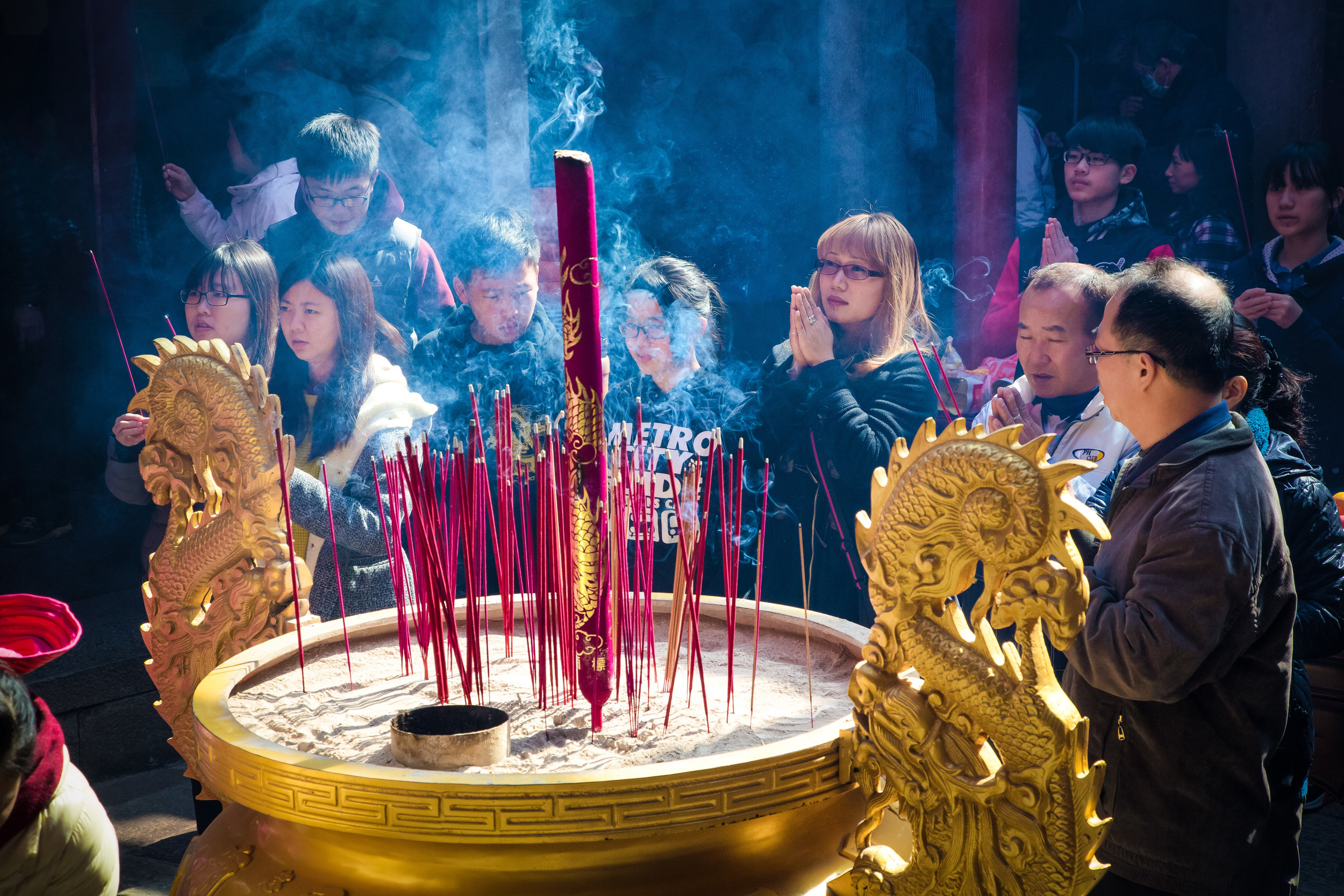
One of the things that I tell people who have just arrived in Taiwan is that the temples here are pretty much like living museums for the culture, art and history of this country. You can learn so much more about Taiwan by visiting temples than you ever could from a museum.
I've written a lot about temples over the past few years on my blog and even though it might seem like overkill at times, I really do love taking photos of these wonderful buildings while at the same time telling a bit of their story so that people around the world can understand them better.
This time I'm not going to be introducing a three hundred year old temple nor one that really comes across as the 'living museum' type. The temple I'm introducing today is a relatively new one yet despite its lack of history it has become a very important one for the people of Taipei and also attracts its fair share of tourists.
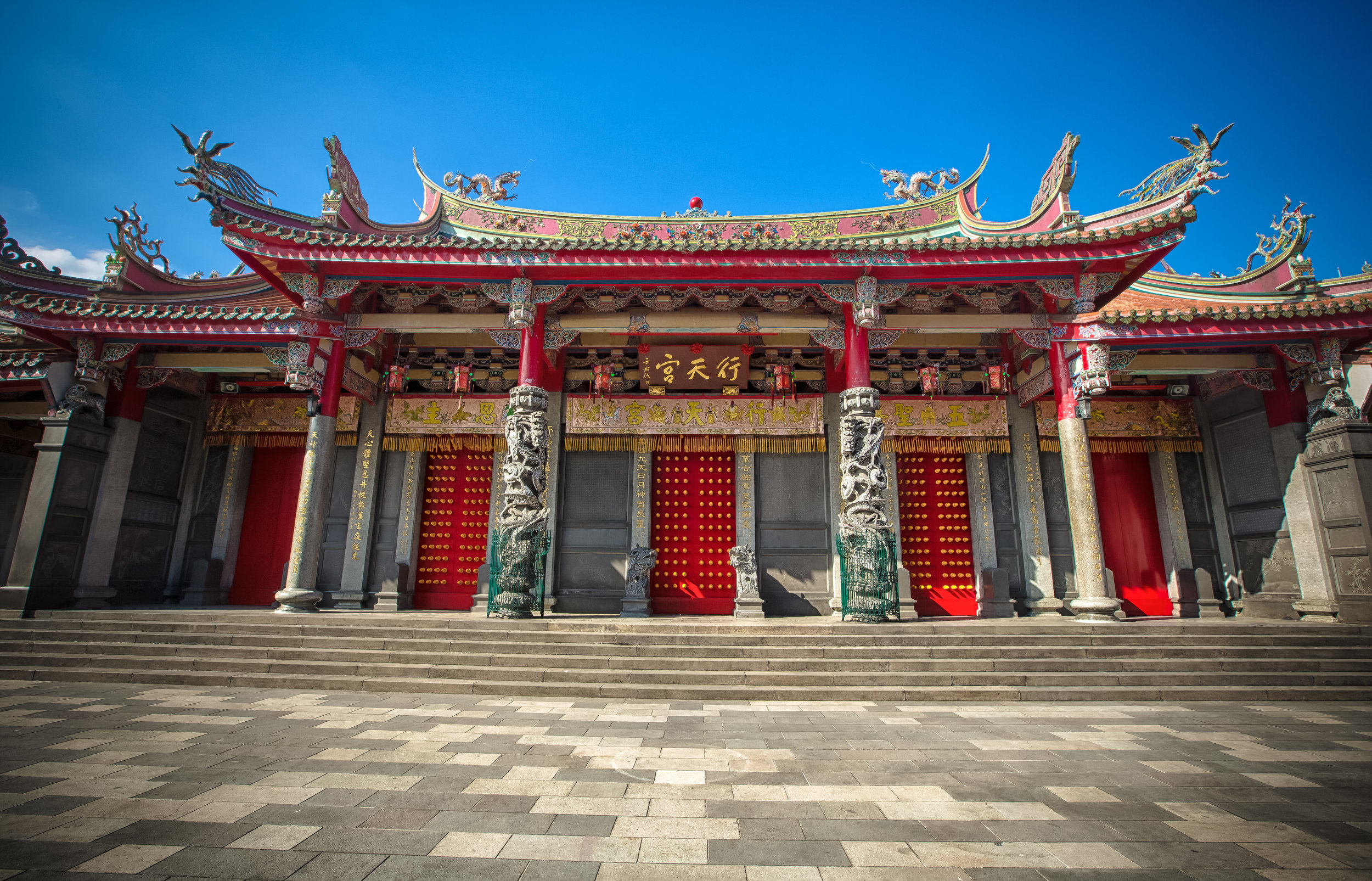
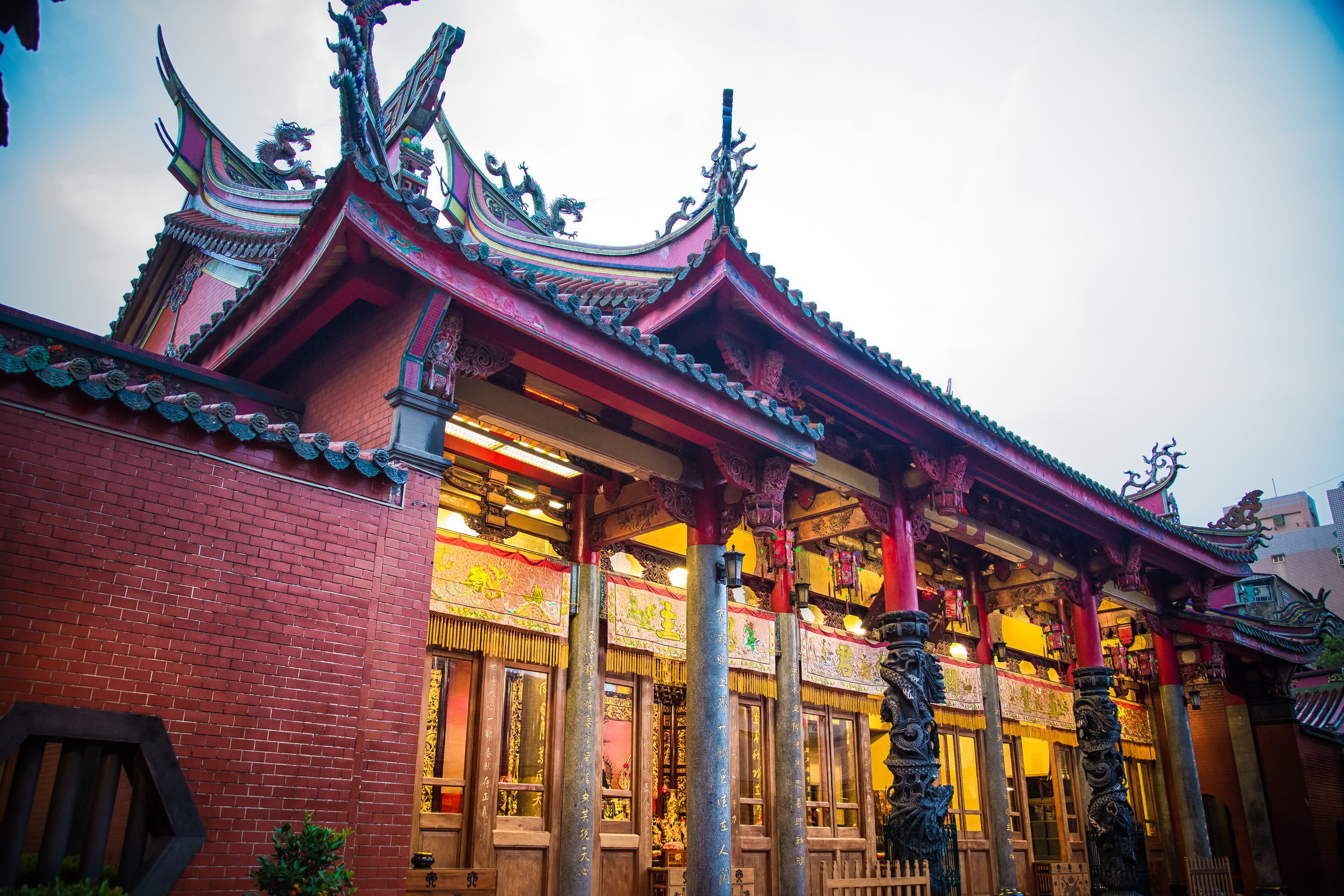
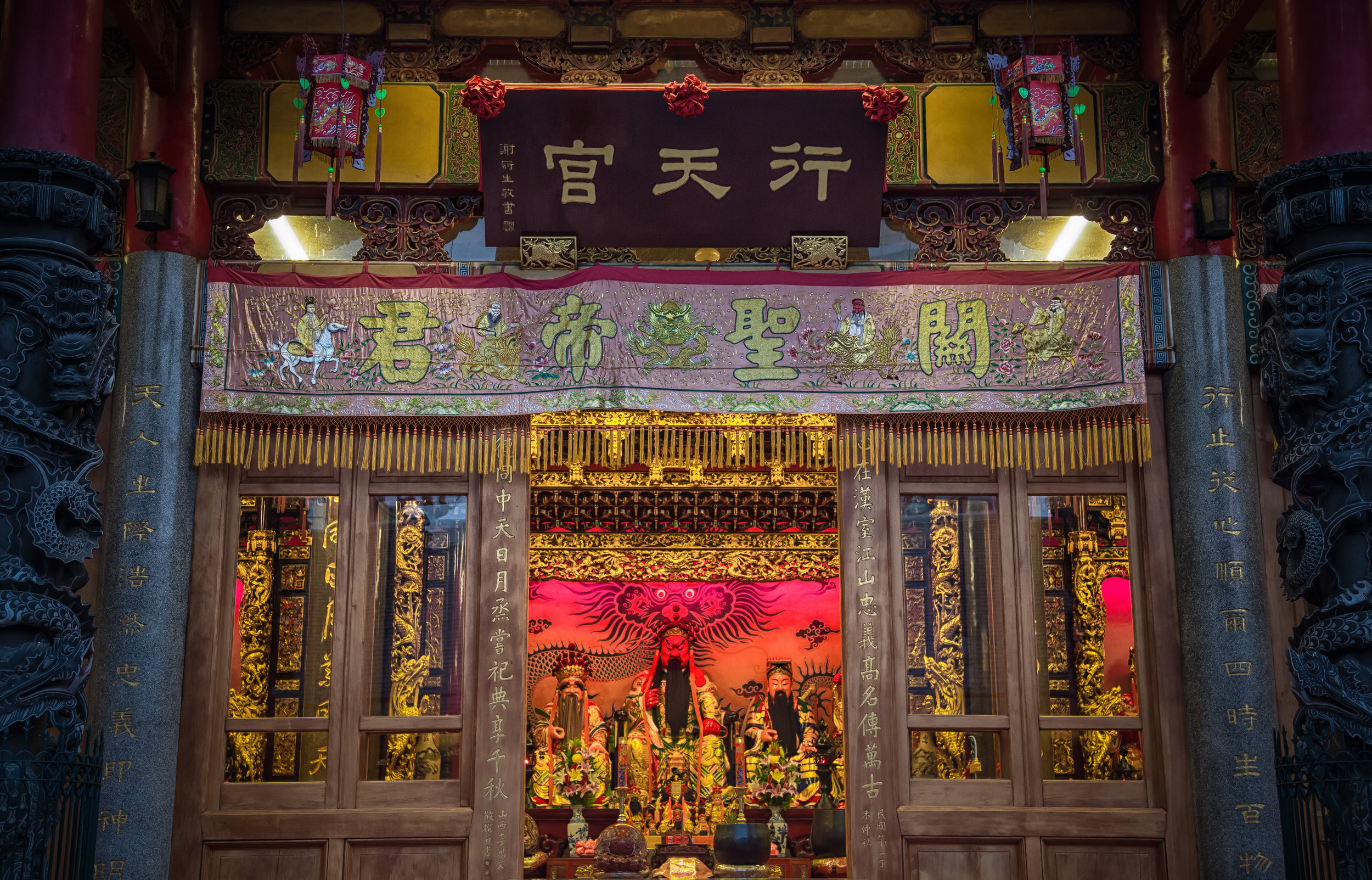
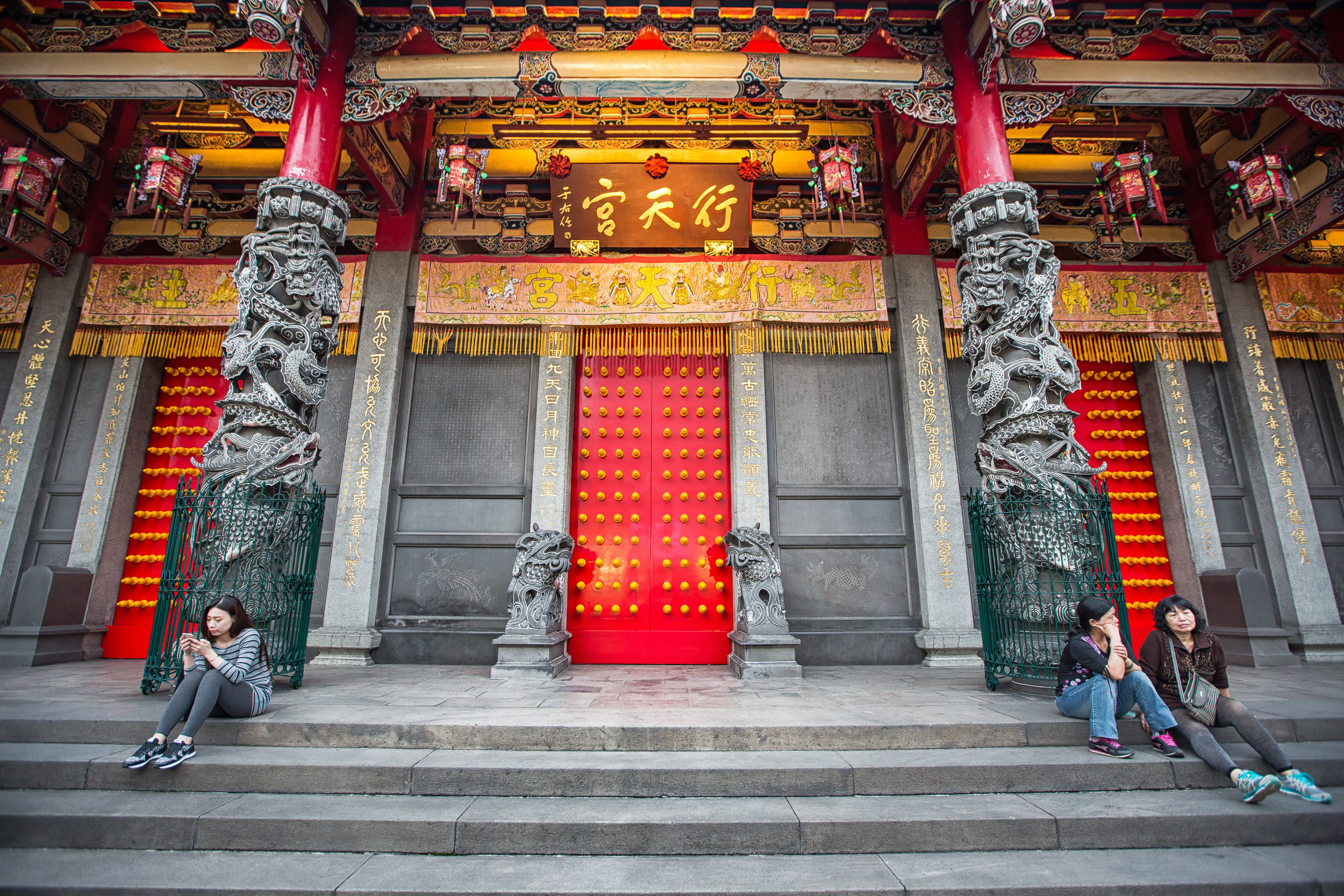
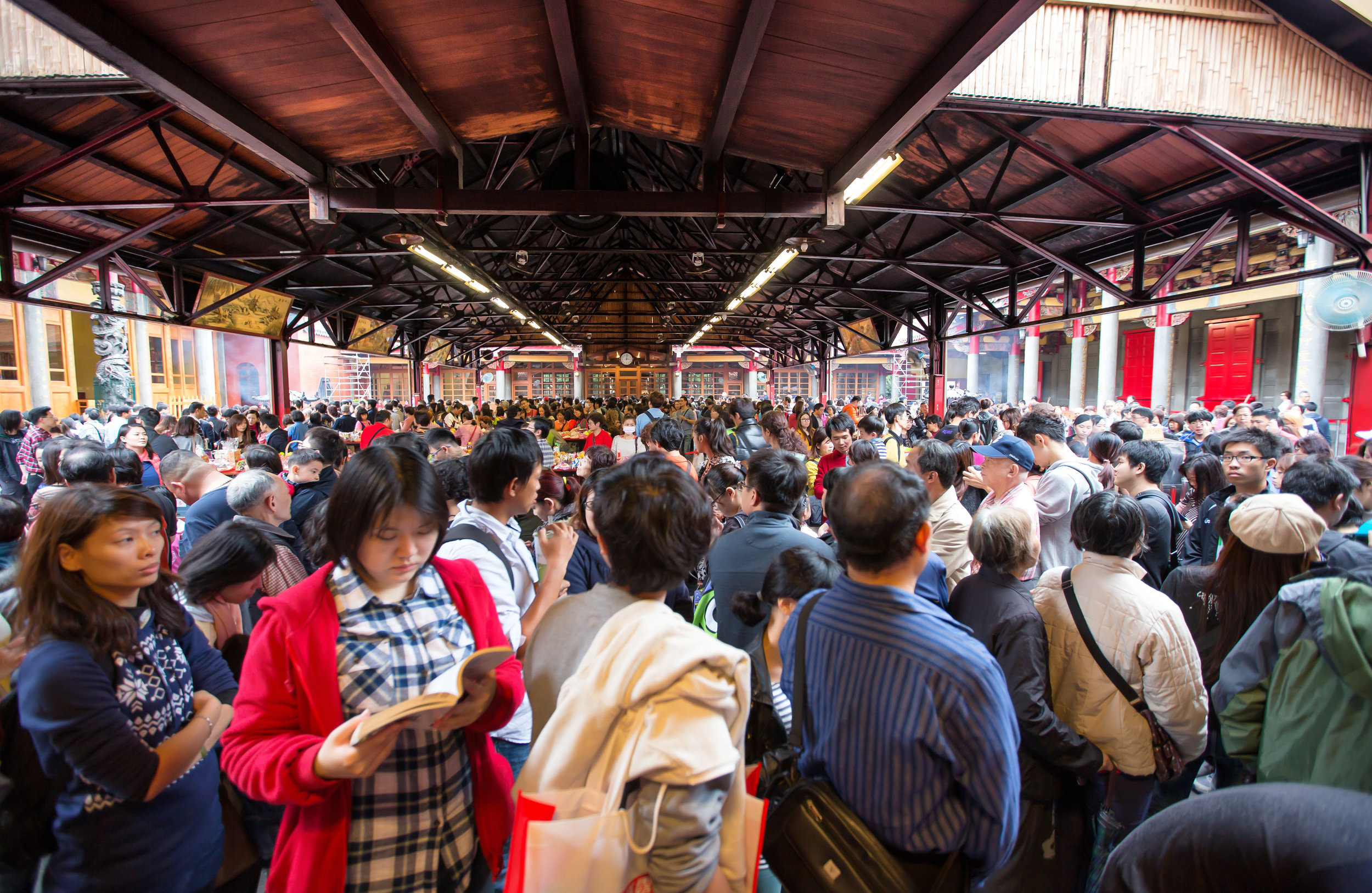
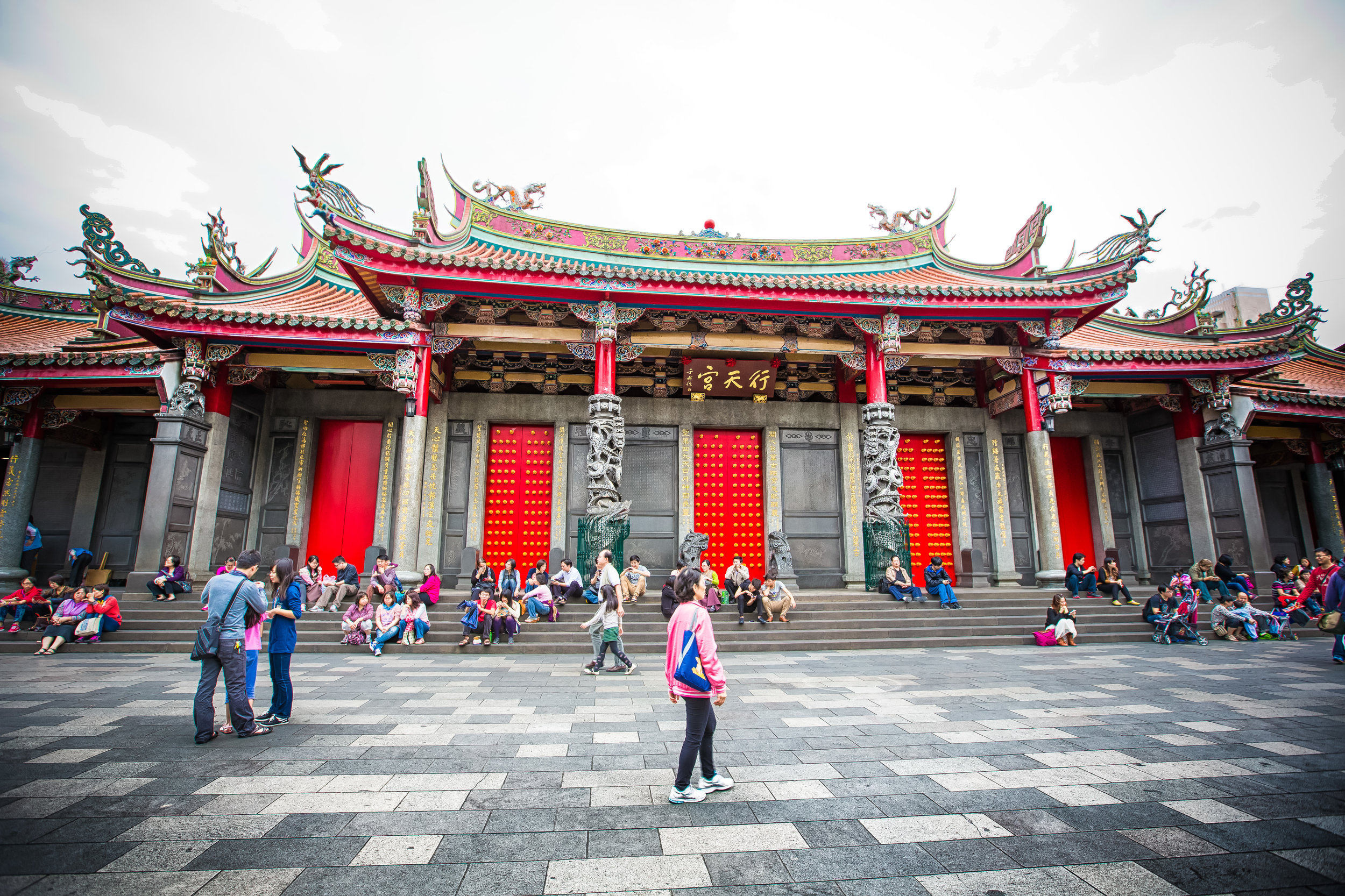
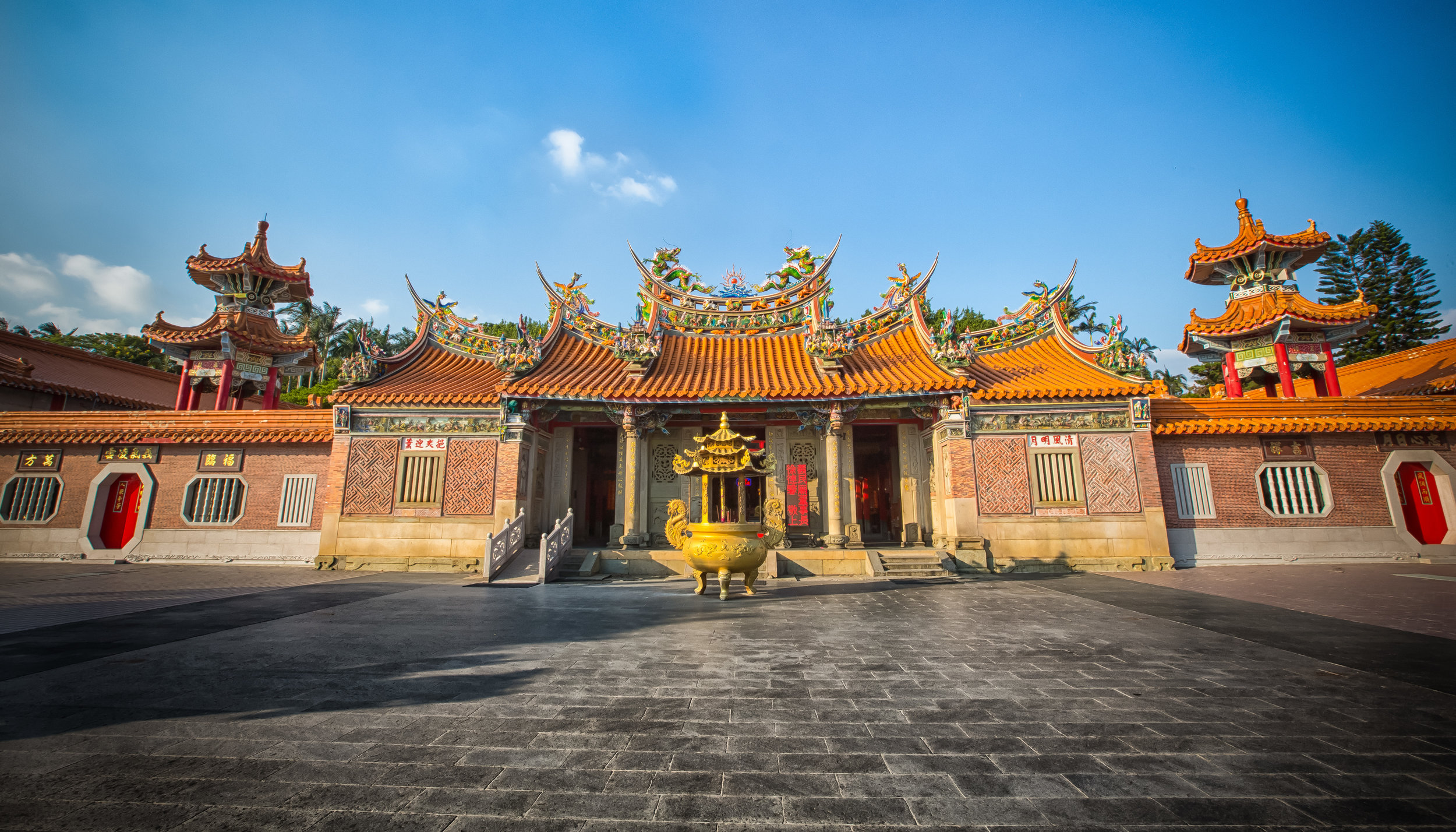
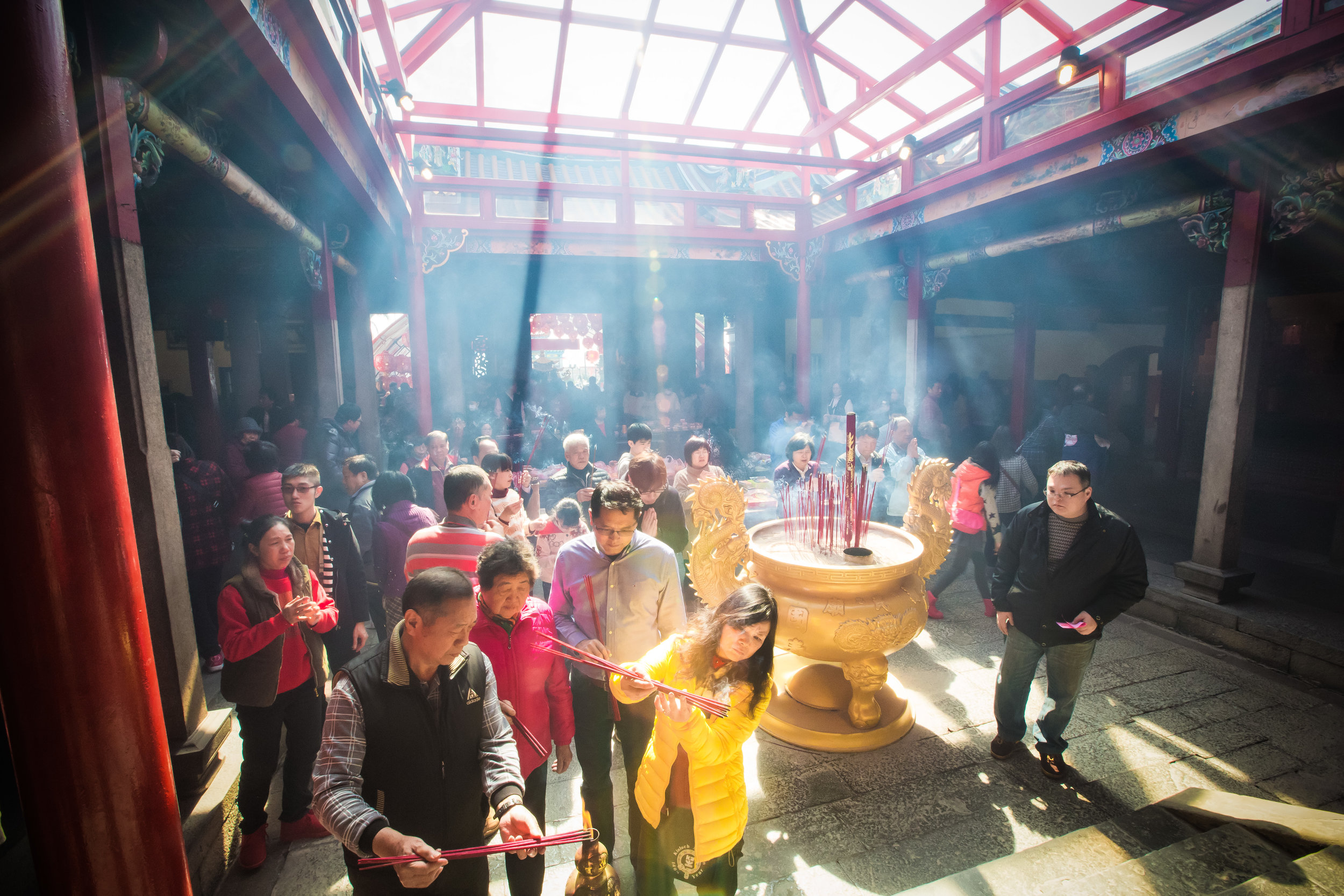
Xingtian Temple (行天宮), constructed in 1967 is a relatively young temple by Taiwan's standards - Yet if you compare its popularity to other temples around the country it would seem that age isn't always the deciding factor in whether a temple is considered important or not. It is estimated that over 10,000 people visit the temple each day and while it has become a major tourist destination for the city, it is also an extremely important place of worship for the Taoists of Taipei.
While most of the older temples in Taiwan are steeped in hundreds of years of tradition, it often seems that those traditions have a habit of preventing them from adapting to modern times and attitudes towards certain practices and beliefs. A young temple like Xingtian Temple on the other hand is a bit freer to be more progressive with its policies and is one of the reasons why this temple has received so much positive publicity over the past few years and why it has become so loved.
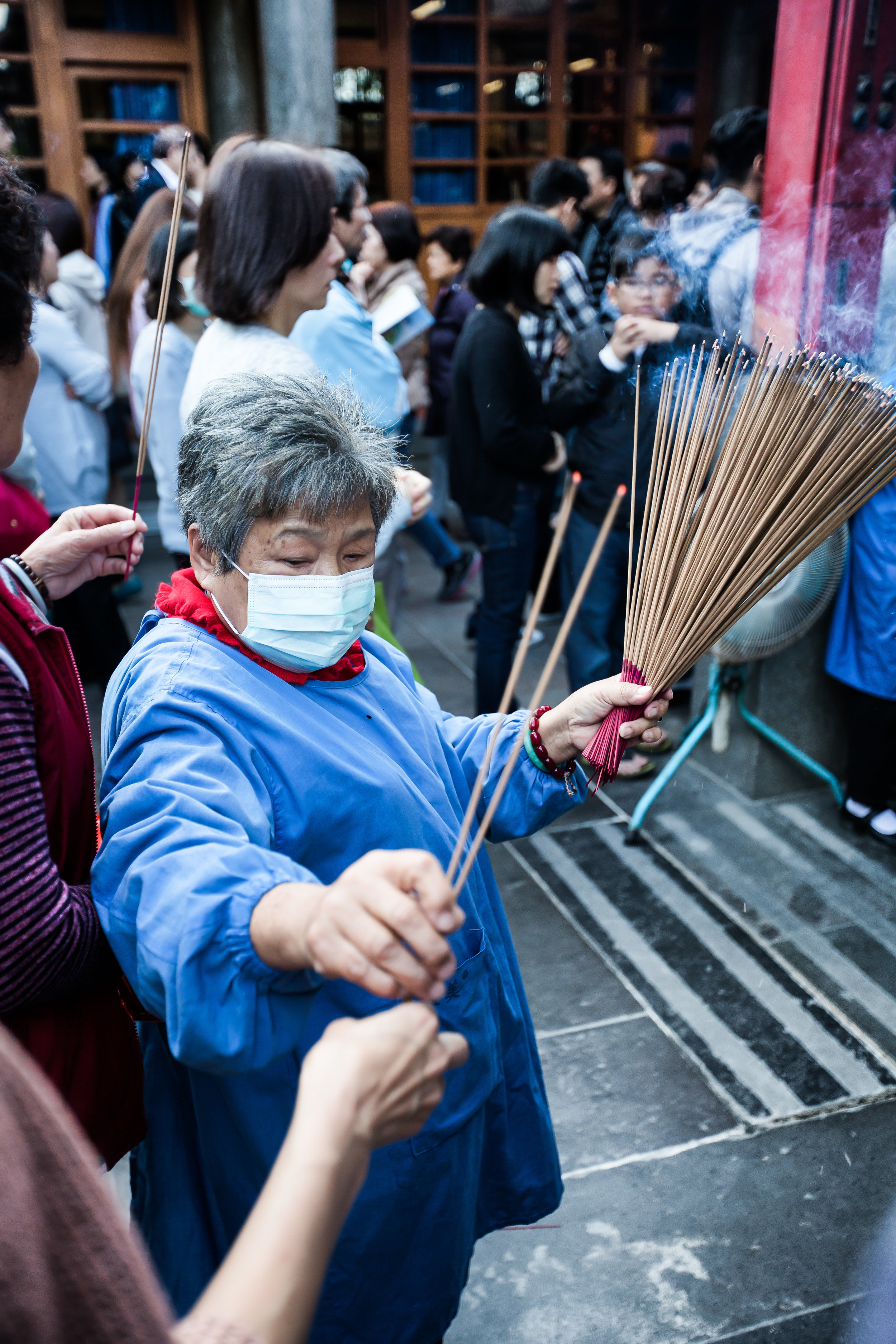
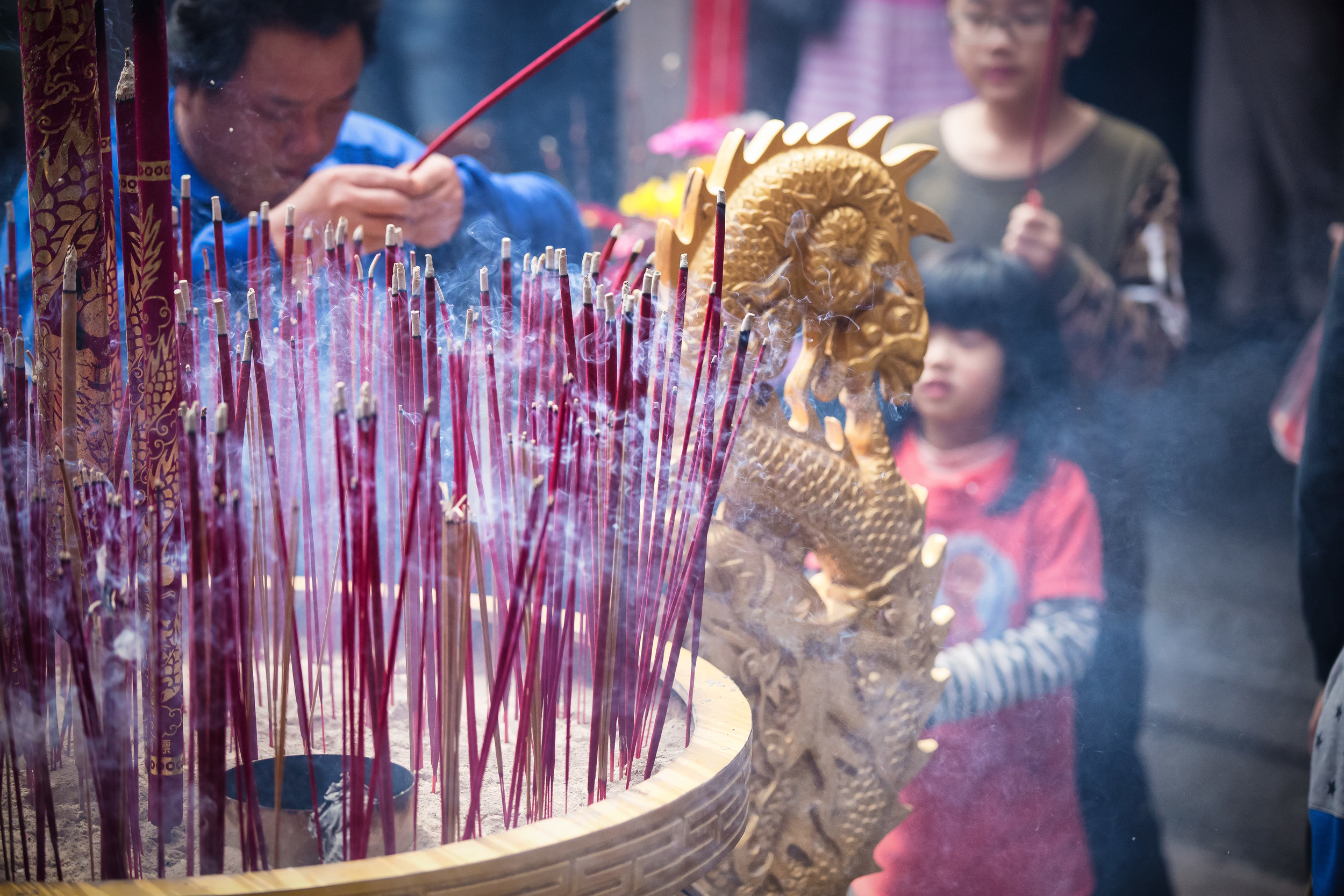
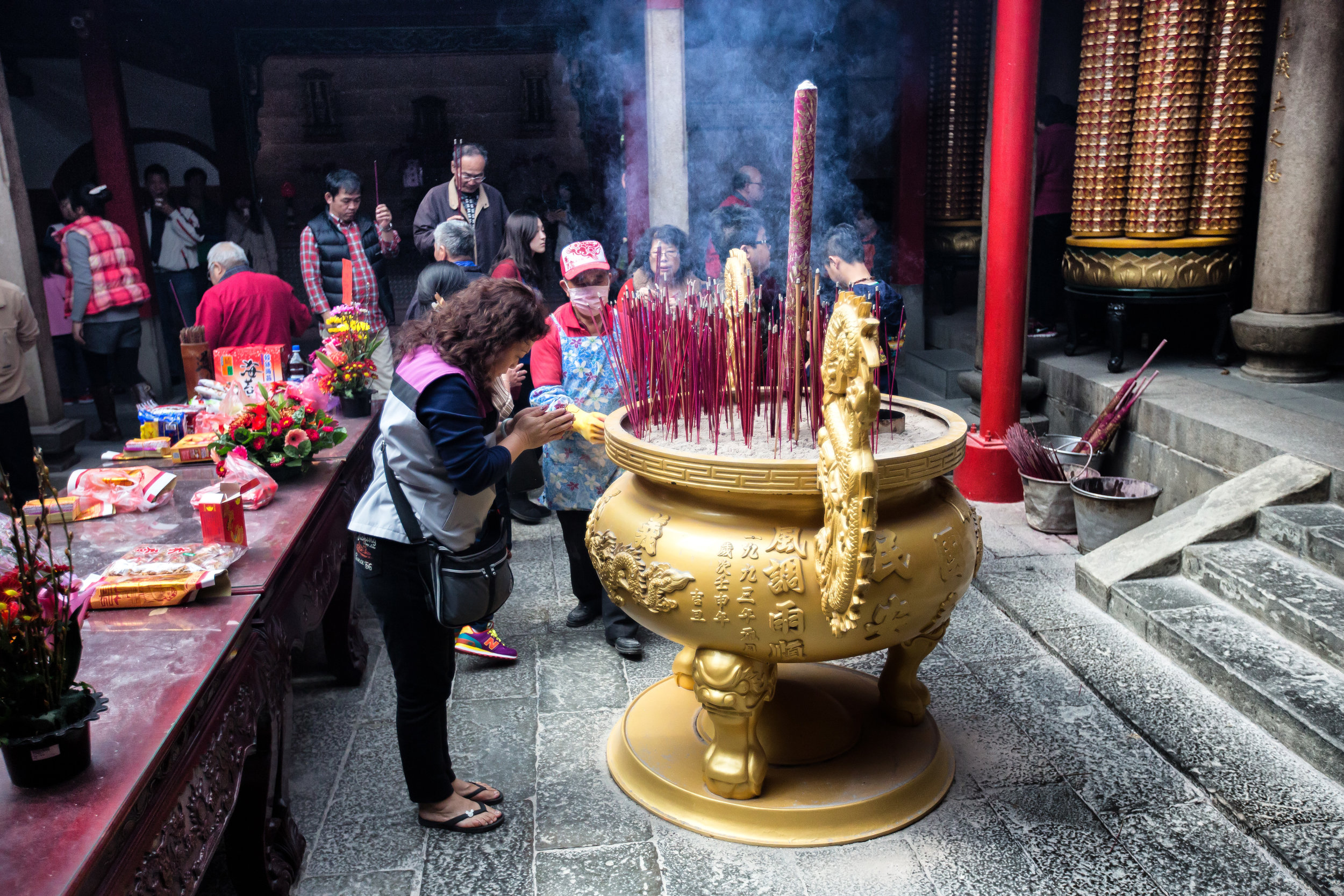
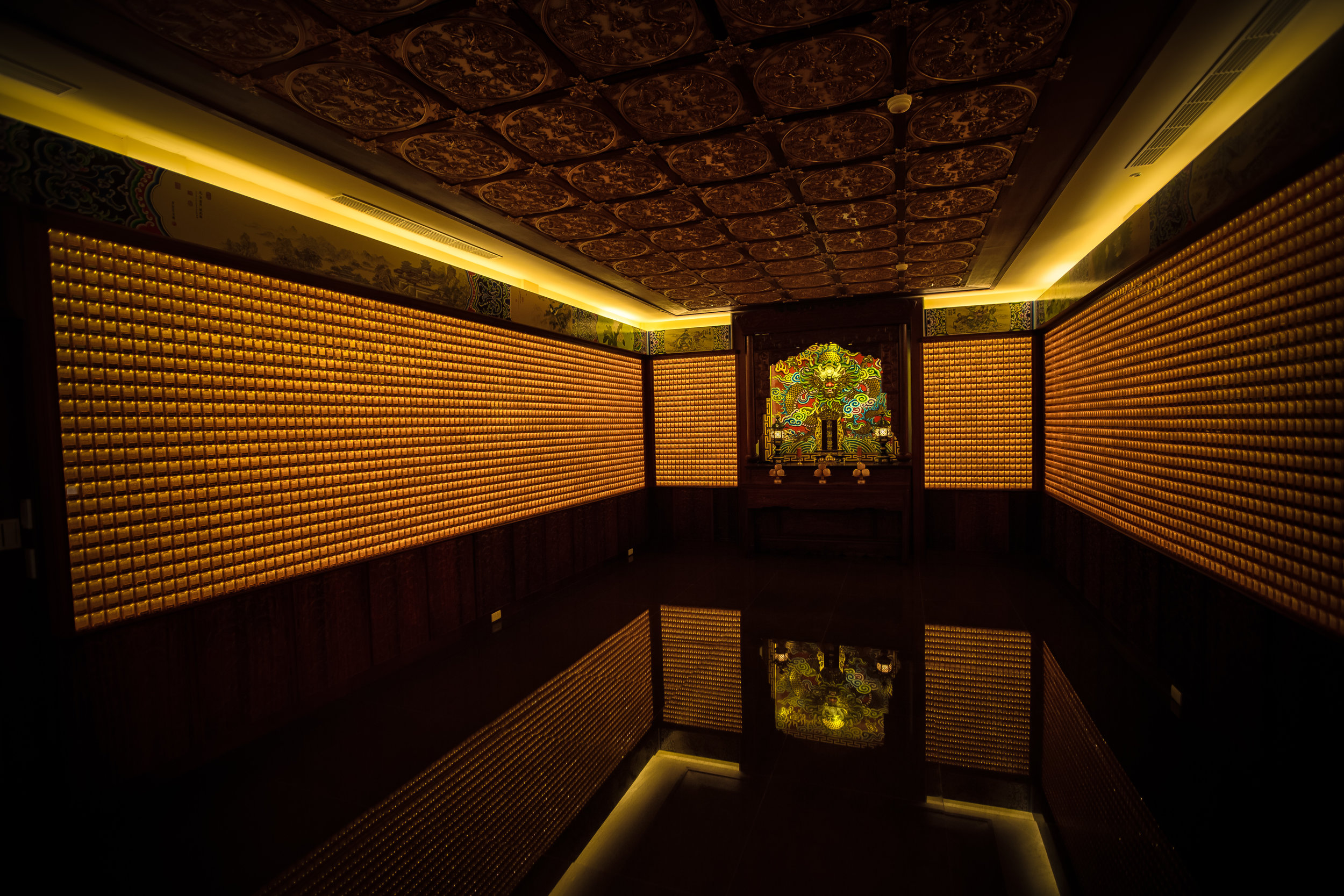
In 2014 the temple made headlines across Taiwan when it announced that it would institute measures to protect the environment which included removing offering tables and no longer offering incense to visitors - a very bold move on part of the temple! (and ultimately followed by a few others since then).
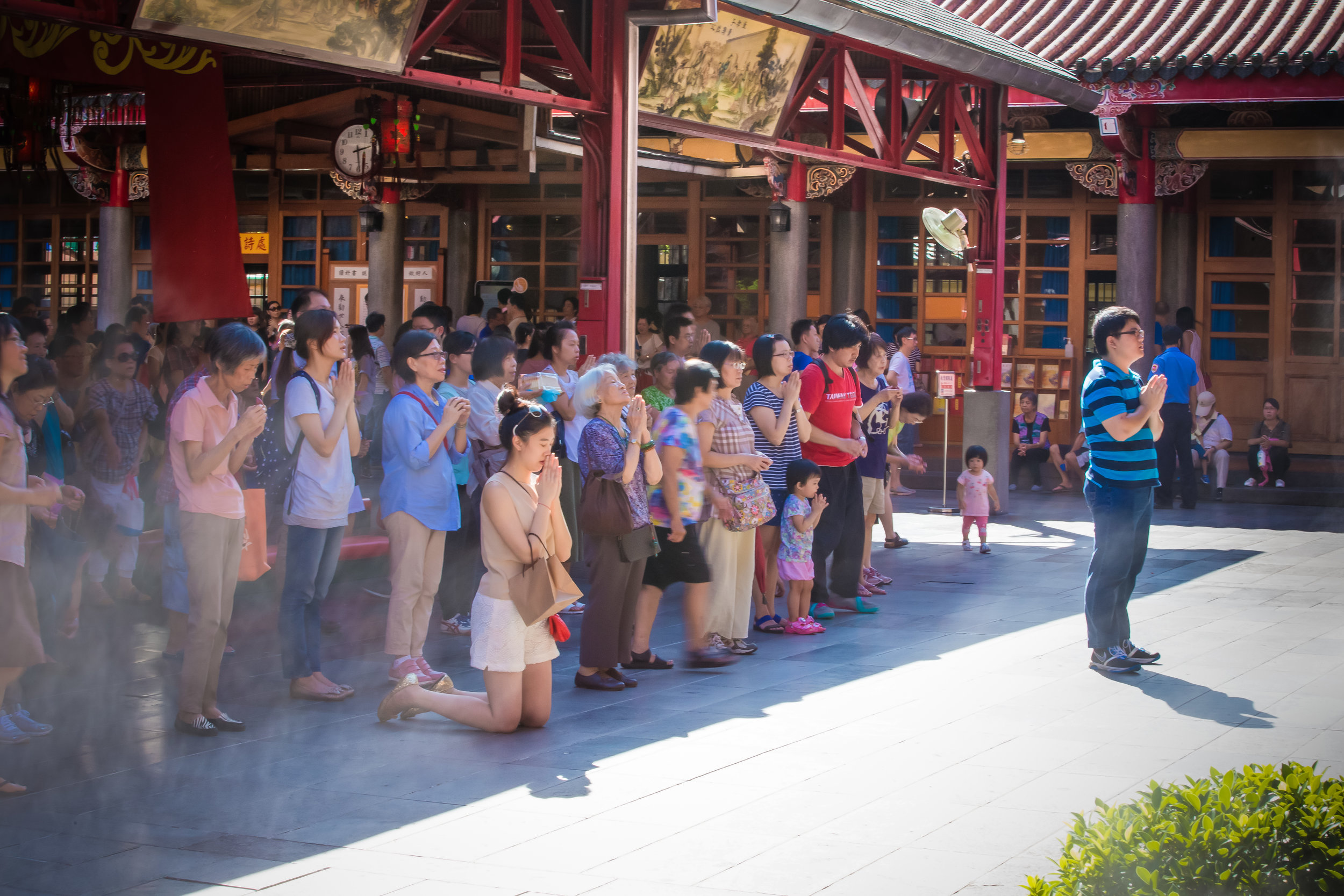
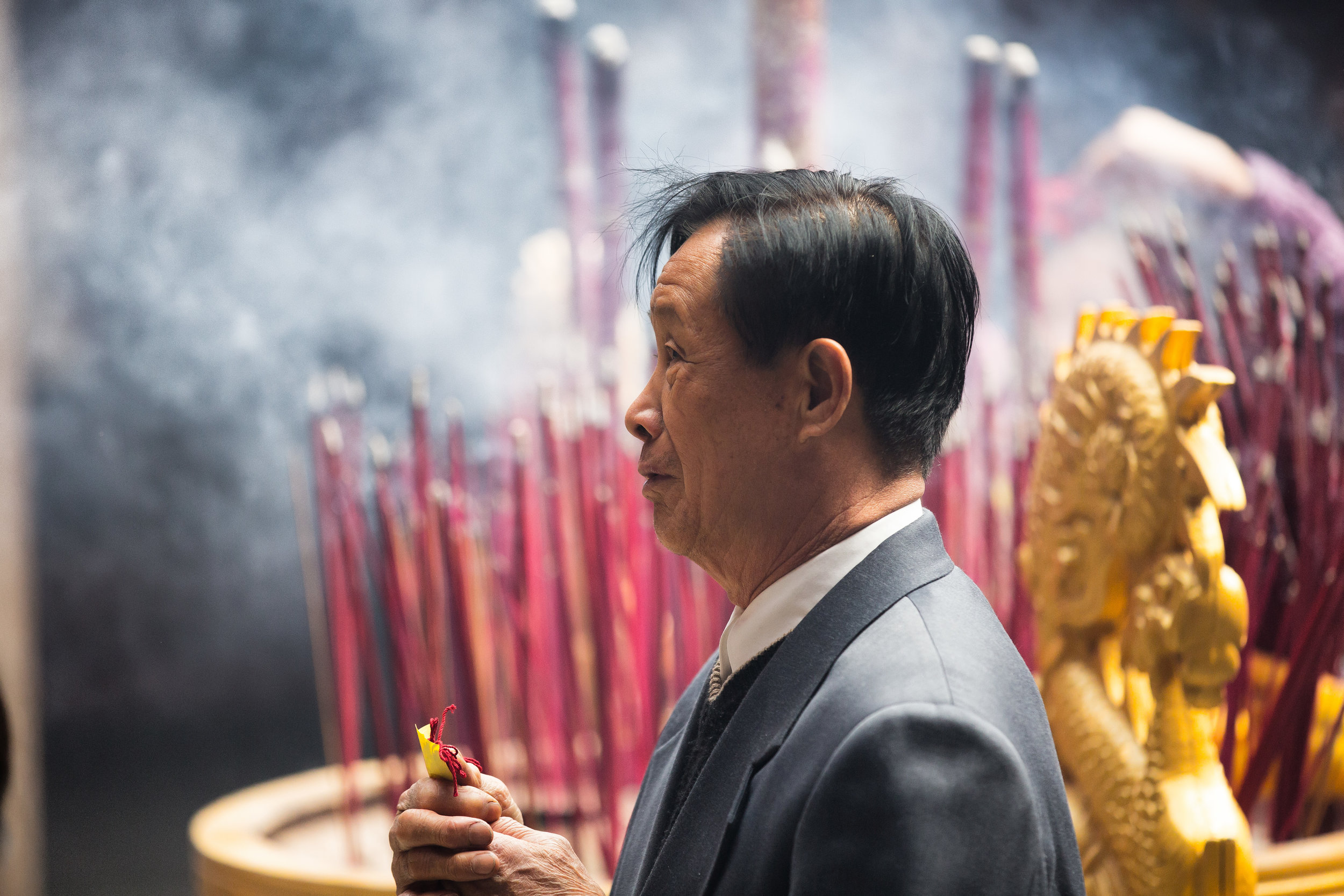
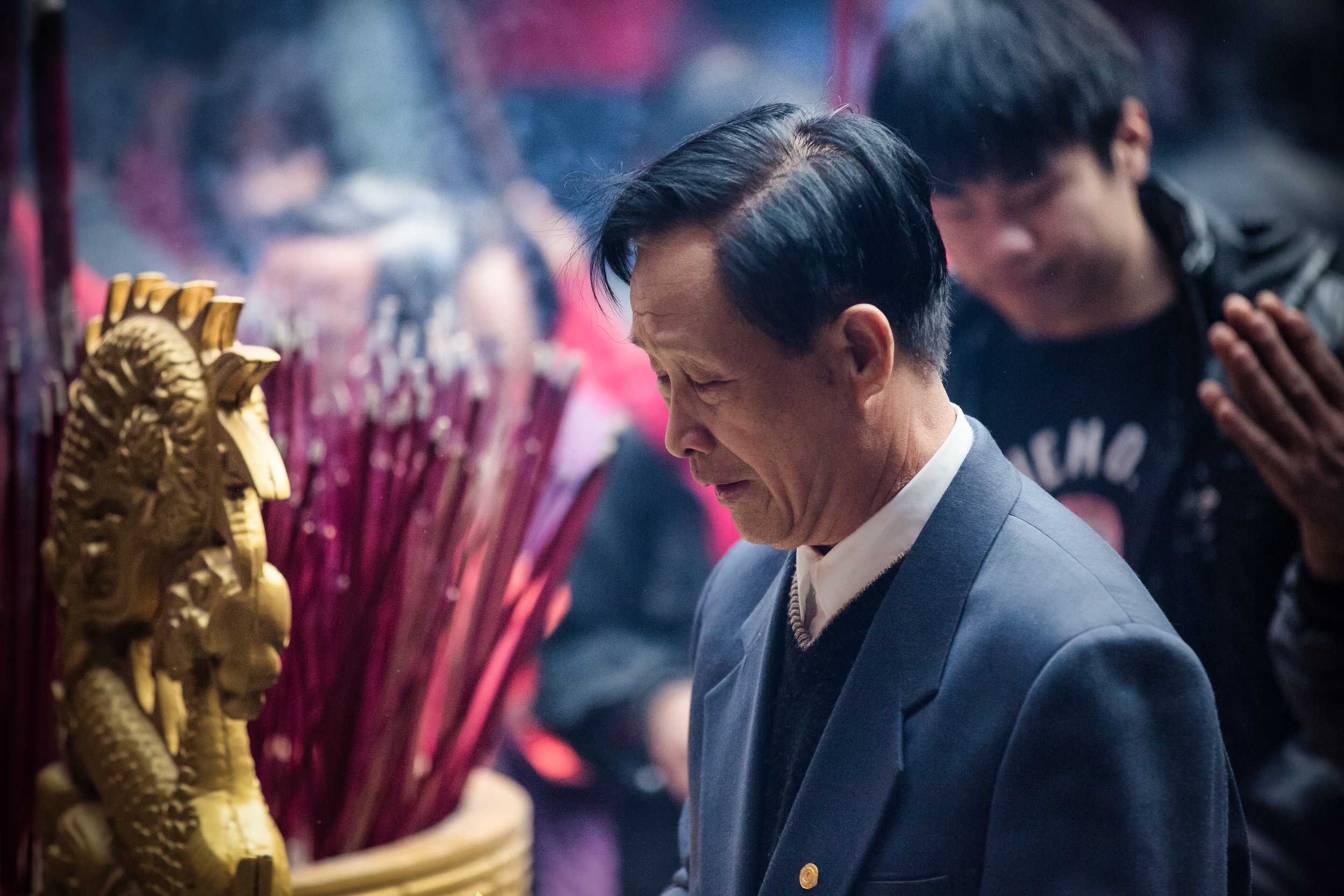
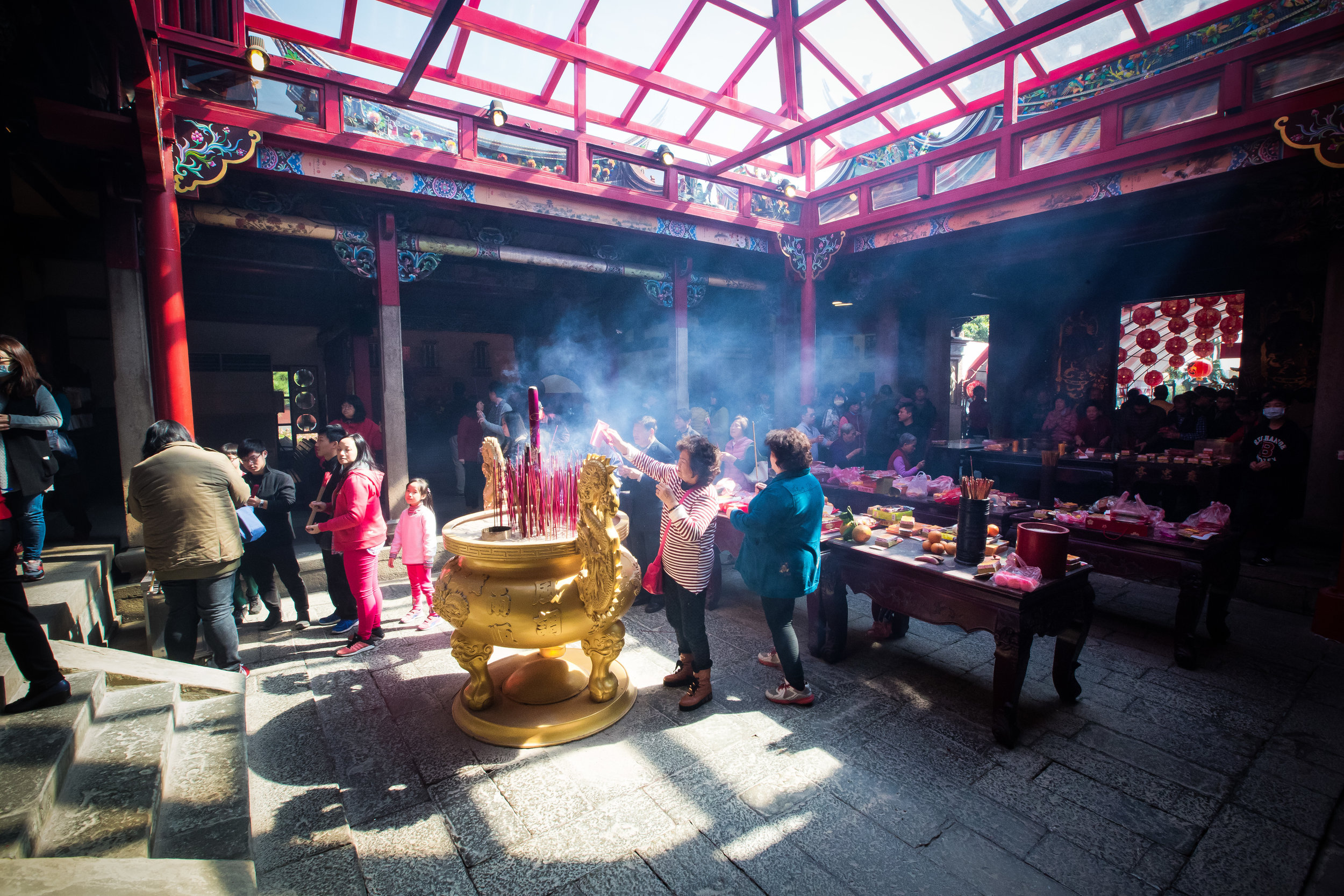
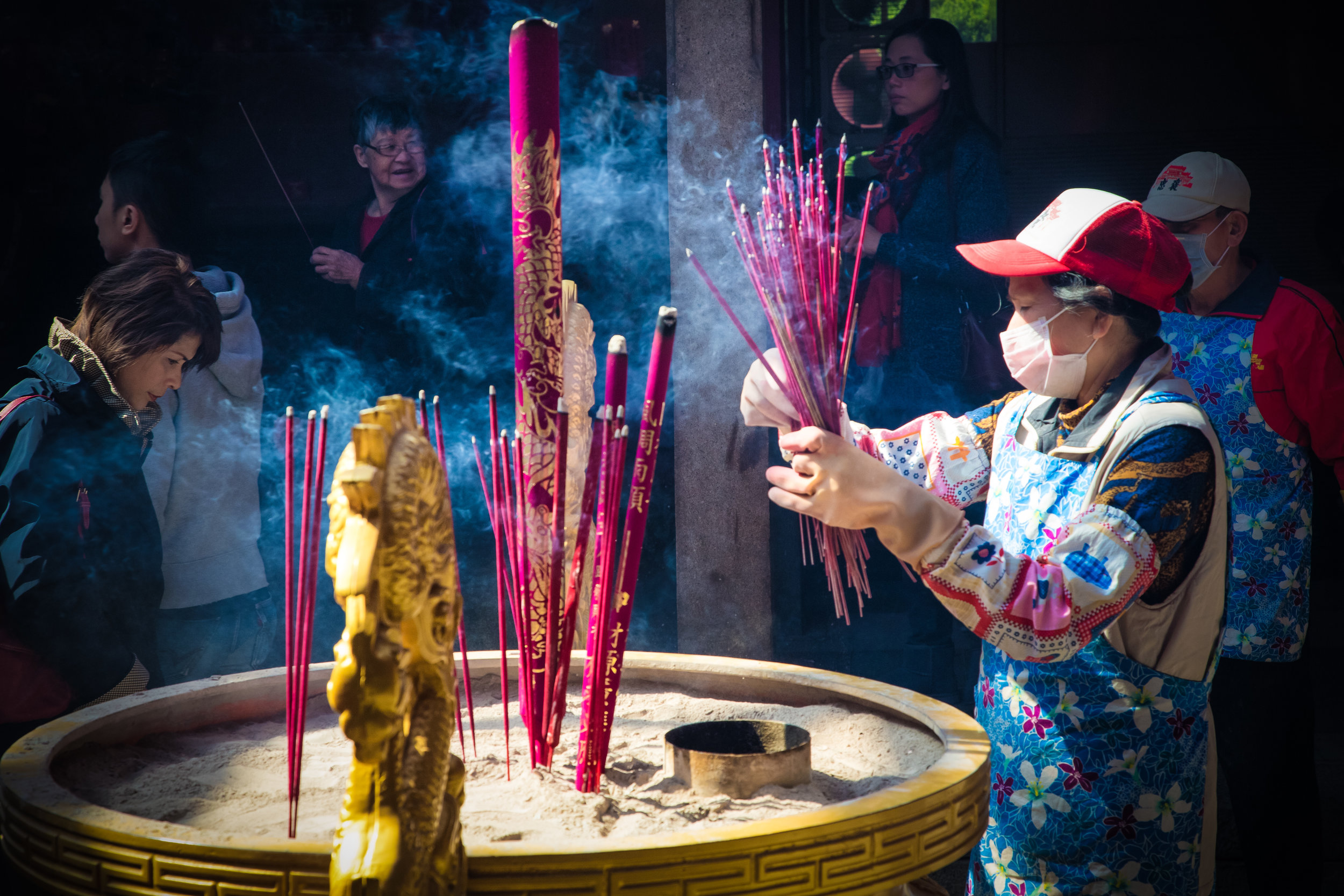
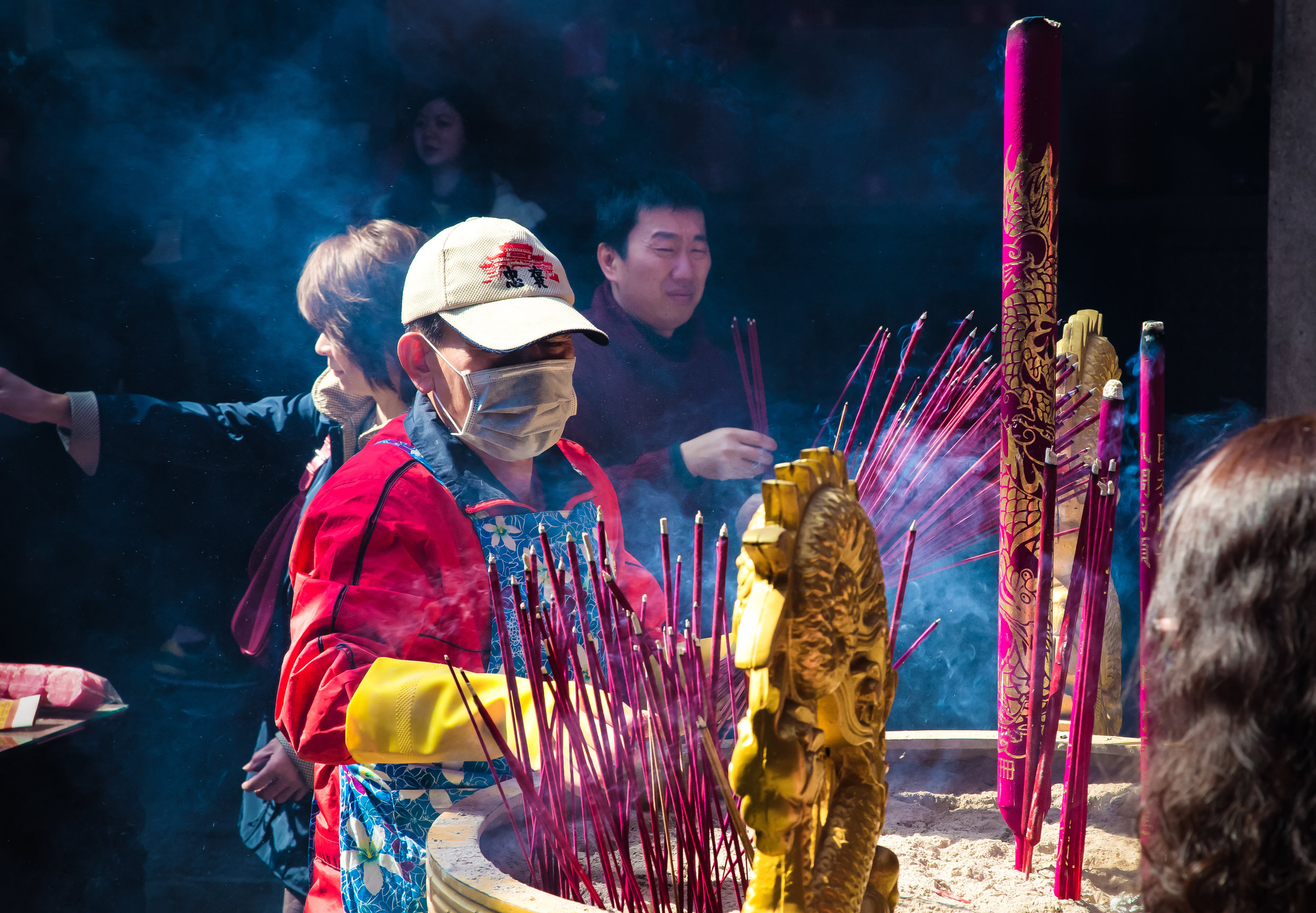
Temples in Taiwan are constantly filled with clouds of incense as sticks of incense are thought to portray a certain level of respect when Taoists are conversing the the spiritual world. I really do like the smell of incense, but when you visit temples it can sometimes be a little too much and your eyes and throat start to hurt if you stick around for too long.
The progressive policies that the temple instituted were not only great for the environment but also for people's health and also the cleanliness of the temple, which is at all times insanely clean.
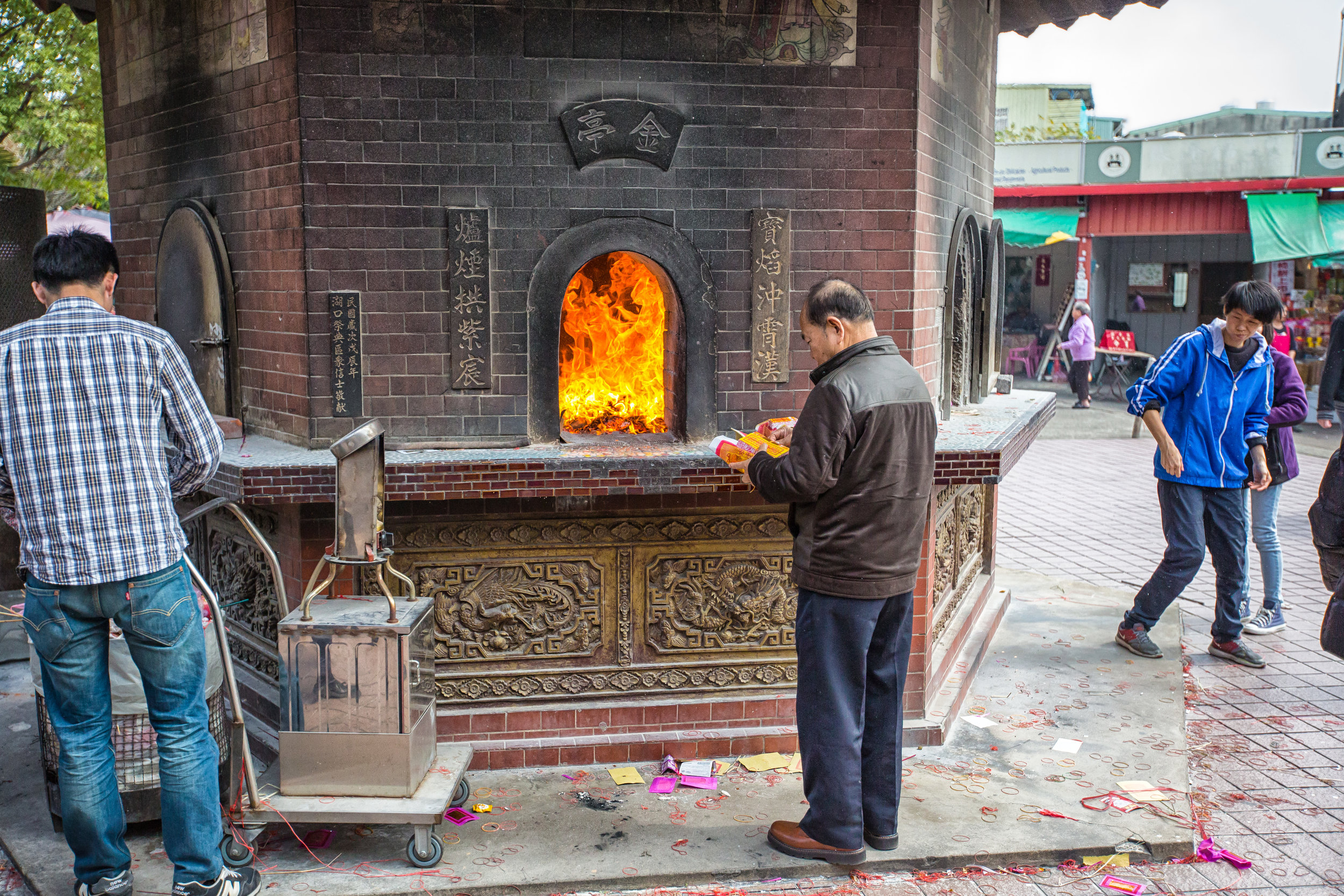
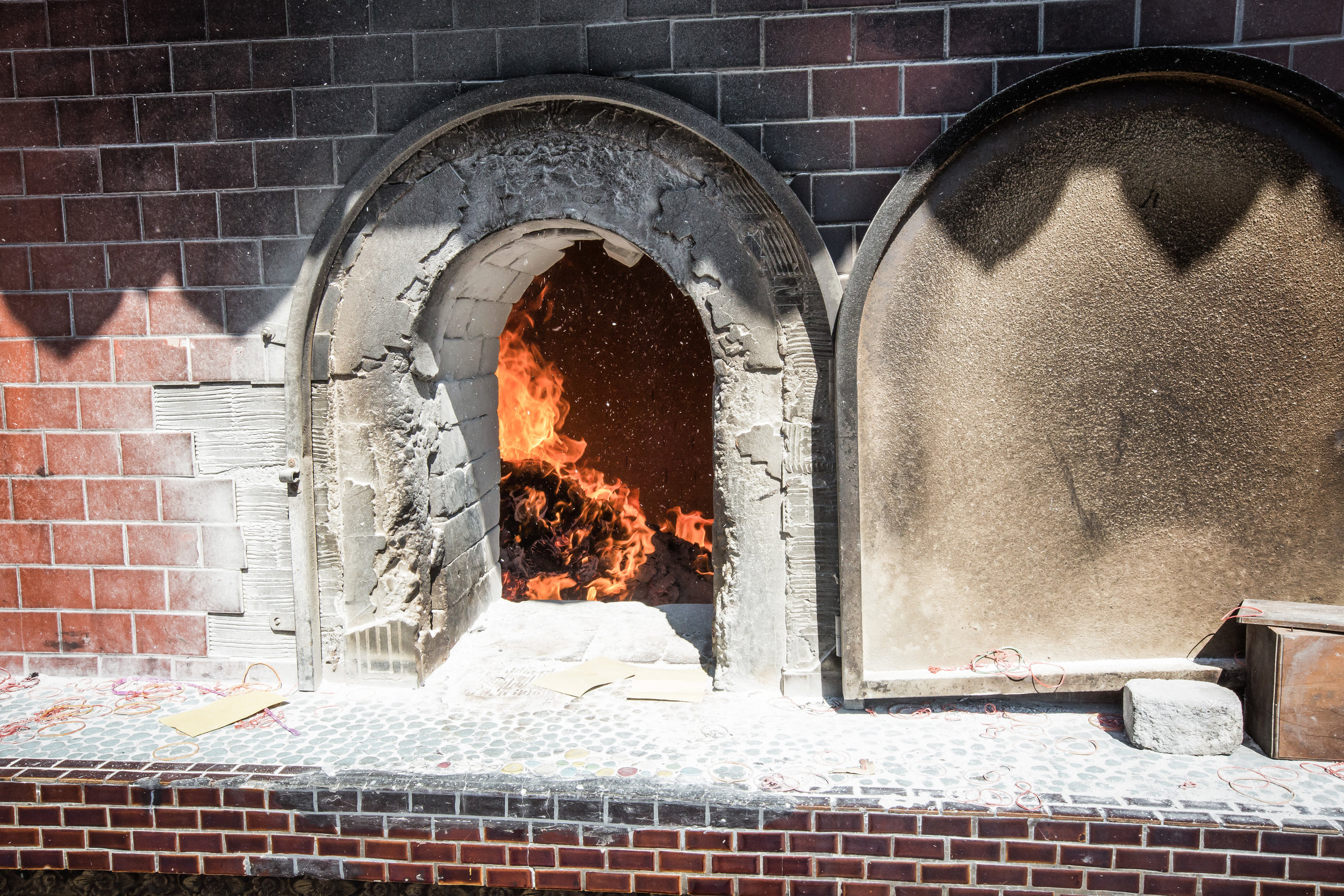
Xingtian Temple also sets itself apart from others due to the fact that it does not have a large furnace for burning ghost money nor does it put on performances or have any donation boxes for accepting money from visitors. A visit to this temple is a no-frills experience which means you're free to look around and enjoy the experience without being pestered for donations like you would in so many other countries.
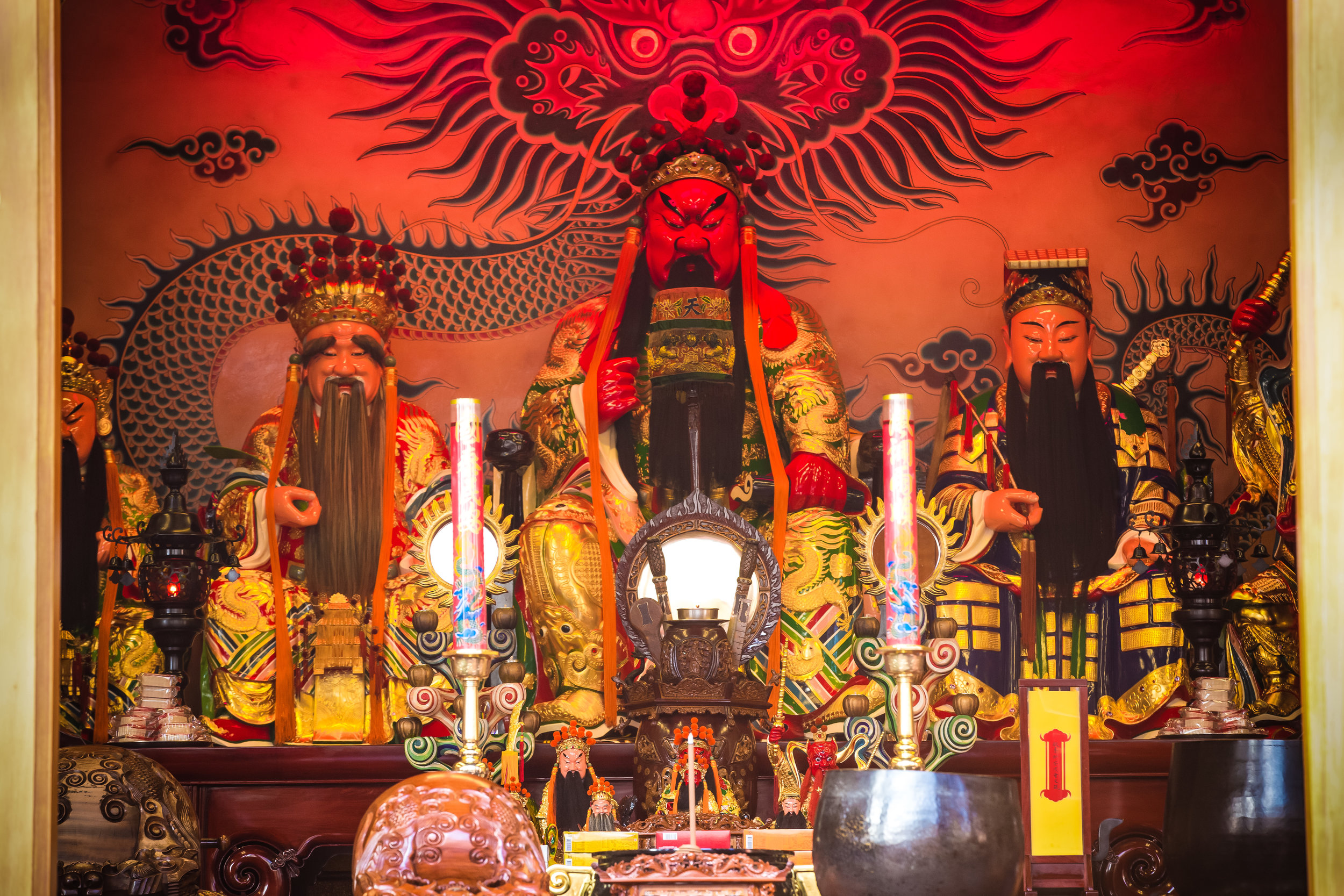
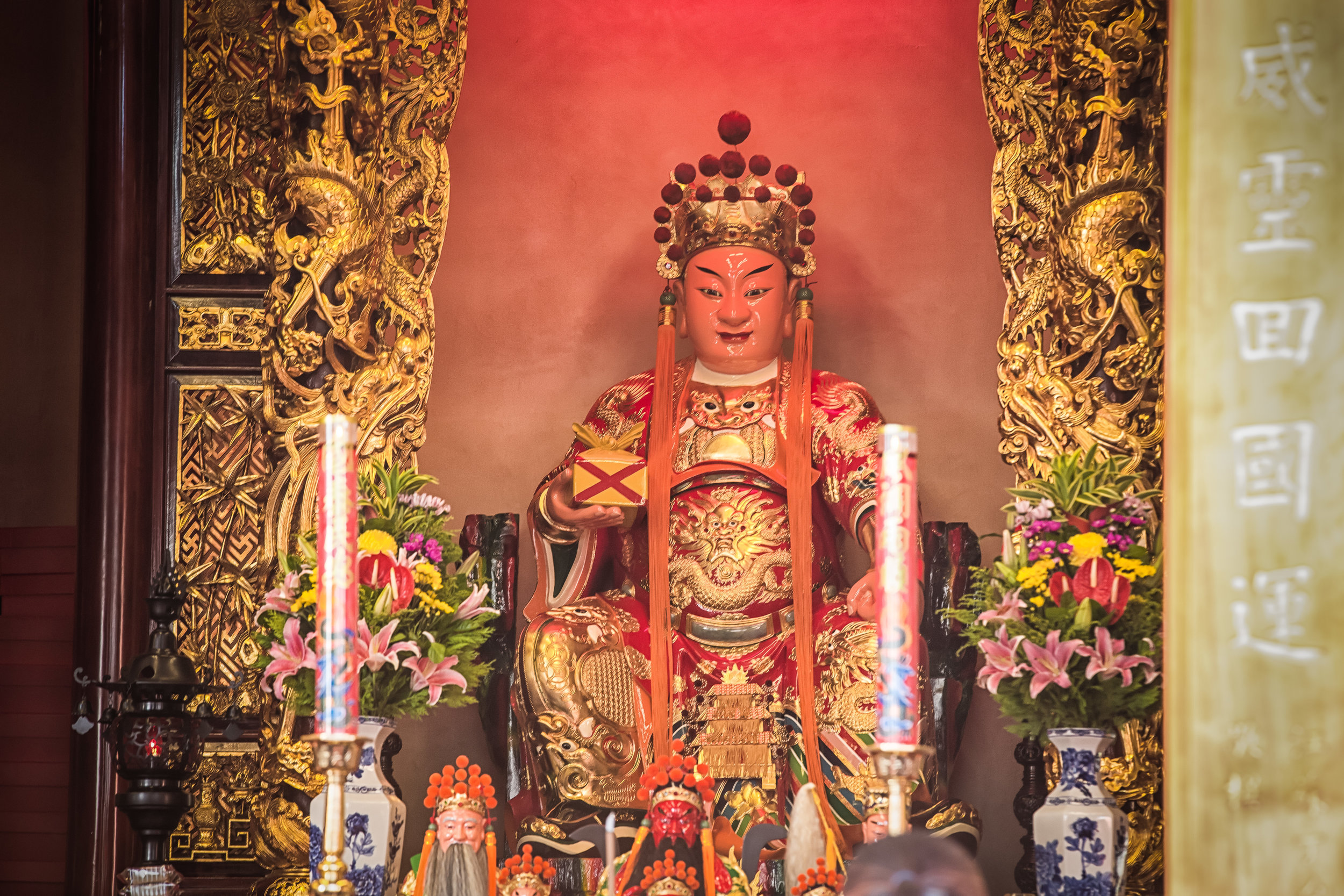
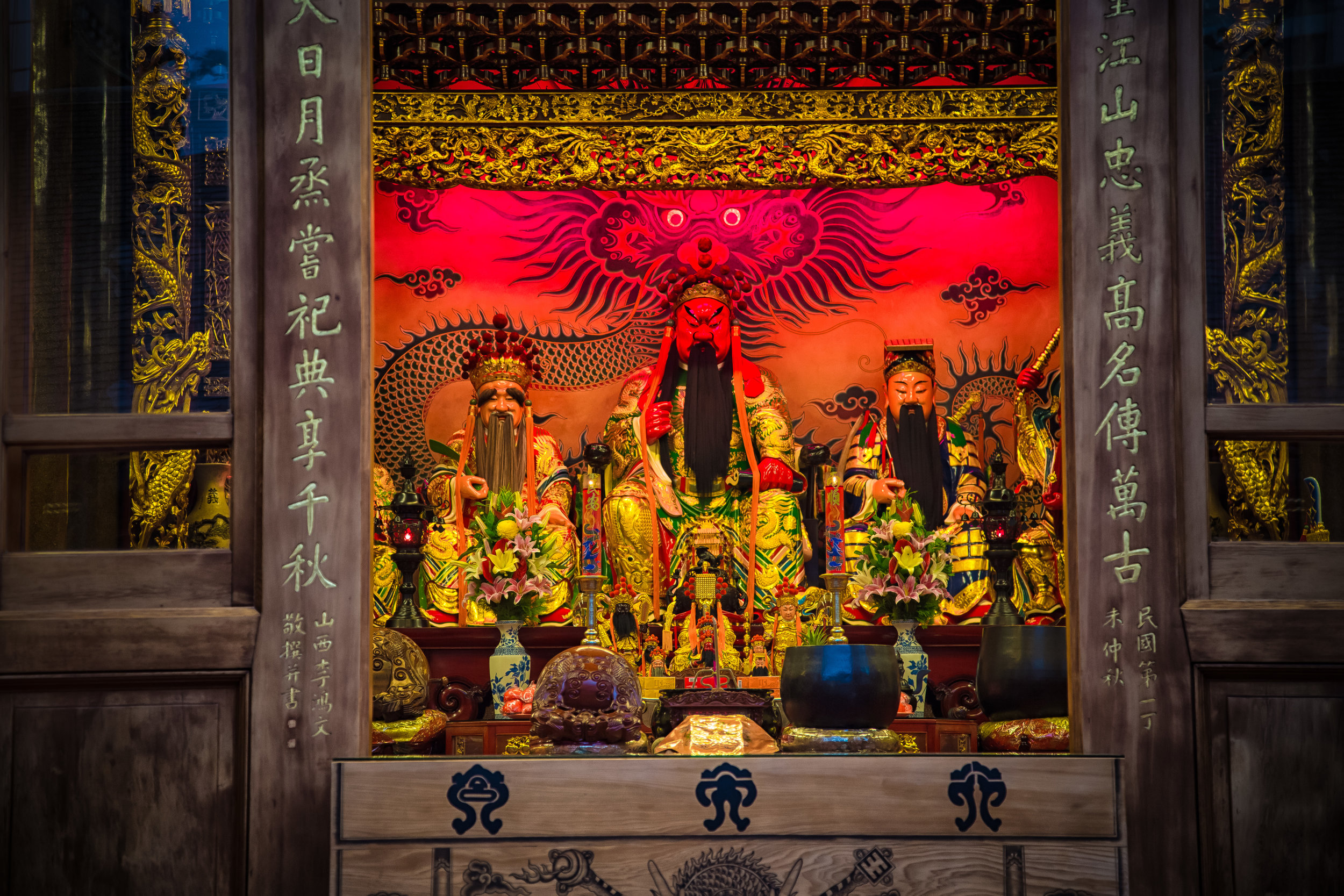
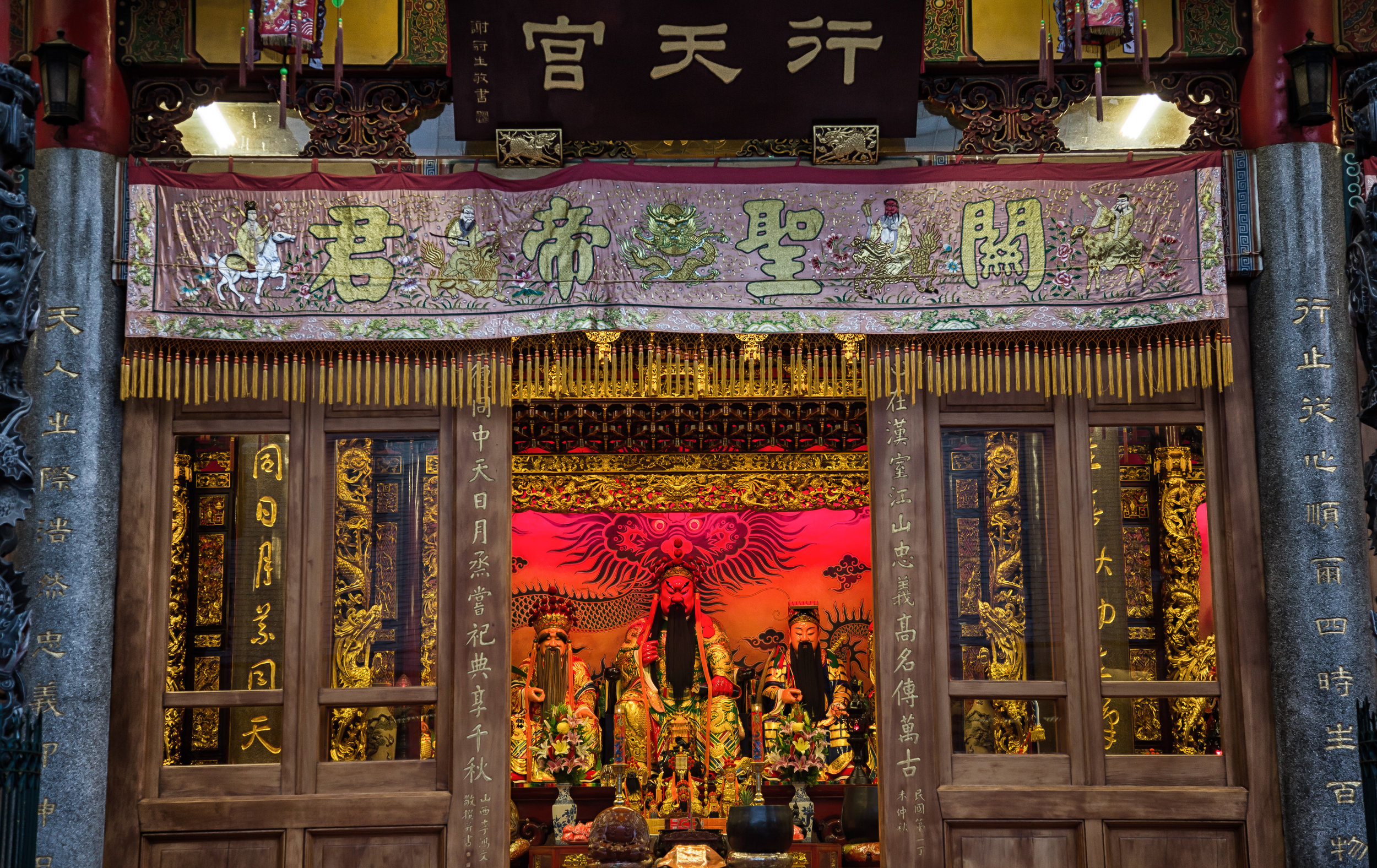
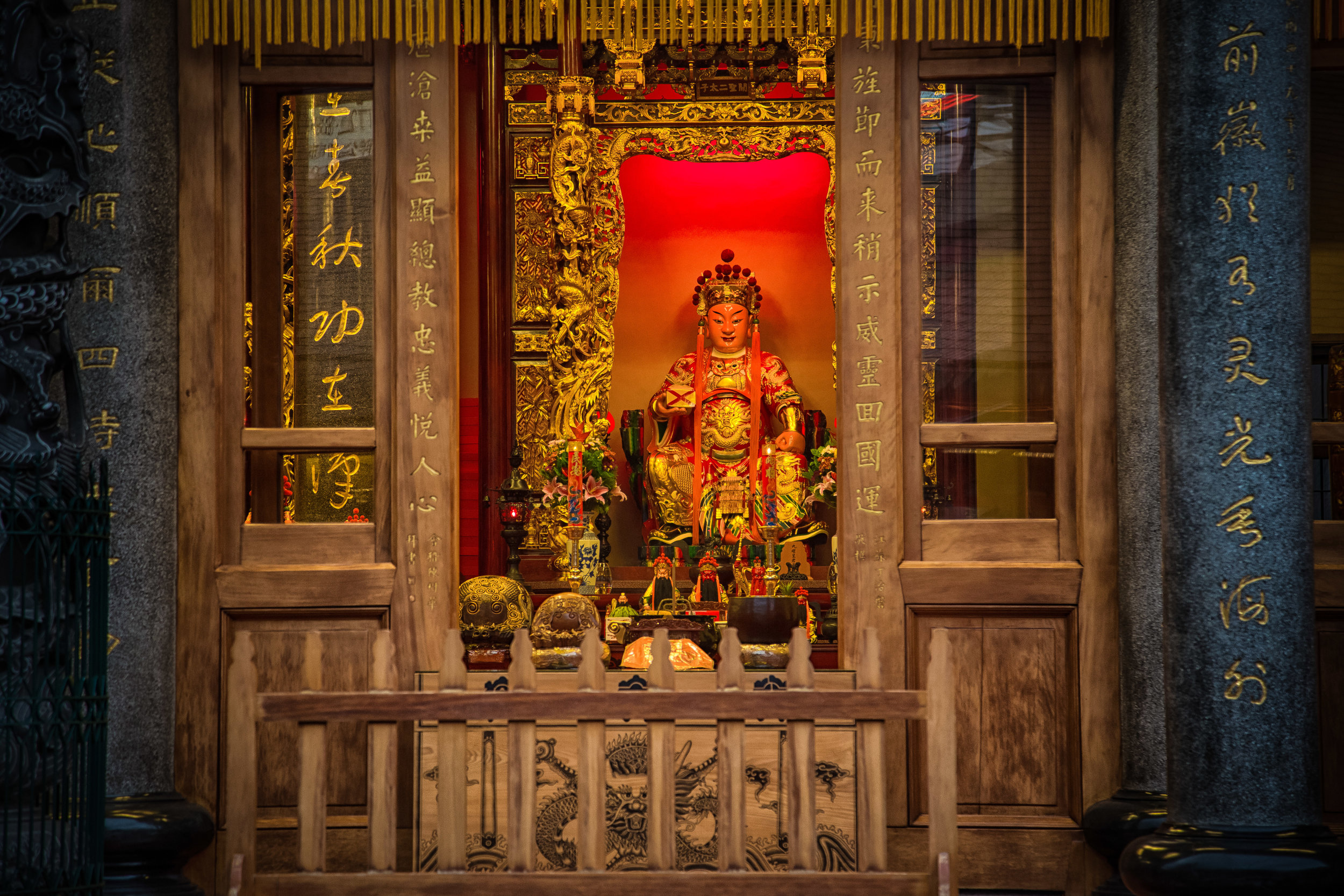
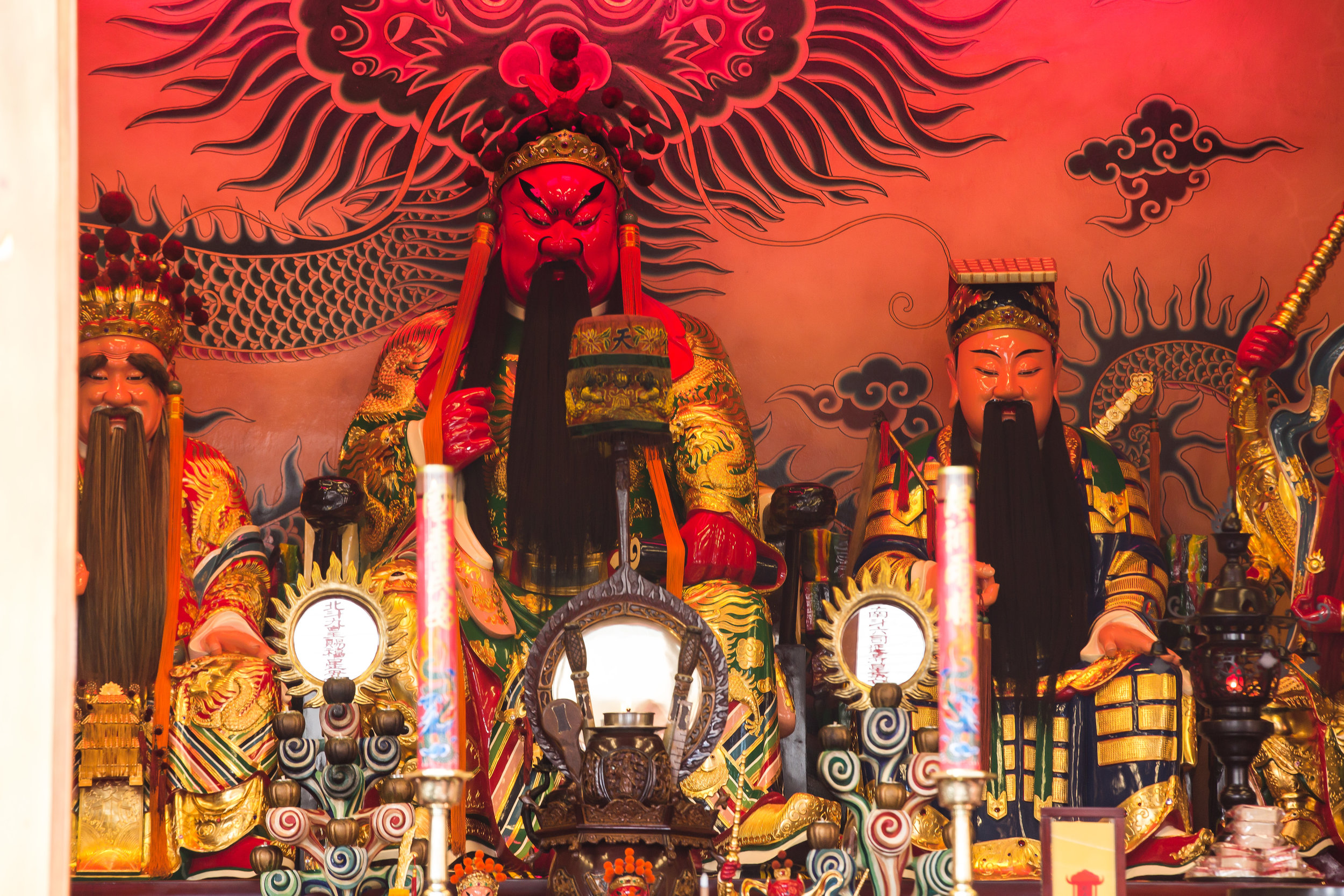
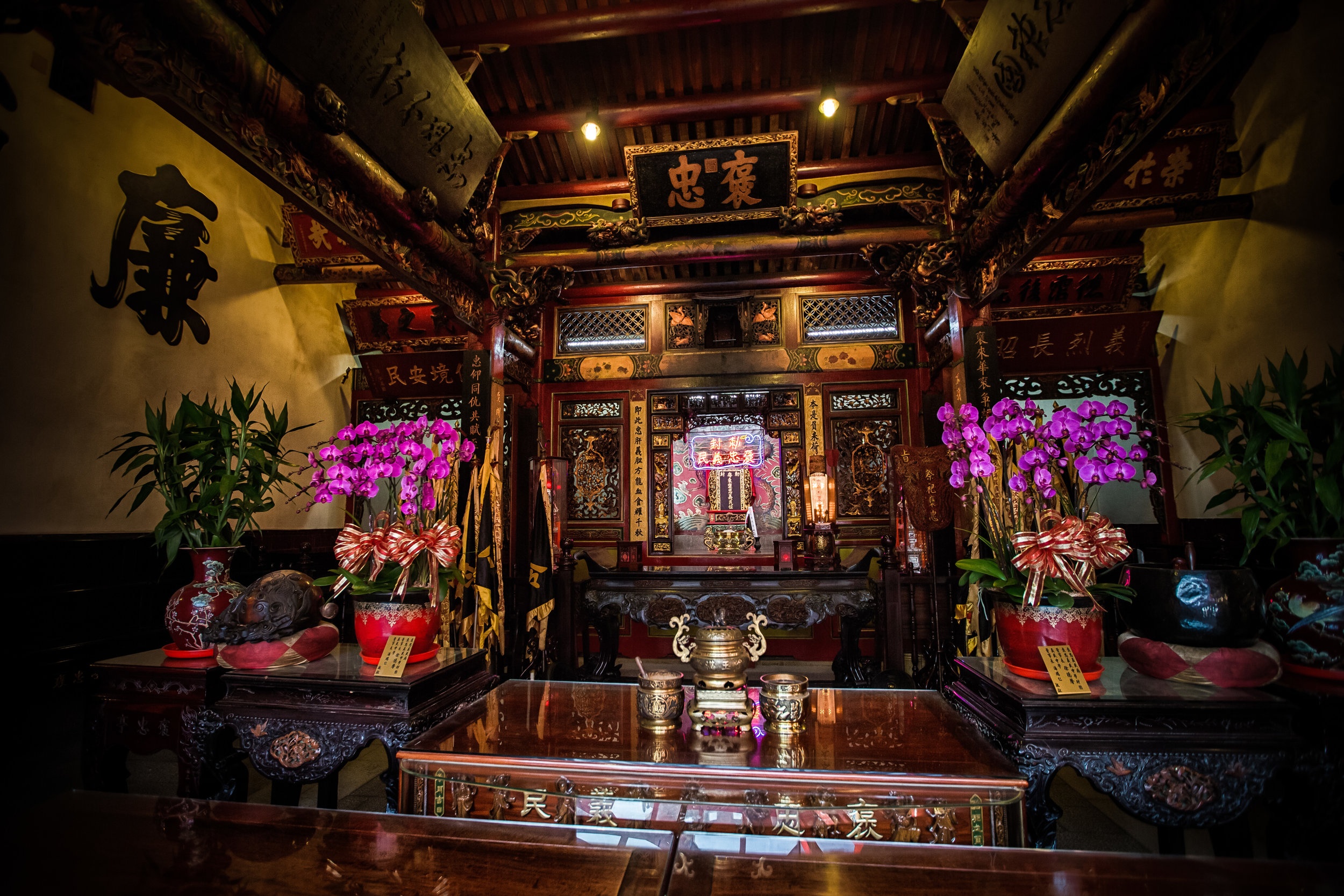
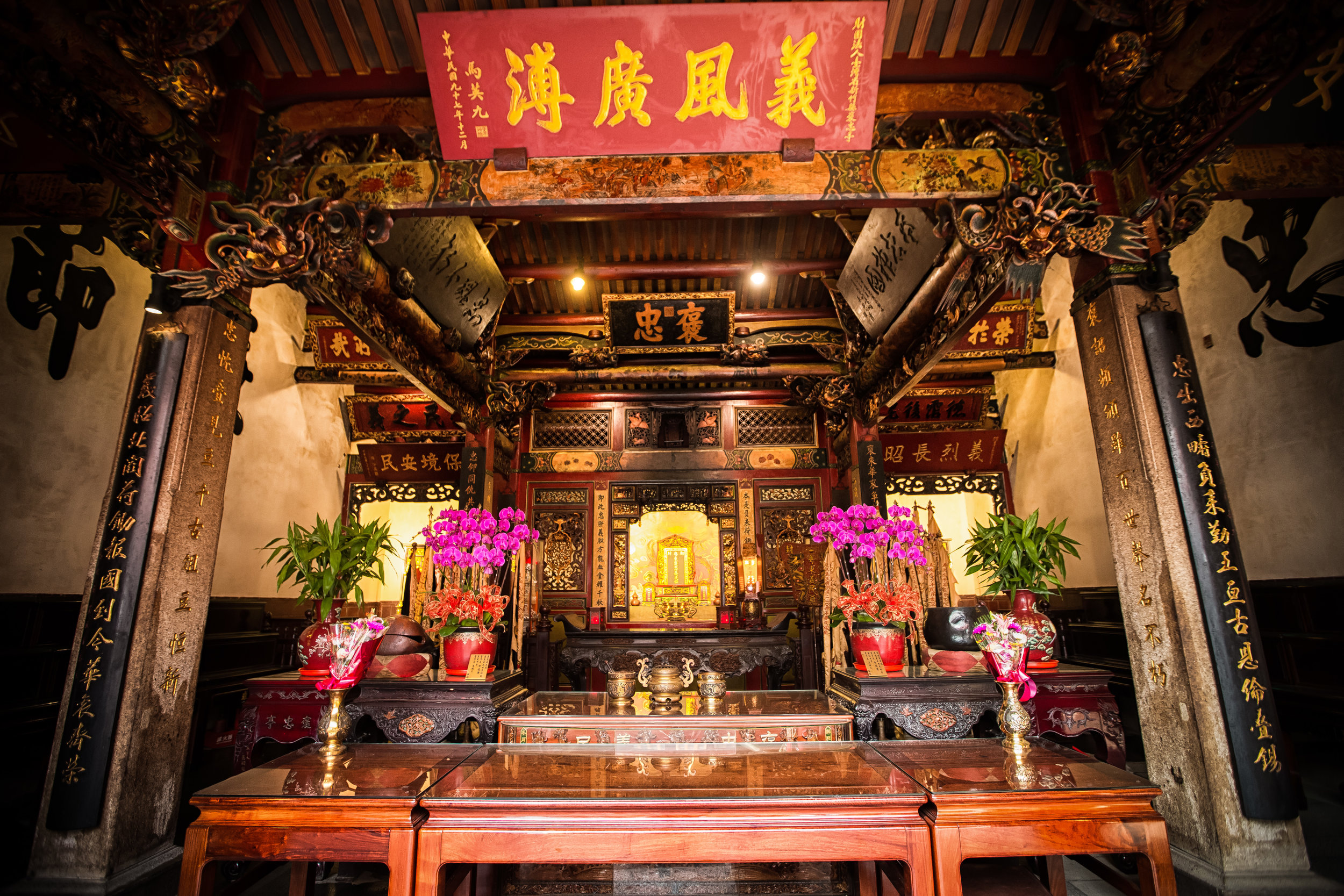
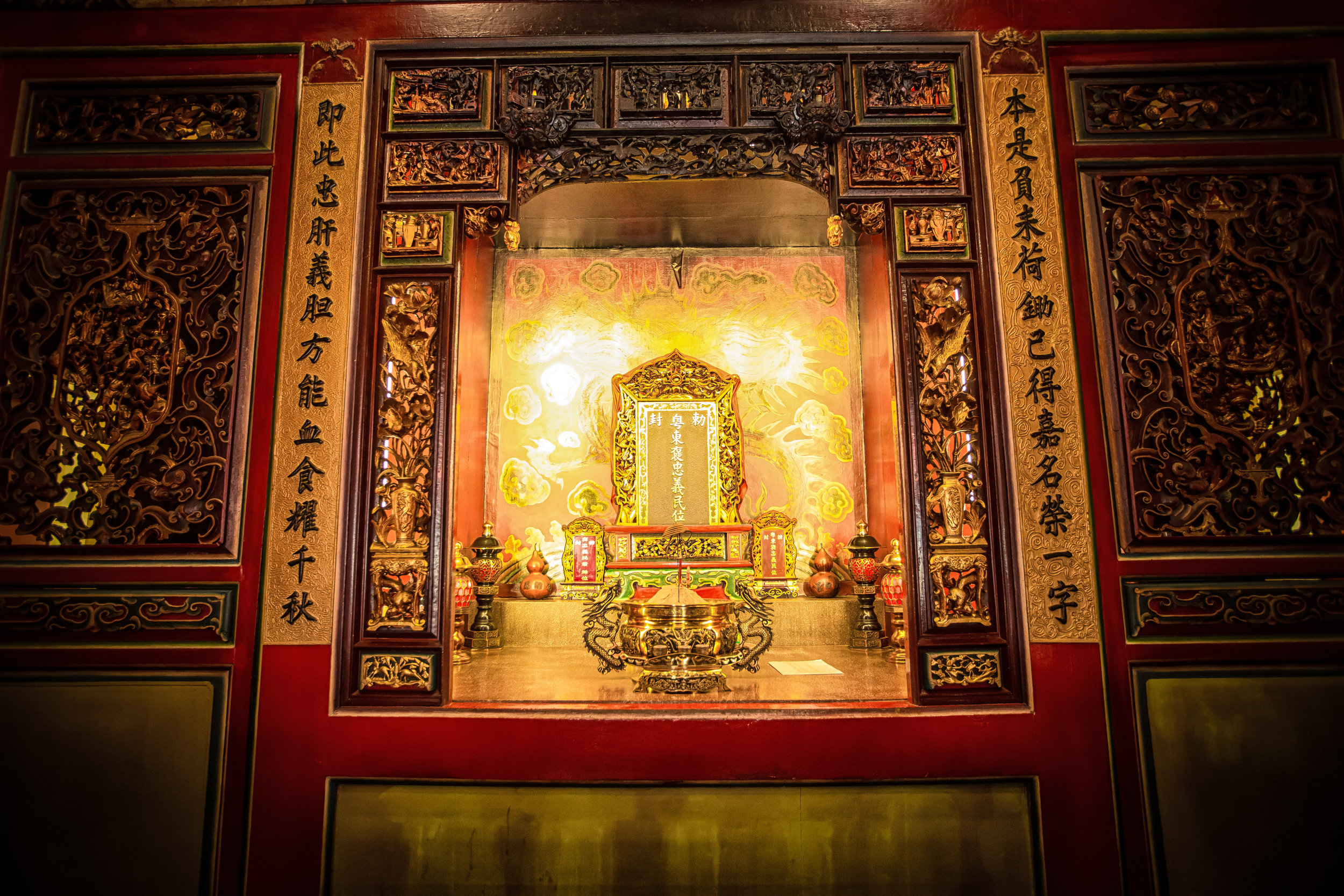
The temple is dedicated primarily to Lord Guan (關聖帝君) who is also known as Guan Yu (關羽) or Guan Gong (關公) and is one of the most recognized figures within Chinese culture. Guan was a leading general who served under Liu Bei (劉備) during China's Three Kingdoms period (220-280) and is now immortalized as a deity within Taoism and has also become a celebrated figure within Confucianism and Buddhism as well.
Guan who lived from 160-221AD was deified by Taoists sometime during the Sui dynasty (隋朝) between 581 and 618 and is worshipped in Taiwan, China, Hong Kong and pretty much any place where people of Chinese descent have migrated.
Stories about Lord Guan have been passed down through the generations and he has become somewhat of a legend thanks to the "Romance of the Three Kingdoms" (三國演義) a masterpiece of ancient Chinese literature.
The important thing to remember about Guan Yu however is that while there are a lot of superlative stories that deal with his exploits, he is widely respected within Chinese culture as the epitome of loyalty and righteousness. Today he is not only worshipped as an all-knowing and all-powerful deity but also as the god of war and a patron saint of business people and scholars. This is why statues of Lord Guan have become almost synonymous with Chinese businesses around the world as his presence is thought to help bring success.
As the god of war, he has also become a patron figure for the many different organized criminal groups within Chinese society and paying respect to Lord Guan is important for keeping discipline within the ranks. Don't expect to be brushing noses with scary-looking gangsters at Xingtian Temple though - the temple is a very zen-like and peaceful place of worship!
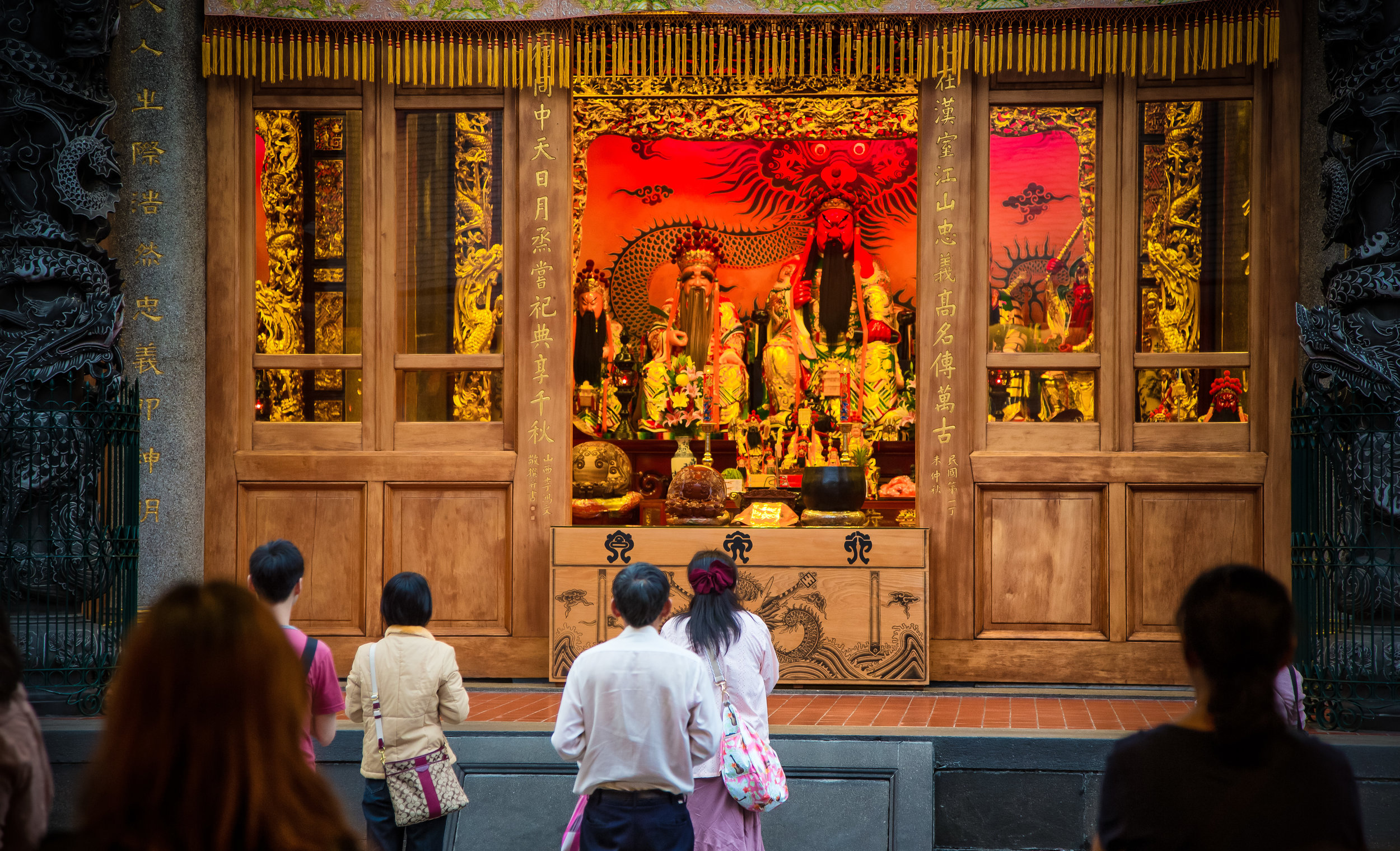
Accompanying Lord Guan in the temple are Lu Dongbin (呂洞賓), Zhang Dan (張單), Wang Shan (王善) and Yue Fei (岳飛) who together make up a group of important deities known to Taoists as the "Five Saviours" (五聖恩主) and are thought to help bring enlightenment and bestow benevolence to society.
Each of the gods accompanying Lord Guan in the temple has a specific role: Lu Dongbin has a sword which is supposed to destroy greed, anger and ignorance in people's hearts. Zhang Dan, who is also known as the 'Kitchen God' keeps records of things people say and do and presents the records to the Jade Emperor (玉皇大帝). Wang Shan who is also known as the 'Thunder God' patrols the heavens and the earth rewarding people for doing good deeds and punishing those who do wrong. Yue Fei is a lot like Lord Guan and was a general in life - Today he is respected for his loyalty and righteousness.
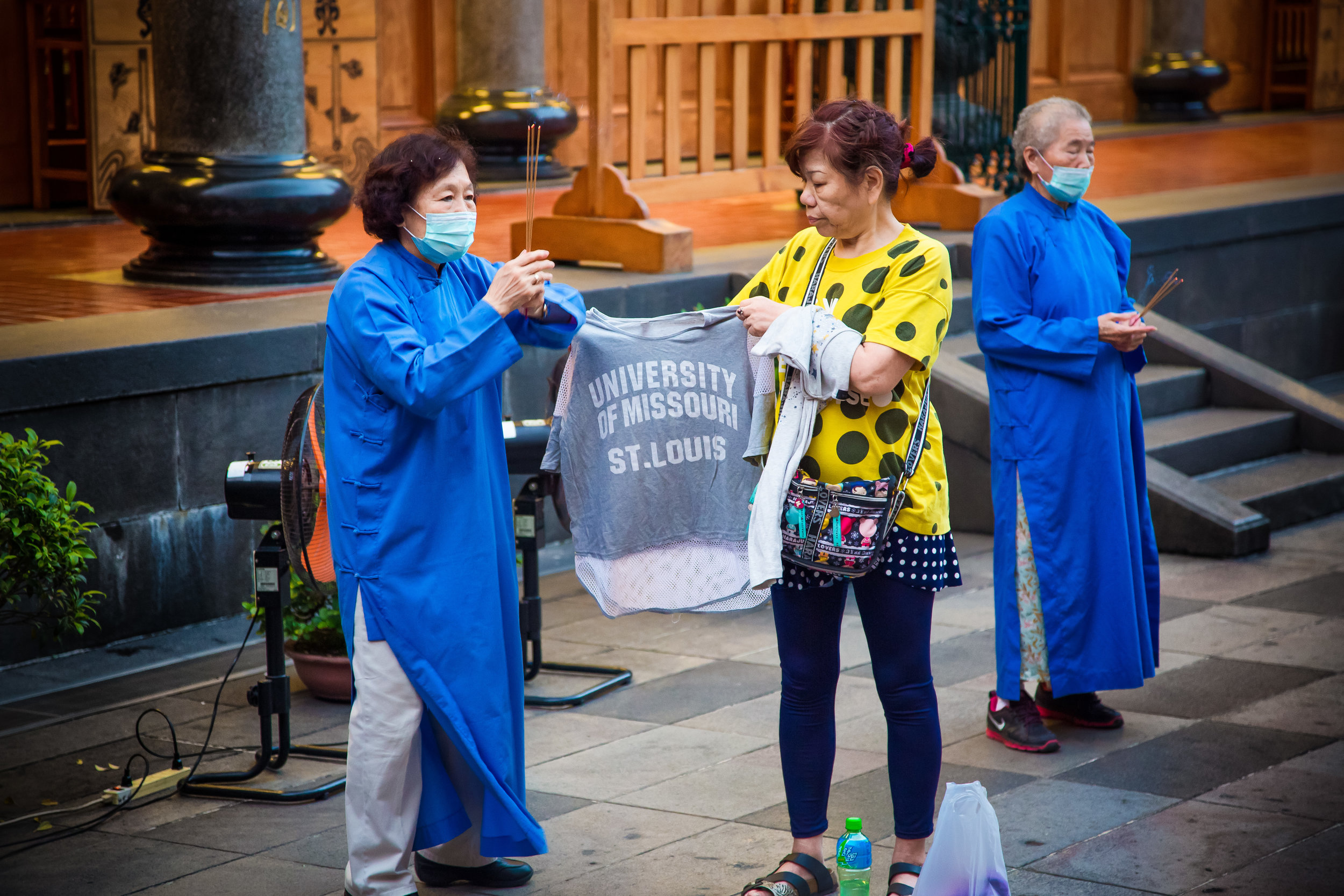
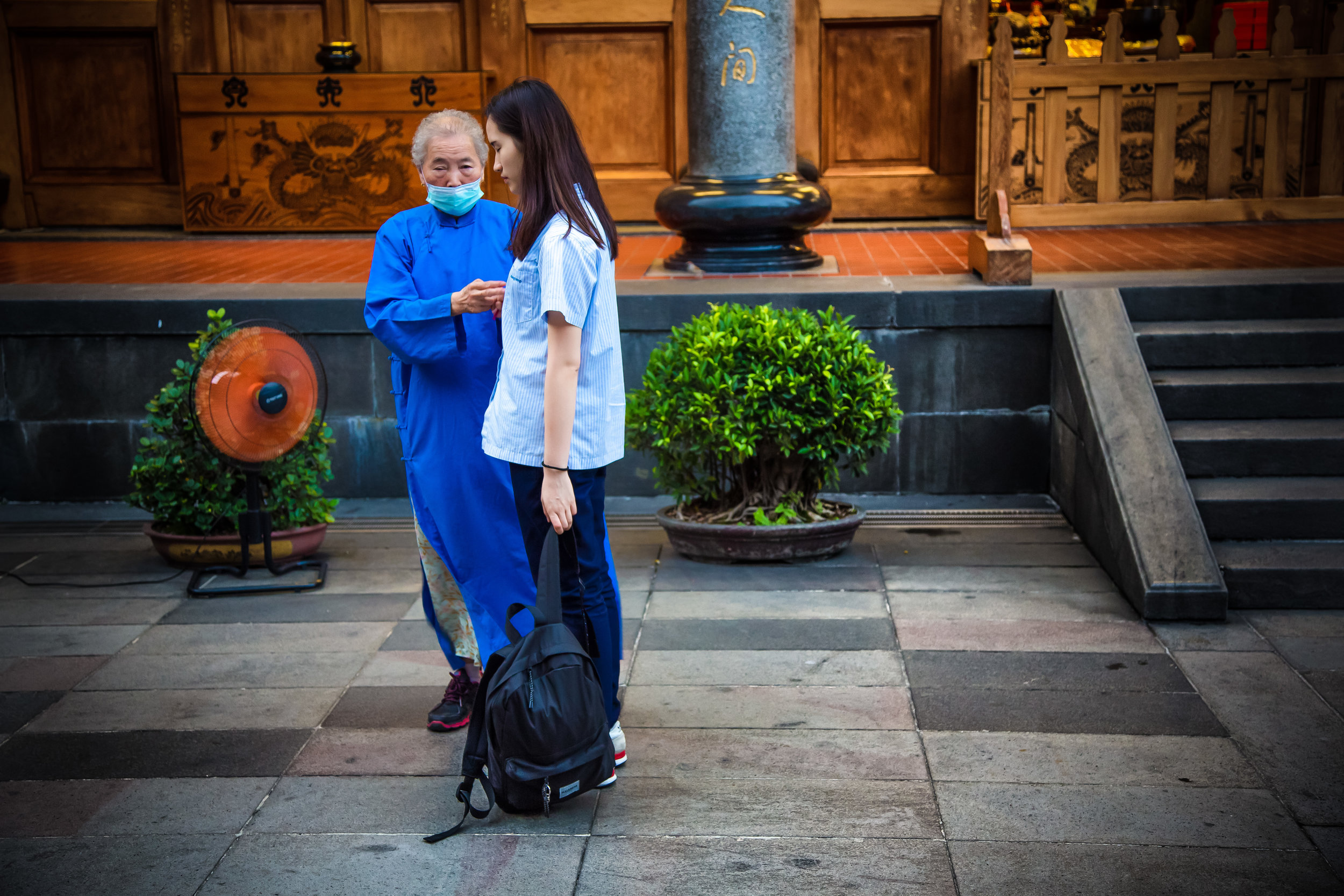
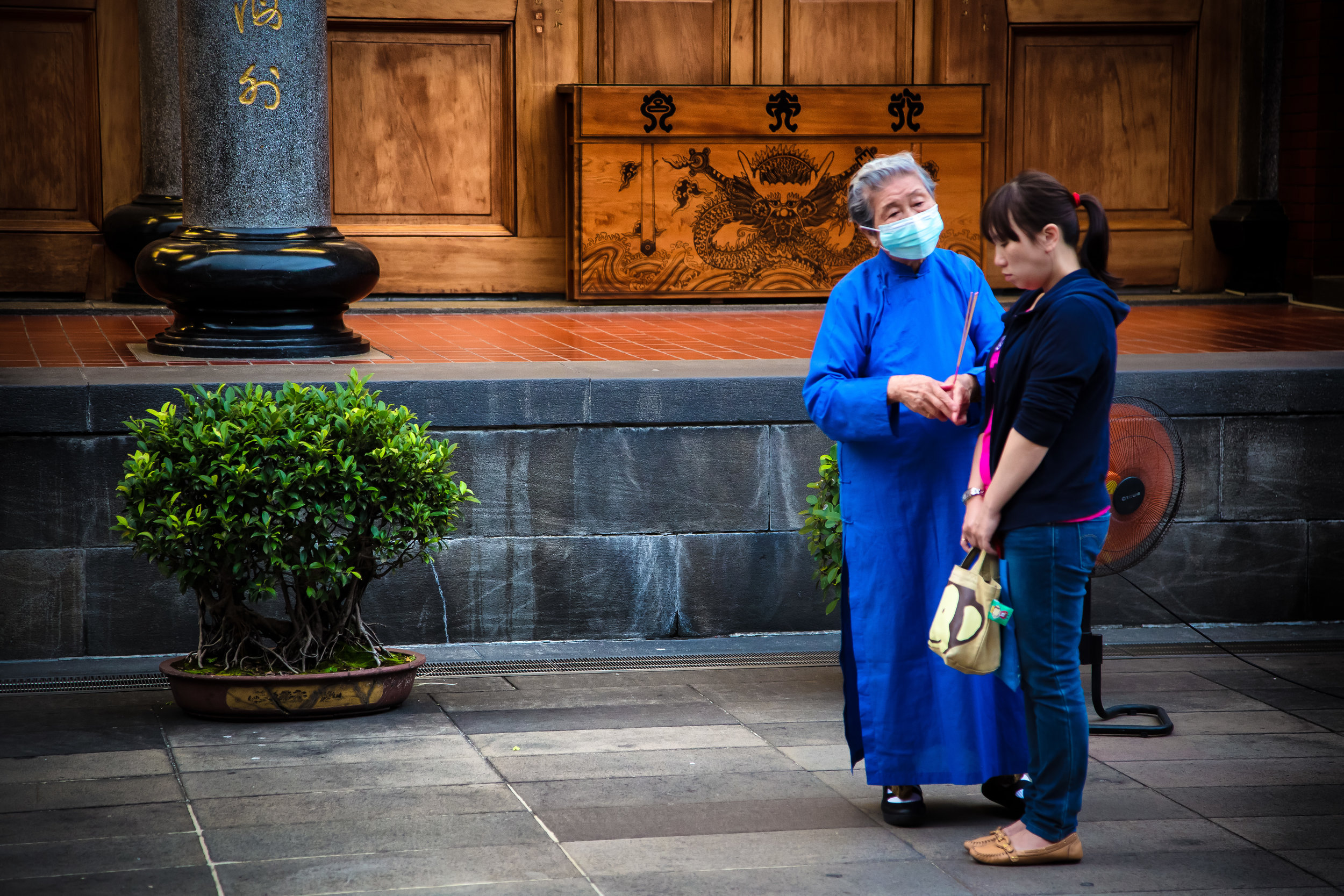
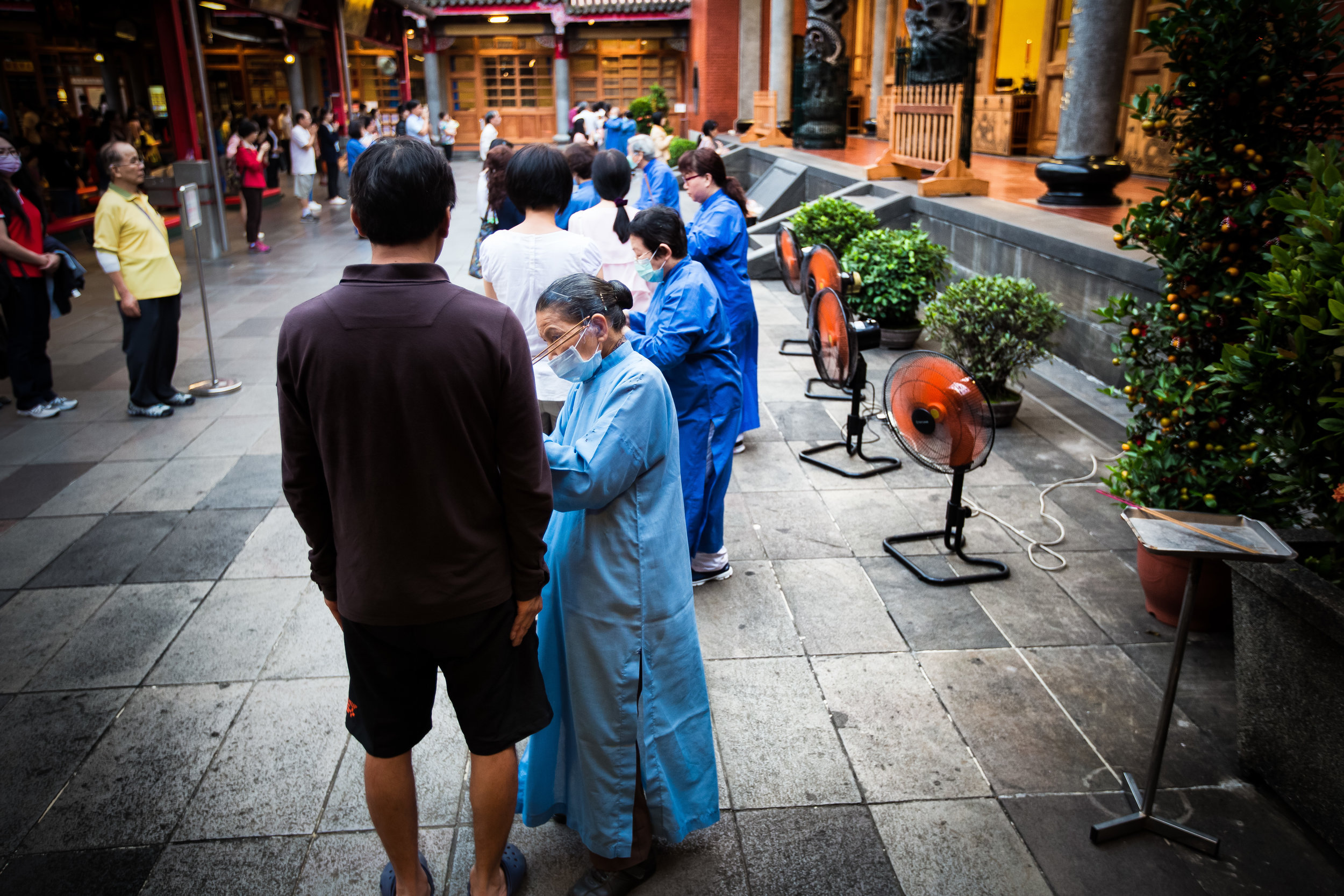
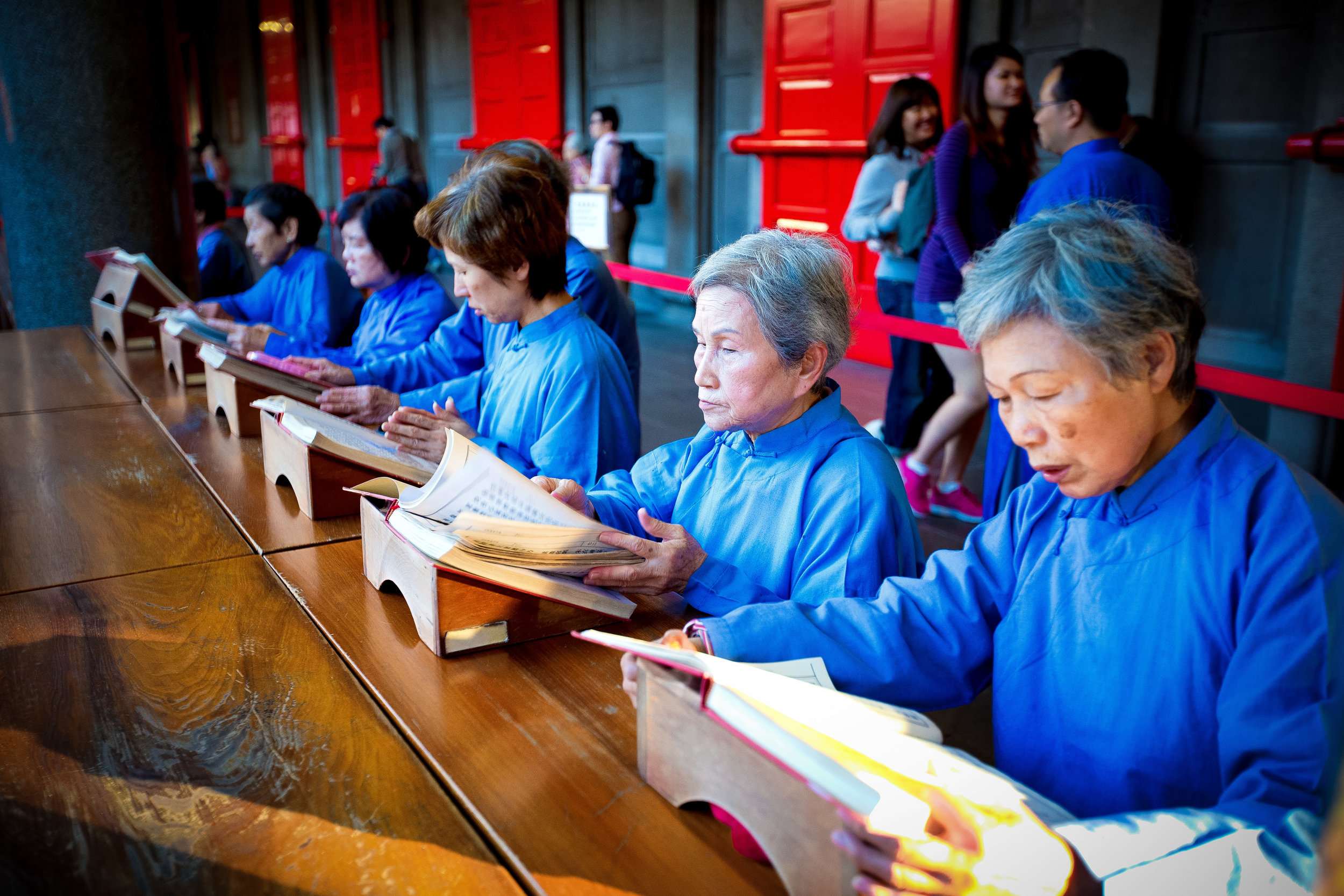
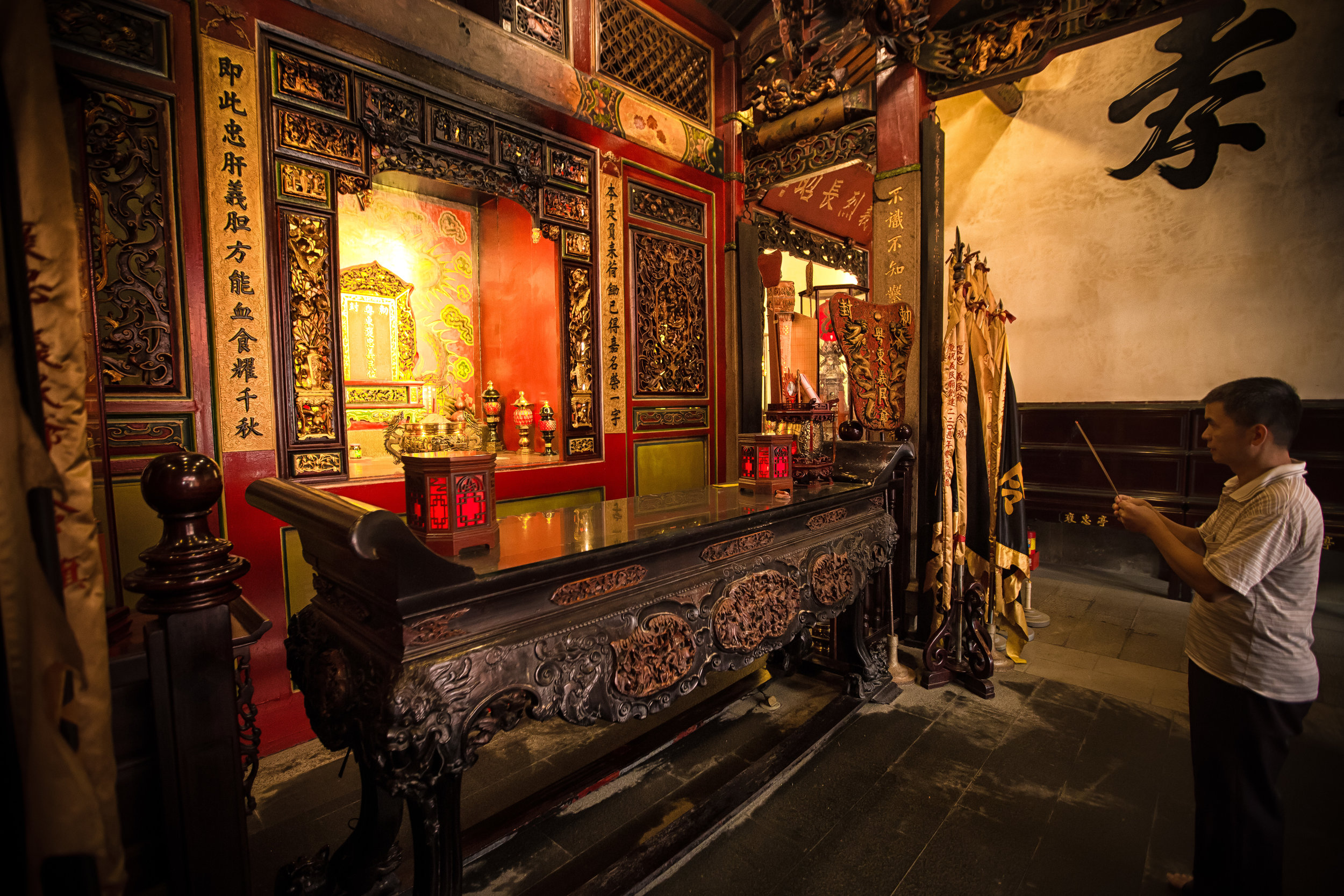
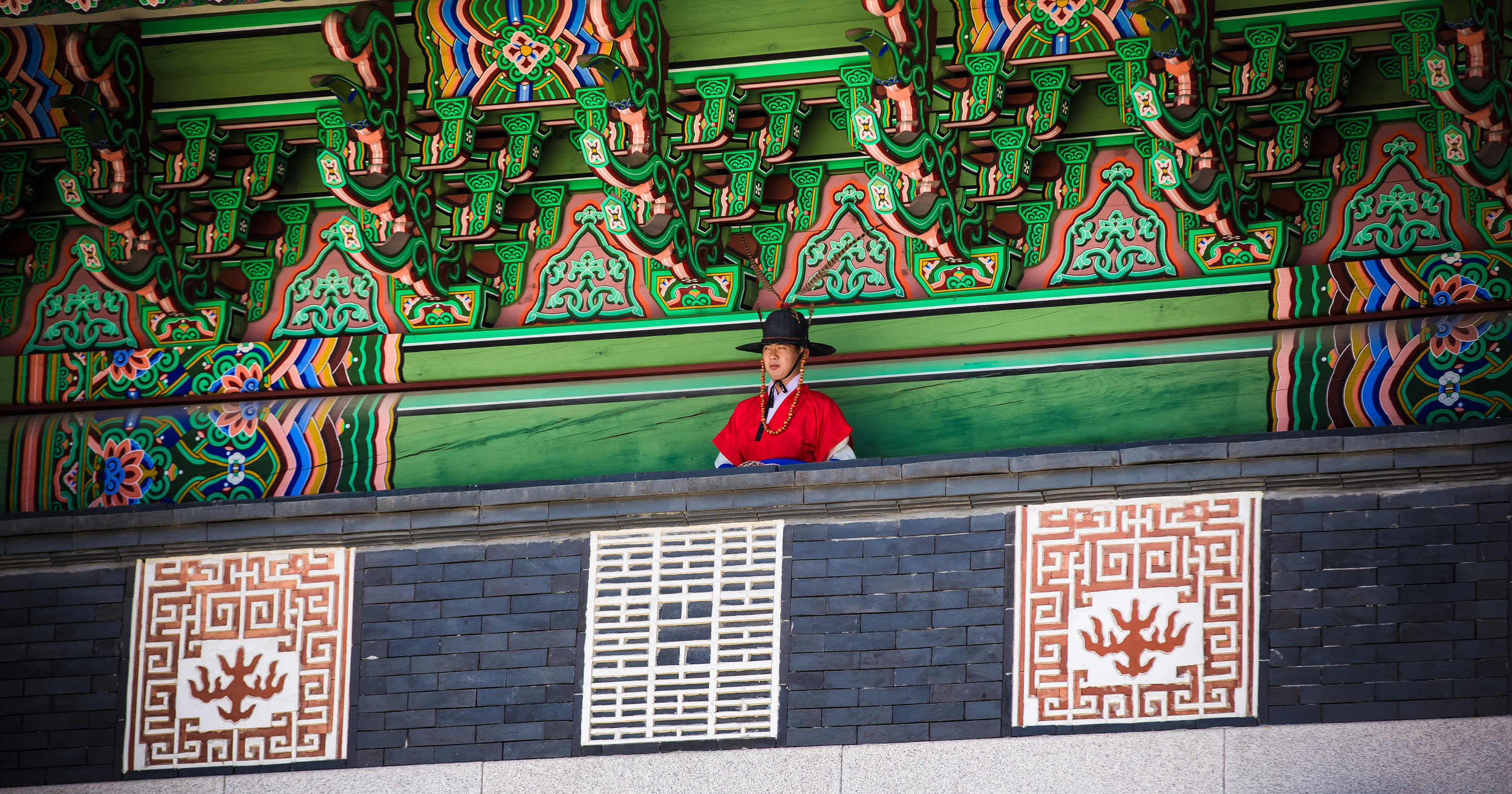
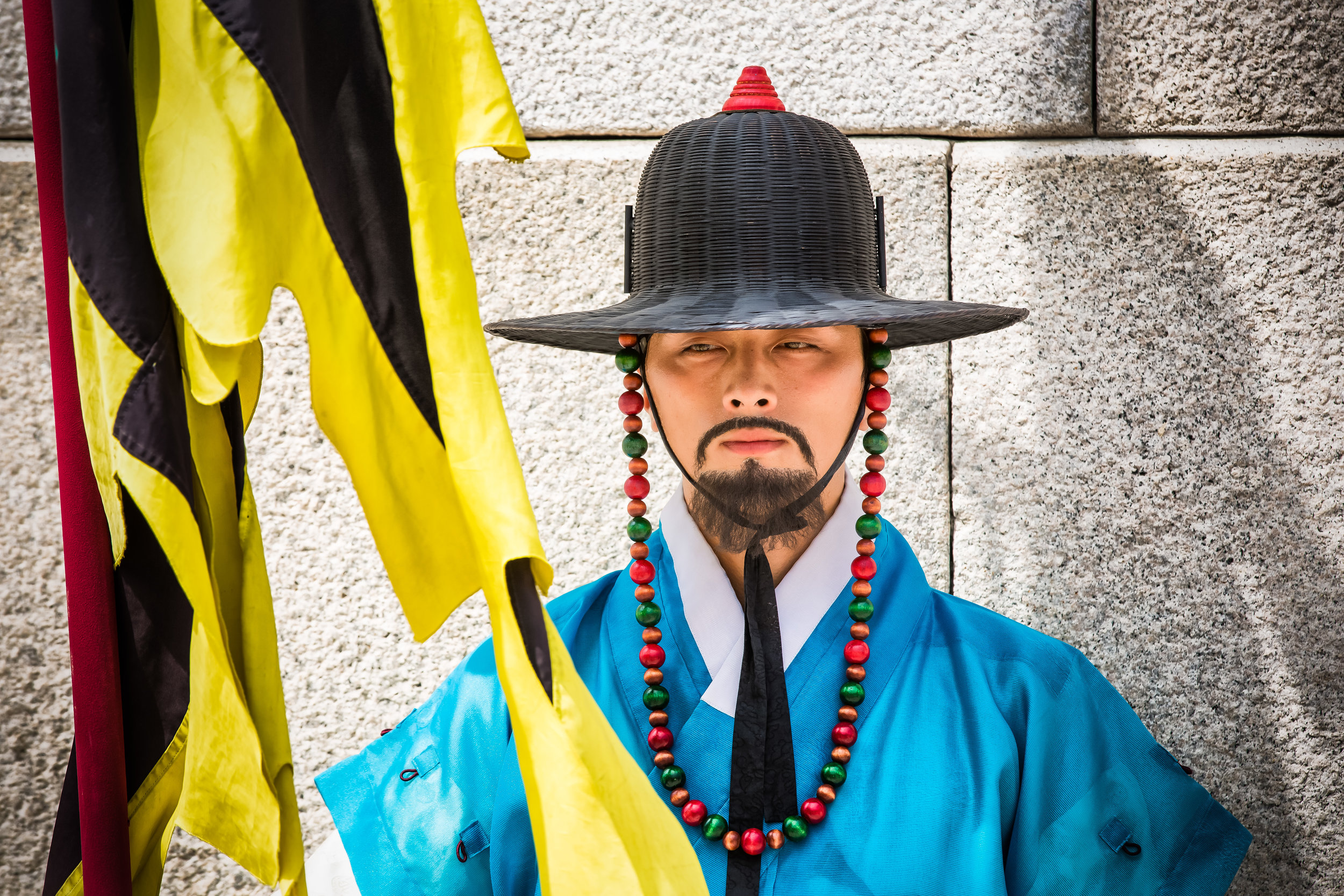
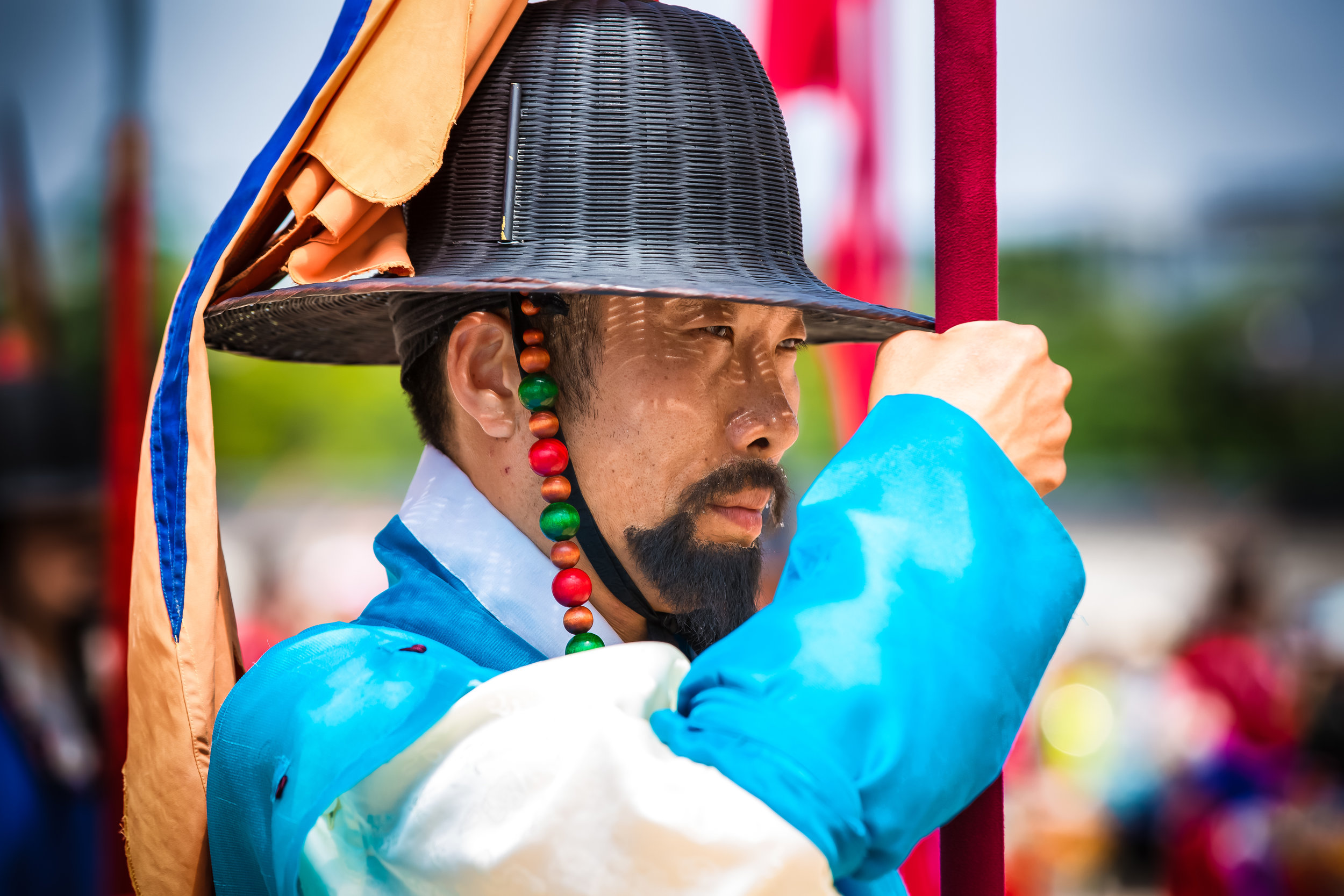
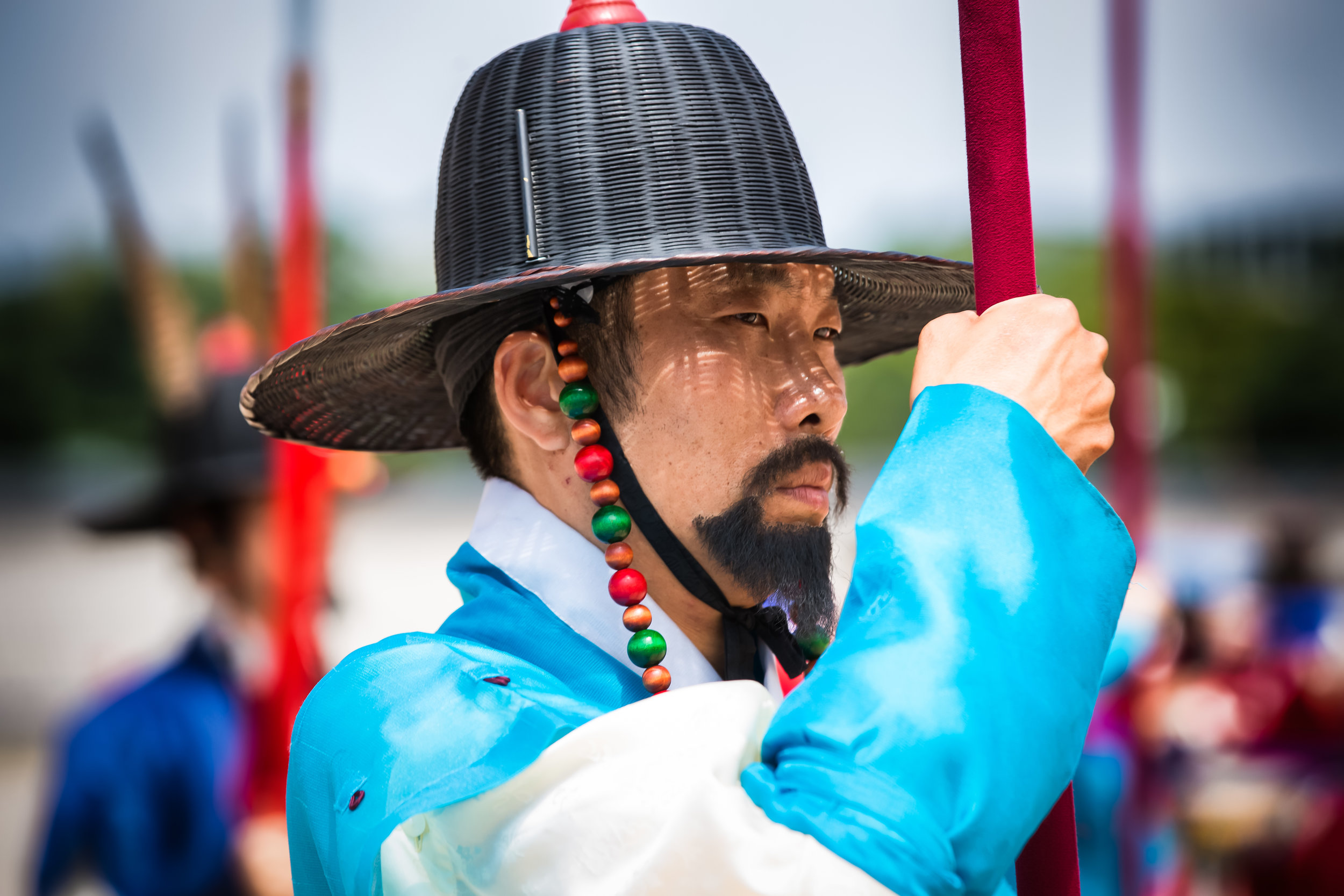
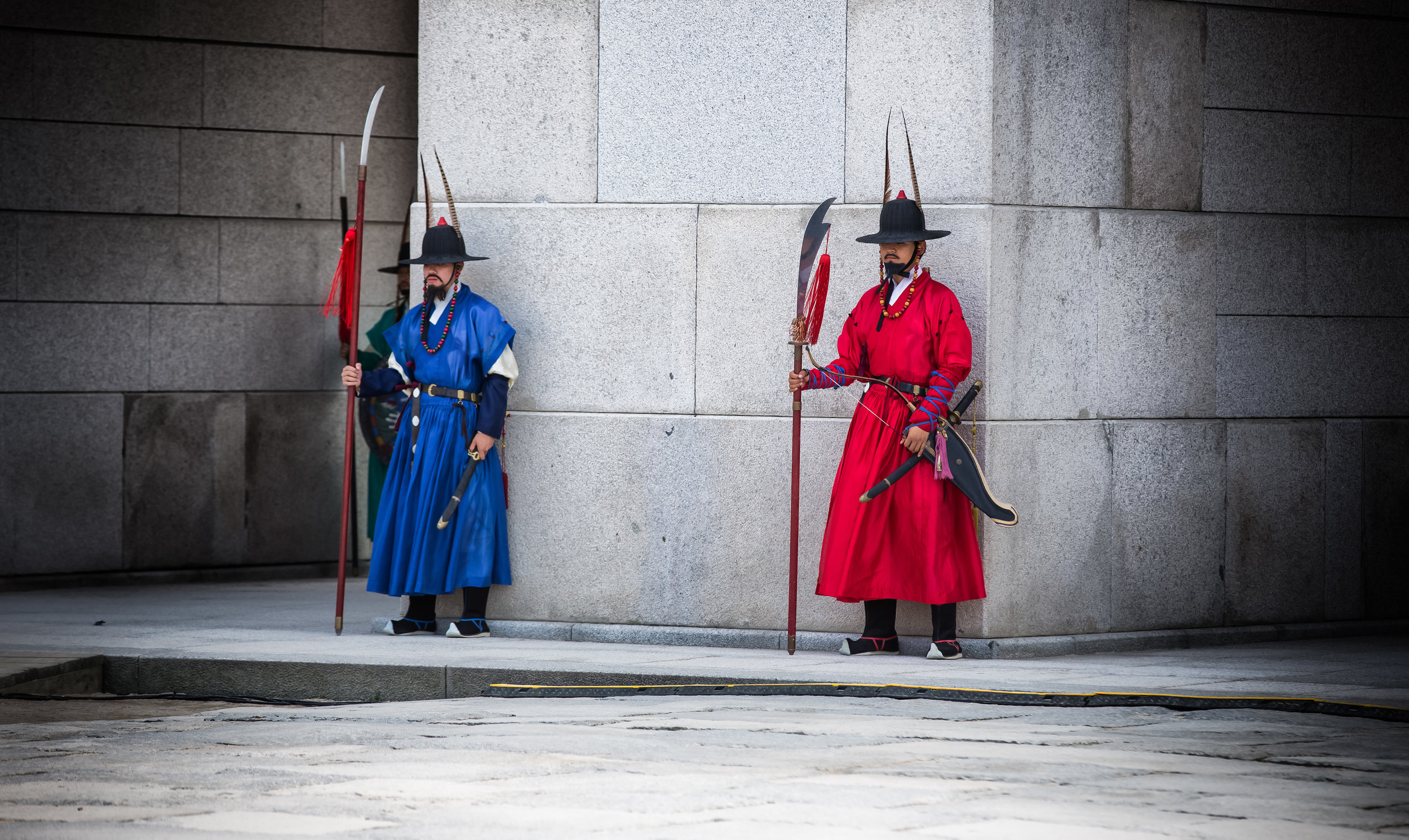
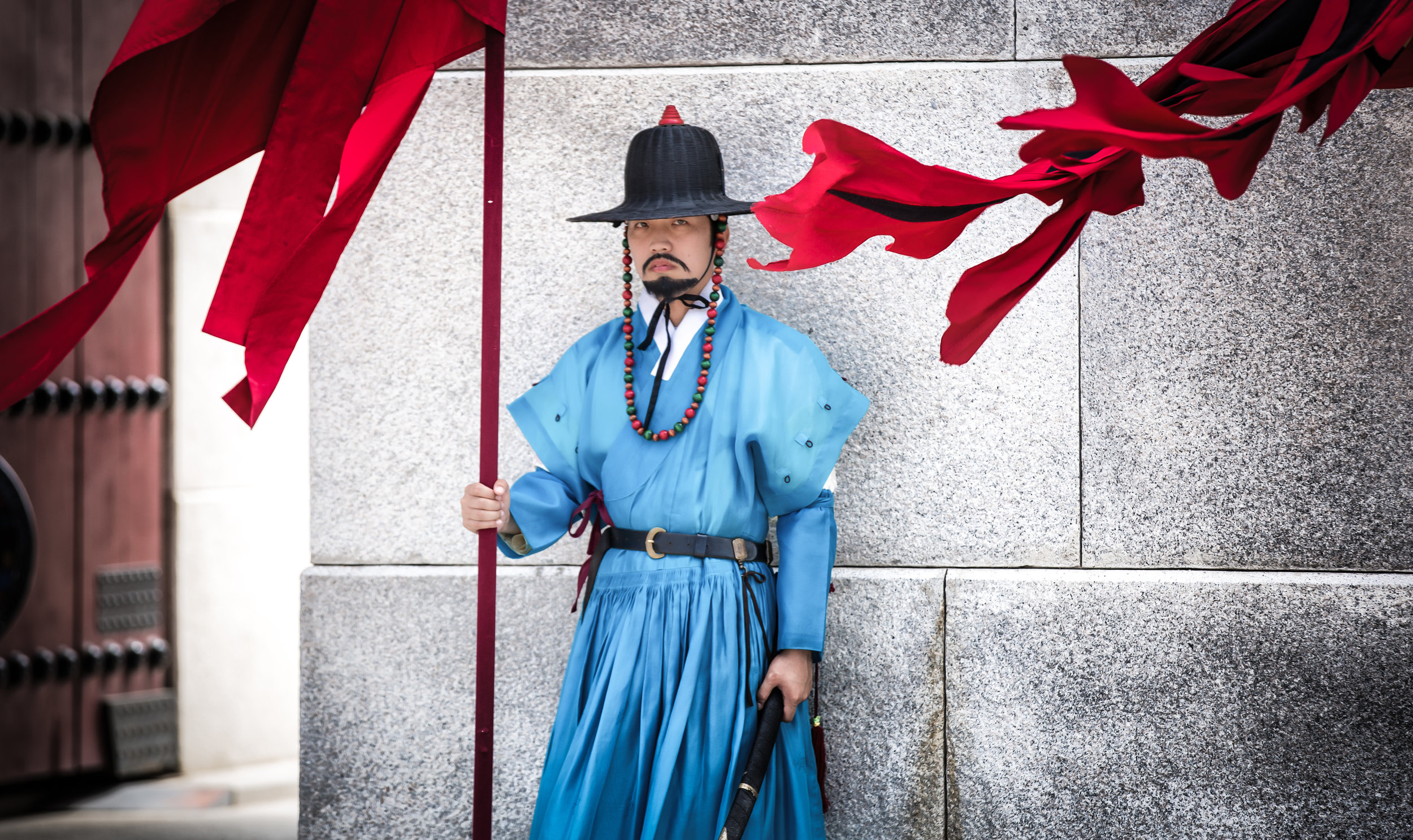
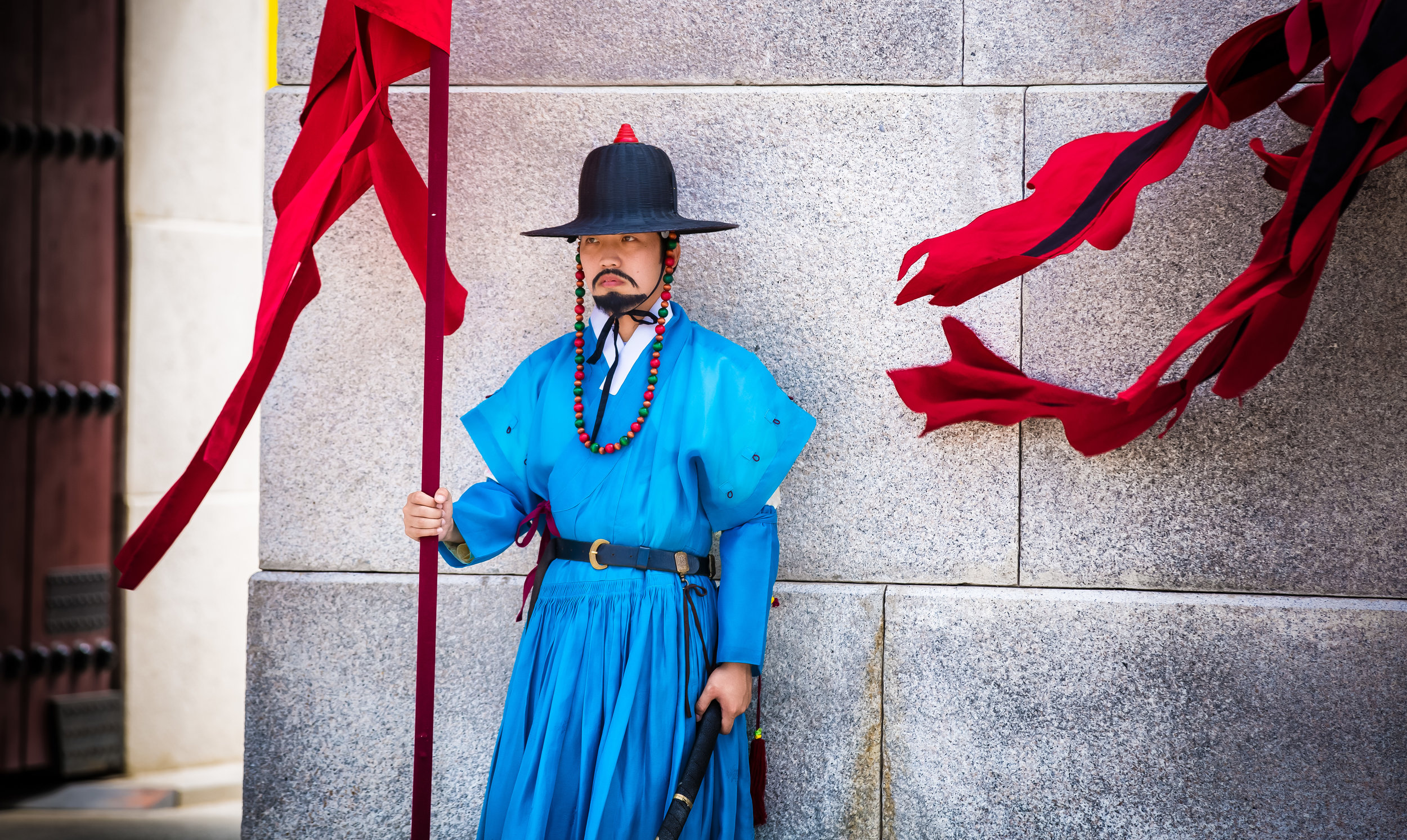
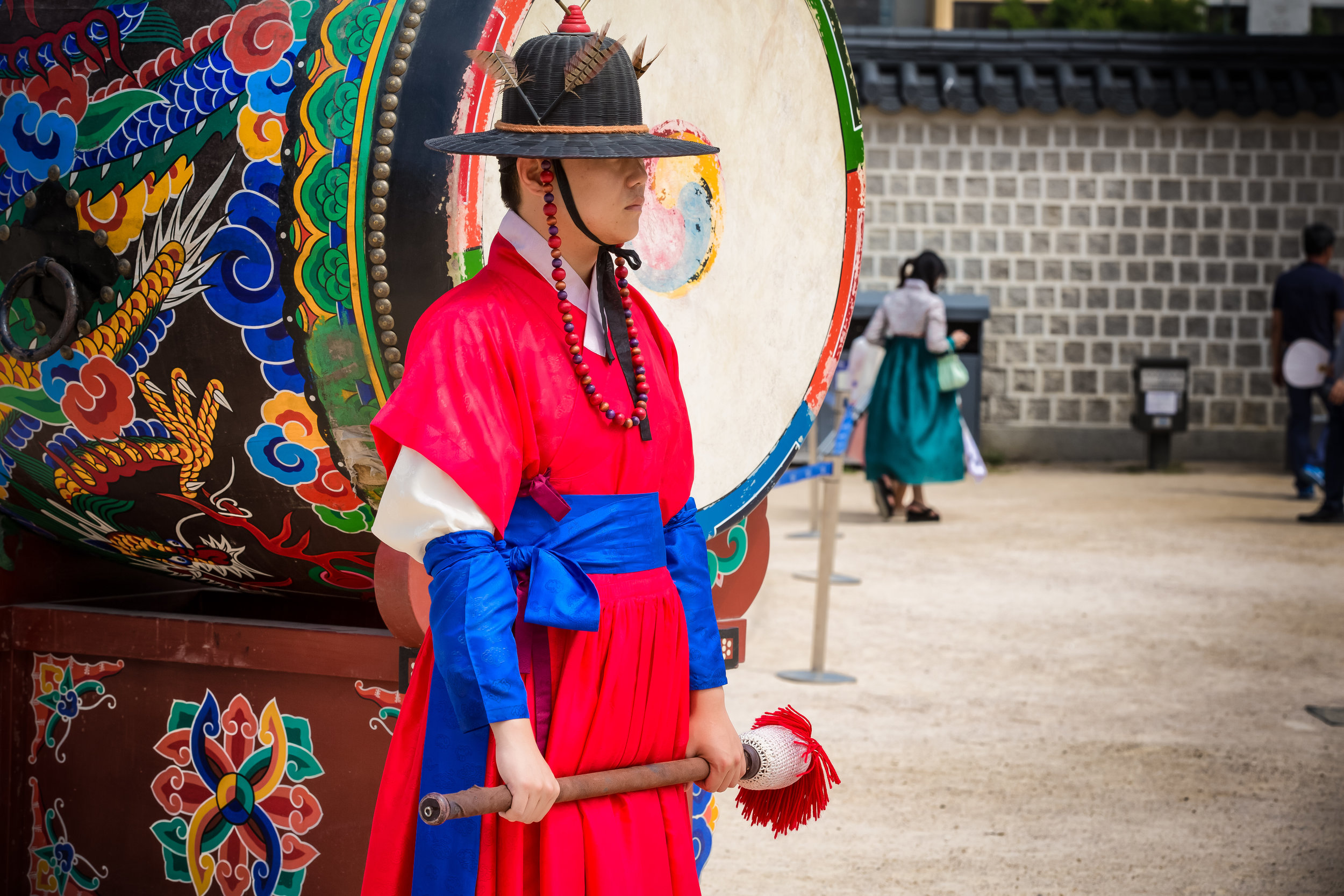
One of the main draws to the temple (prior to 2014) were the temple attendants who are known as Xiaolaosheng (效勞生) or “helpers” wearing blue robes. The helpers walked around with large bouquets of incense to hand out to people who came to the temple to pray. For photographers, the sight of these ladies was actually really cool. Today the ladies in blue don't carry incense but continue to carry out other important duties around the temple.
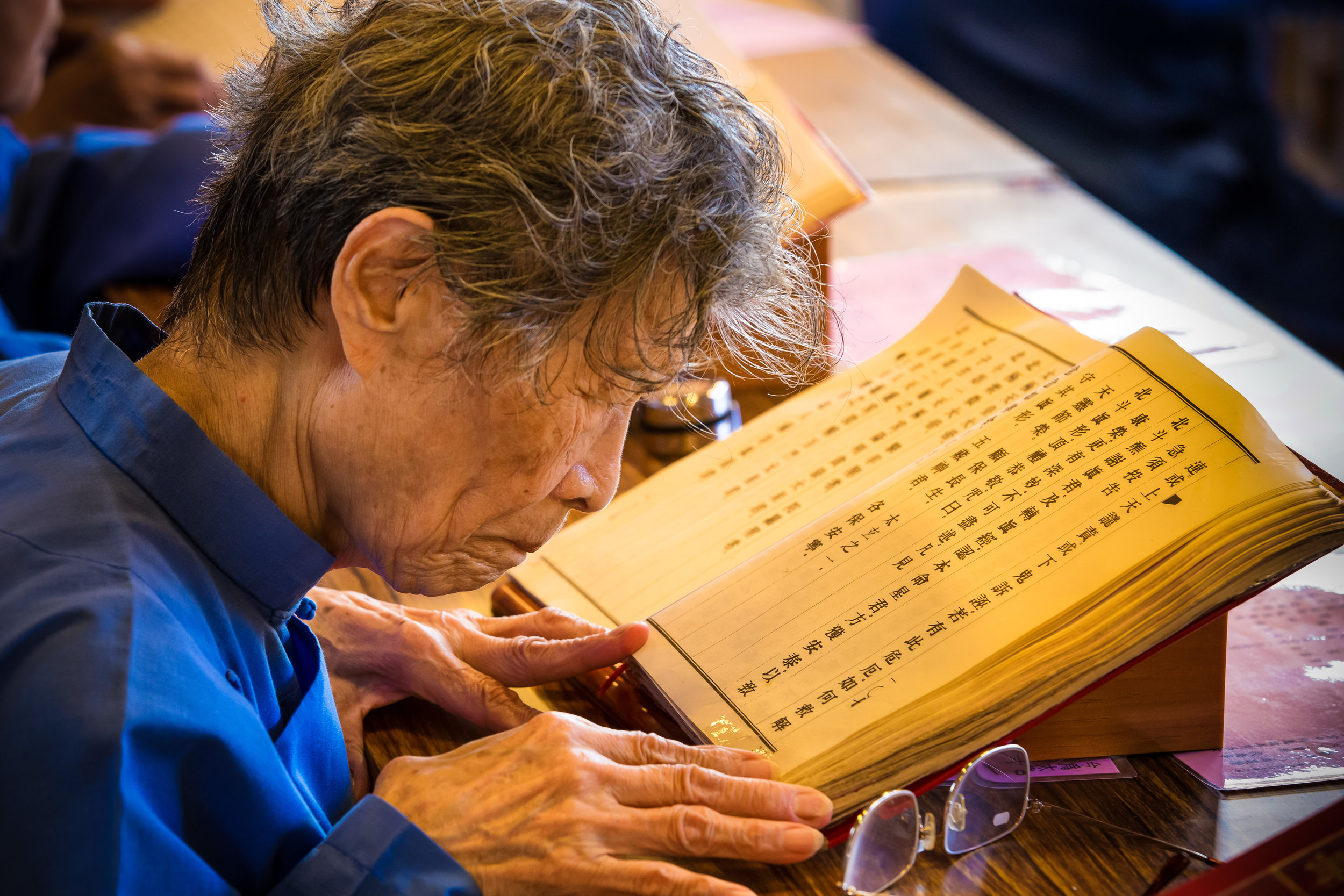
The blue-robed "helpers" are a constant fixture of the temple and no matter when you go or what time of the day you are there they will always be there providing services to the people who visit. While most temples in Taiwan have volunteers of this sort, Xingtian Temple is a bit different in that the "helpers" are a much more organized group who perform quite a few duties throughout the temple - Its common to find them reciting sutras, chanting verses, assisting visitors, answering questions and performing Taoist rituals.
The helpers purpose is to work for the 'benefit of others as well as cultivate their hearts and minds'. While "helper" is a simple translation, you might want to just refer to them as 'Temple Disciples' to make things a little more easy to understand. The helpers comes from all walks of life and speak many languages, so if you have a question they will be happy to answer but before they do so they'll say "ping'an" (平安) which means "safety" as a way to give a blessing to anyone who they come in contact with.
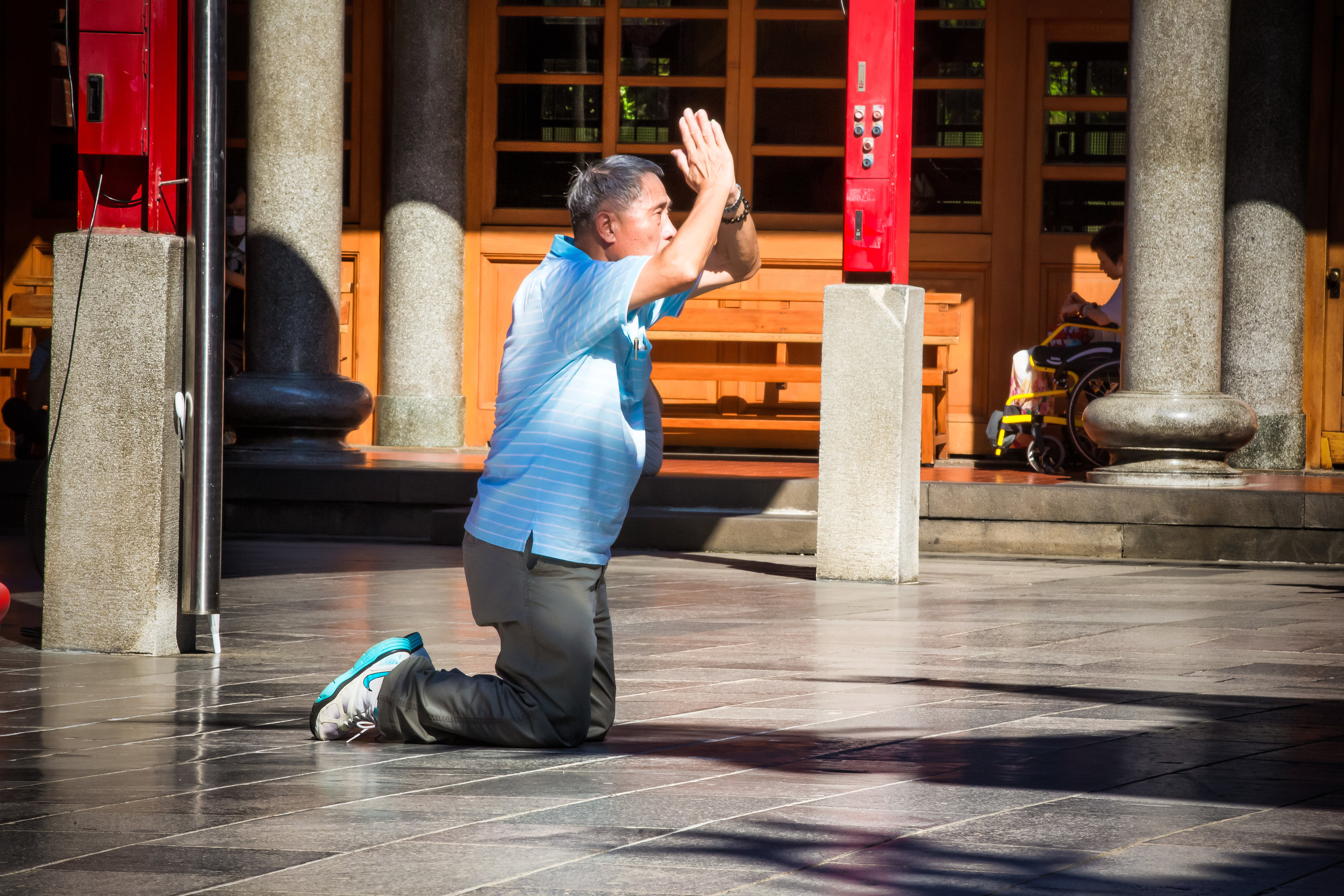
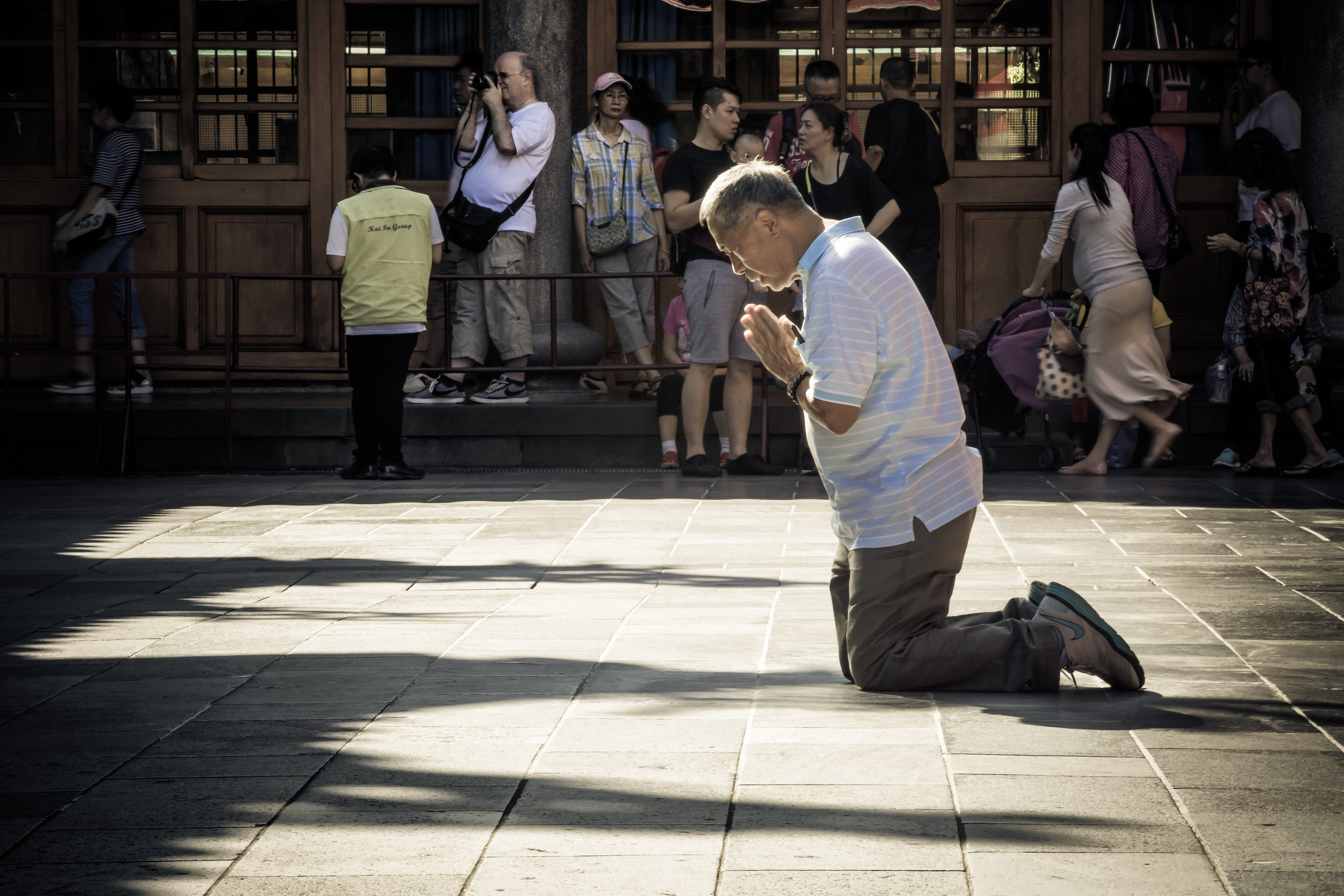
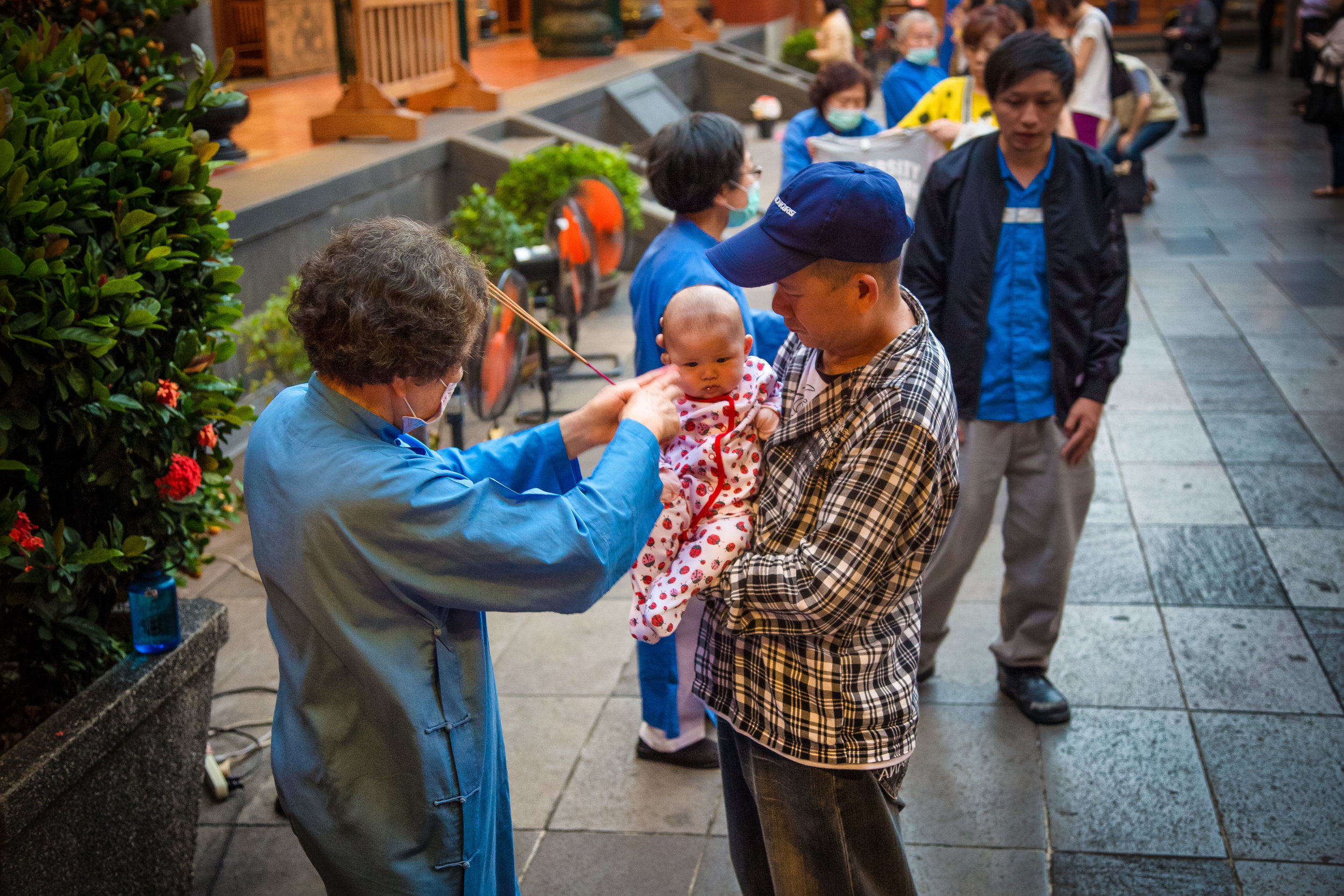
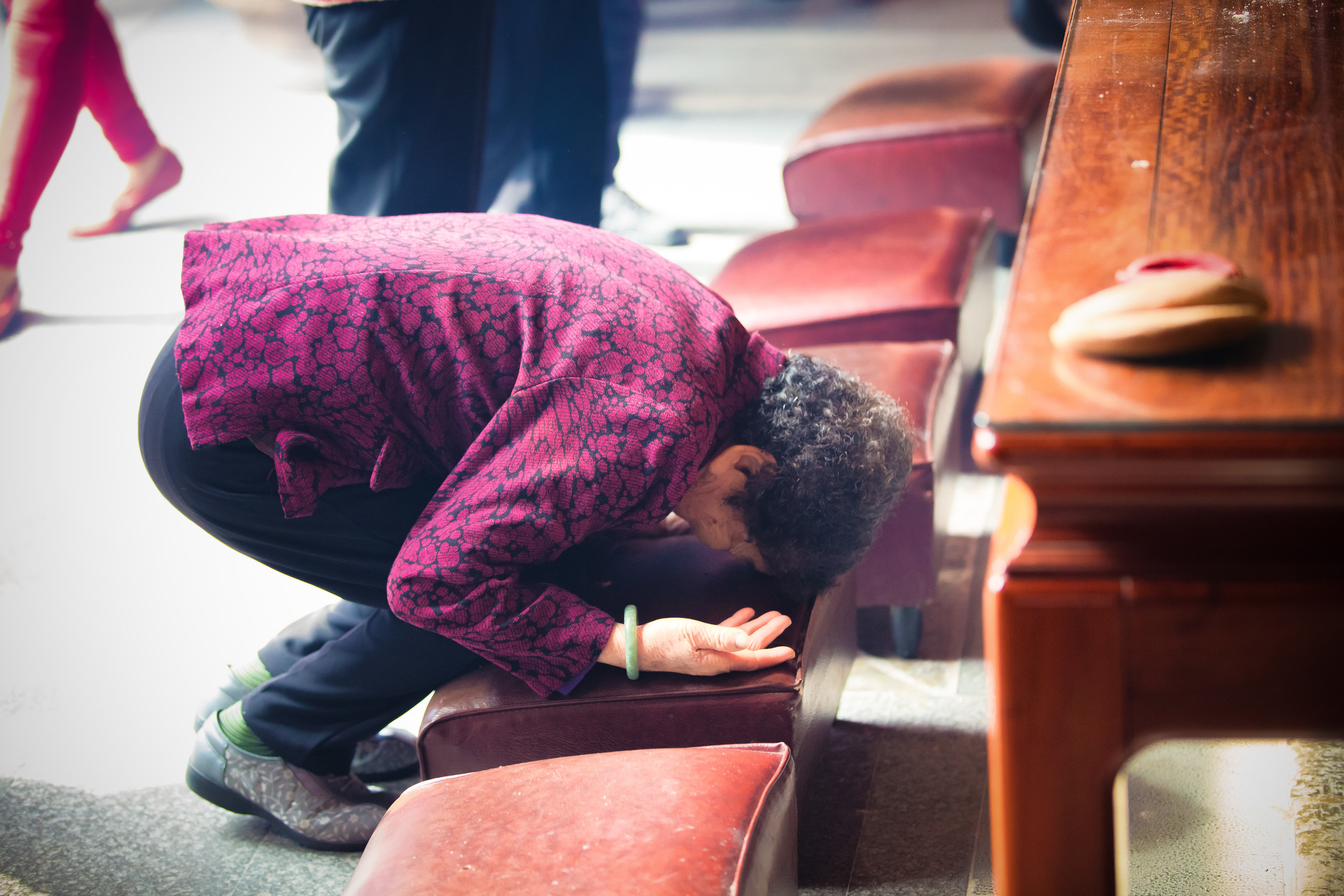
One of more interesting duties for the helpers is for a ritual called "recalling frightening souls" (收驚) which is an age-old Taoist ritual meant to help purify oneself and bring calm to your soul. The thought process behind it is that from time to time, something might happen which frightens you so much that your soul (one of them) attempts to 'escape' from your body. It could be anything from a good scare during a horror movie to a close call on the road. If you feel yourself suffering from this sort of shock, it is quite normal for people to visit a temple to have this ritual performed on them and Xingtian temple is the primary destination for the people of Taipei to have this sort of spiritual therapy done.
The ritual which is a 'cleansing' or even an 'exorcism' of sorts is meant to calm your soul and bring it back into your body so that you are more at ease. The women who perform the ritual at this specific temple will wave a stick of incense around all of your chakra points and whisper a prayer signifying that it is safe for your soul to return to your body.
The most interesting thing for me is that there are always long lines at Xingtian Temple for this ritual which is performed free of charge but probably also a good indication that close calls when it comes to driving in Taiwan are more common than you'd expect. Taiwanese people live a stressful fast-paced life and having this spiritual service available to them is likely very beneficial if you're prone to believe in this kind of thing.
The other interesting point is that you don't actually even have to be there in person to have the ritual performed on you. One one of my visits I noticed an older lady holding up a shirt from an American university and having one of the attendants performing the ritual. My guess was that her son was studying overseas and had something happen to him, so she was helping him out with a spiritual 'dry-cleaning' of sorts.
Design
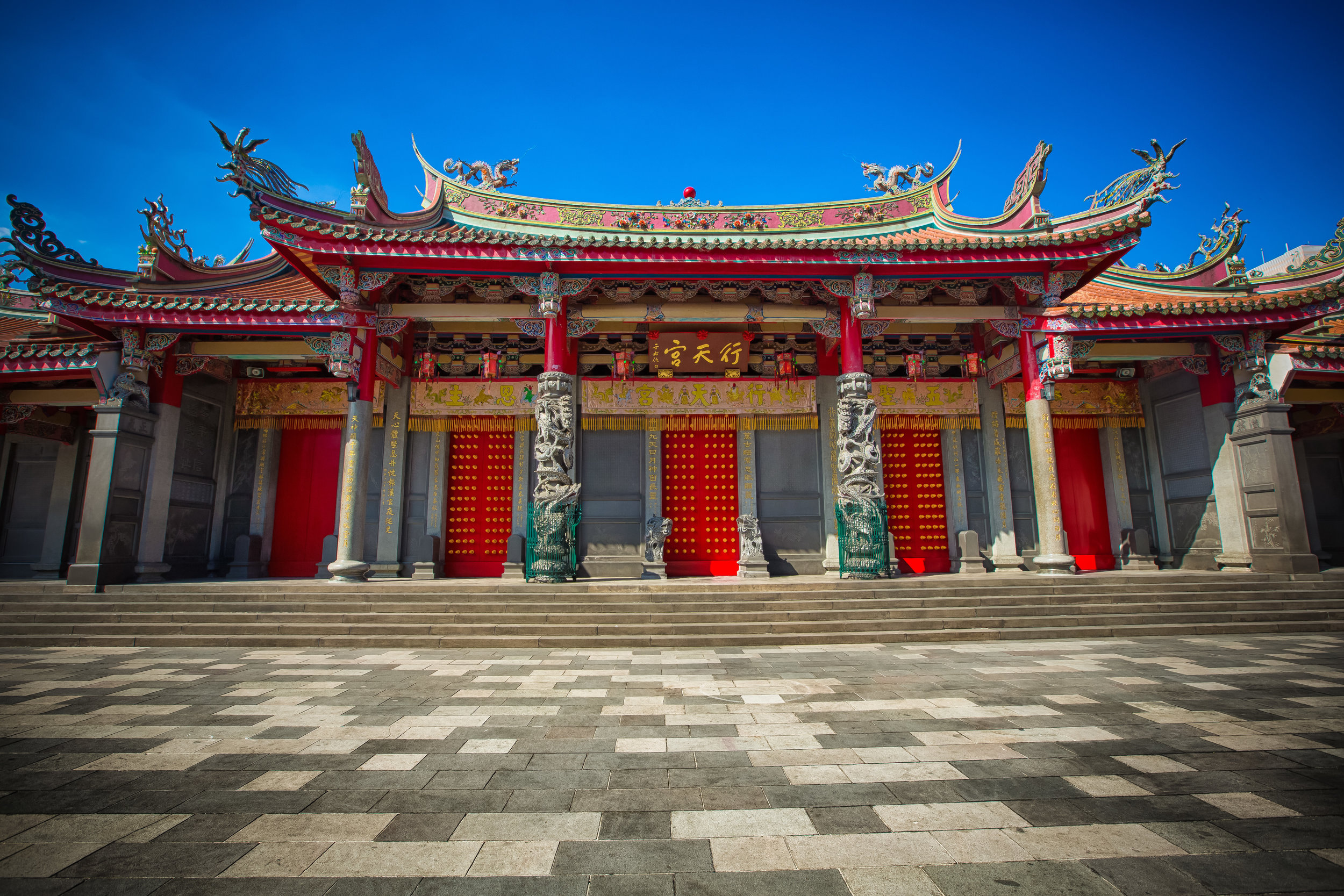
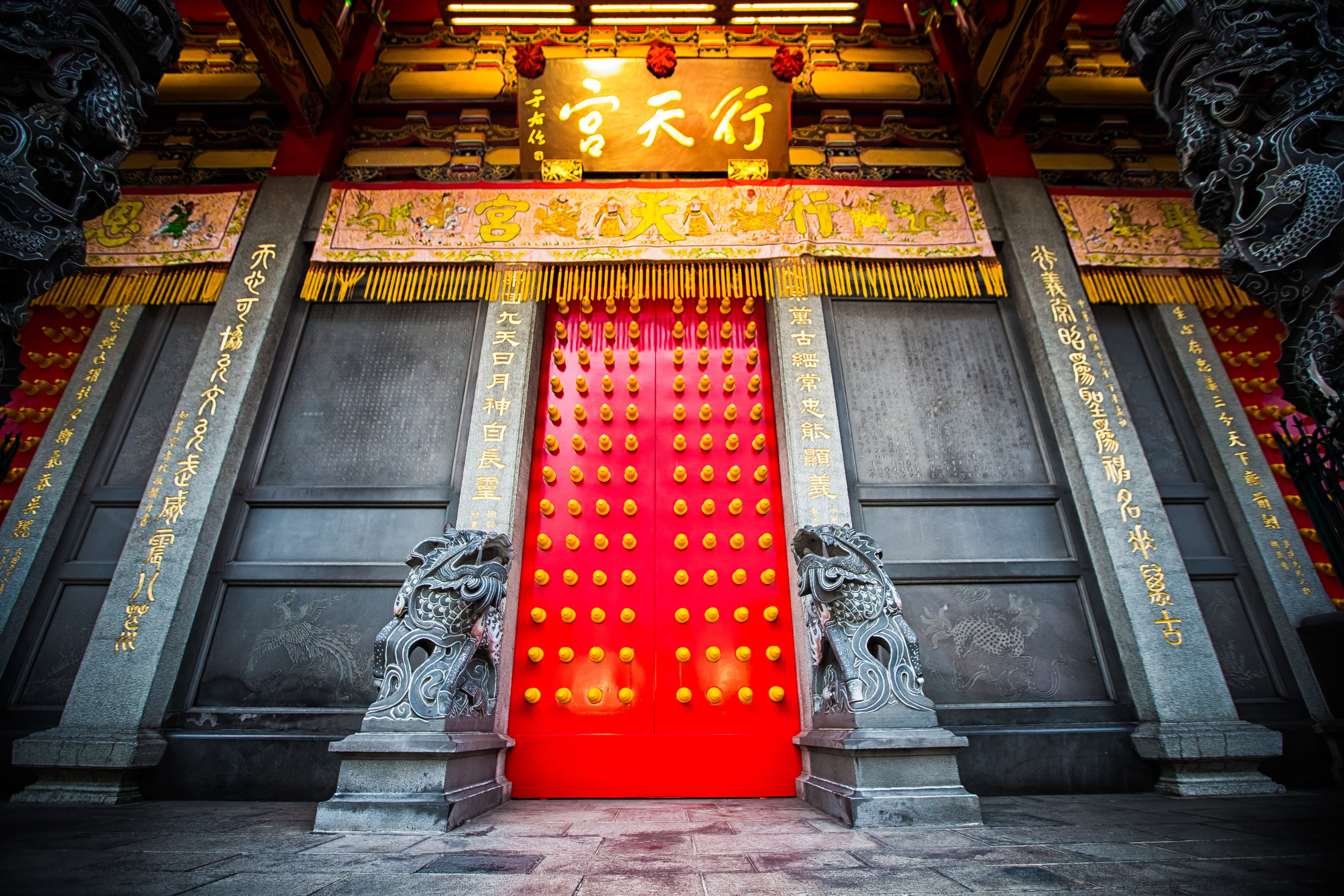
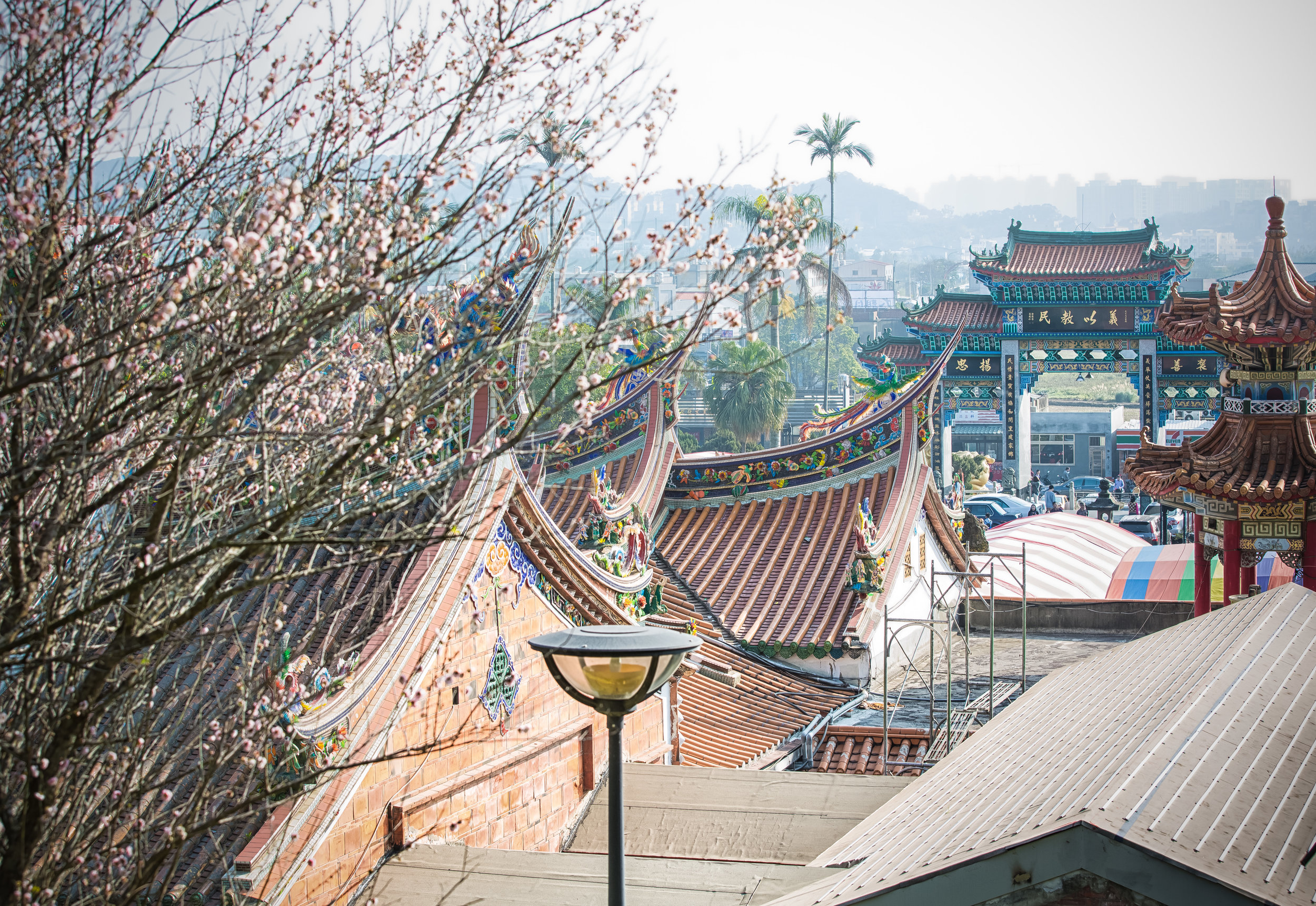
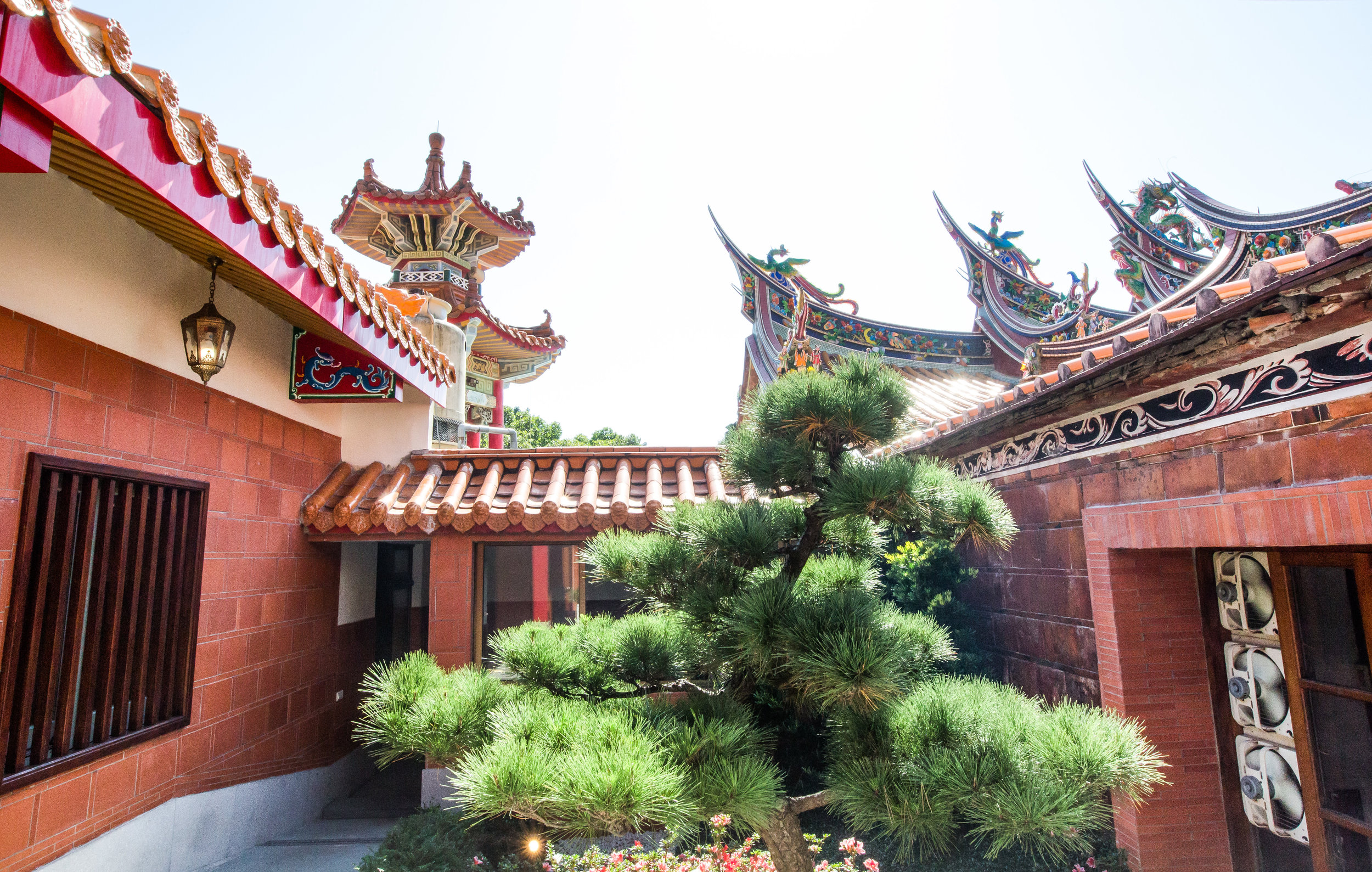
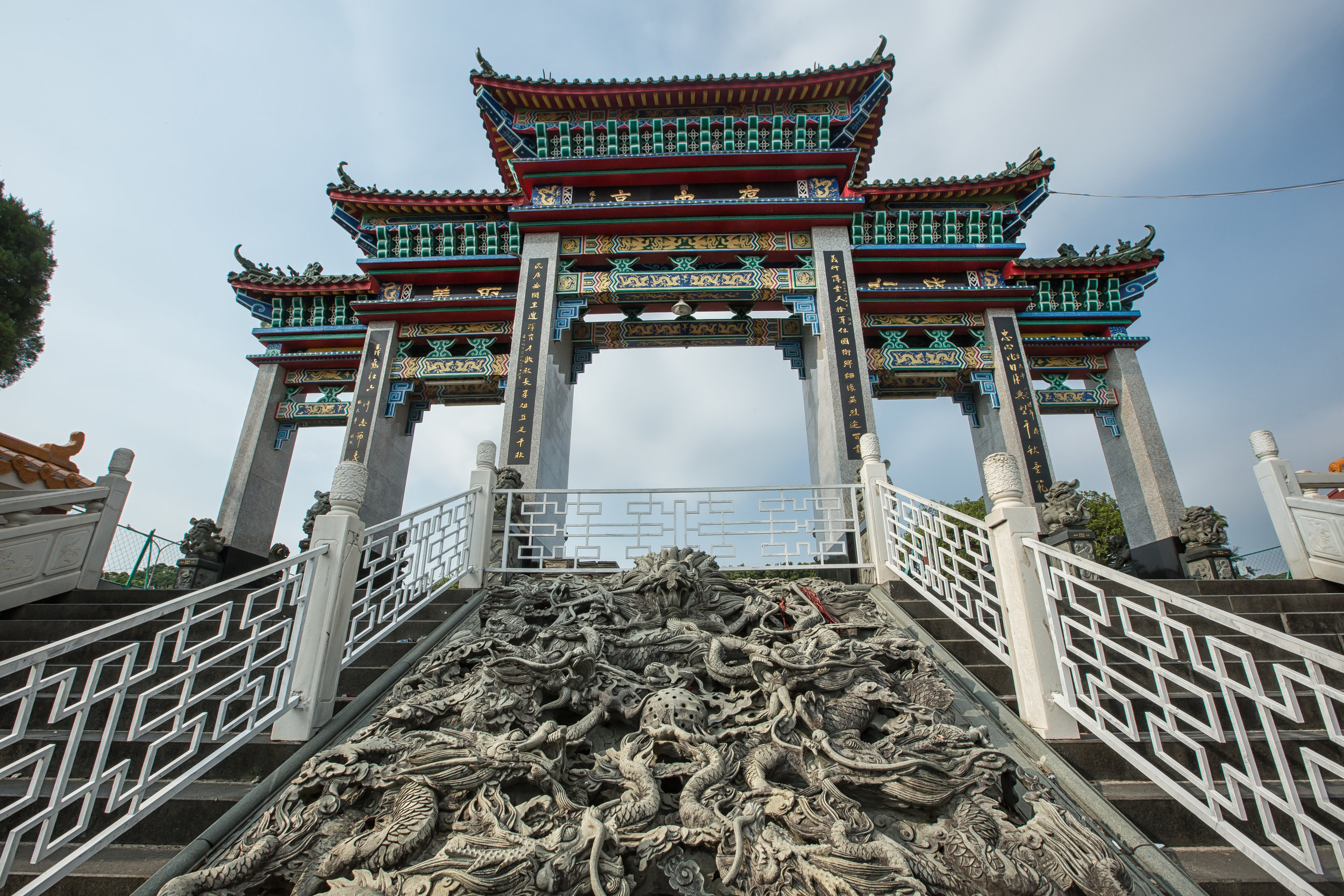
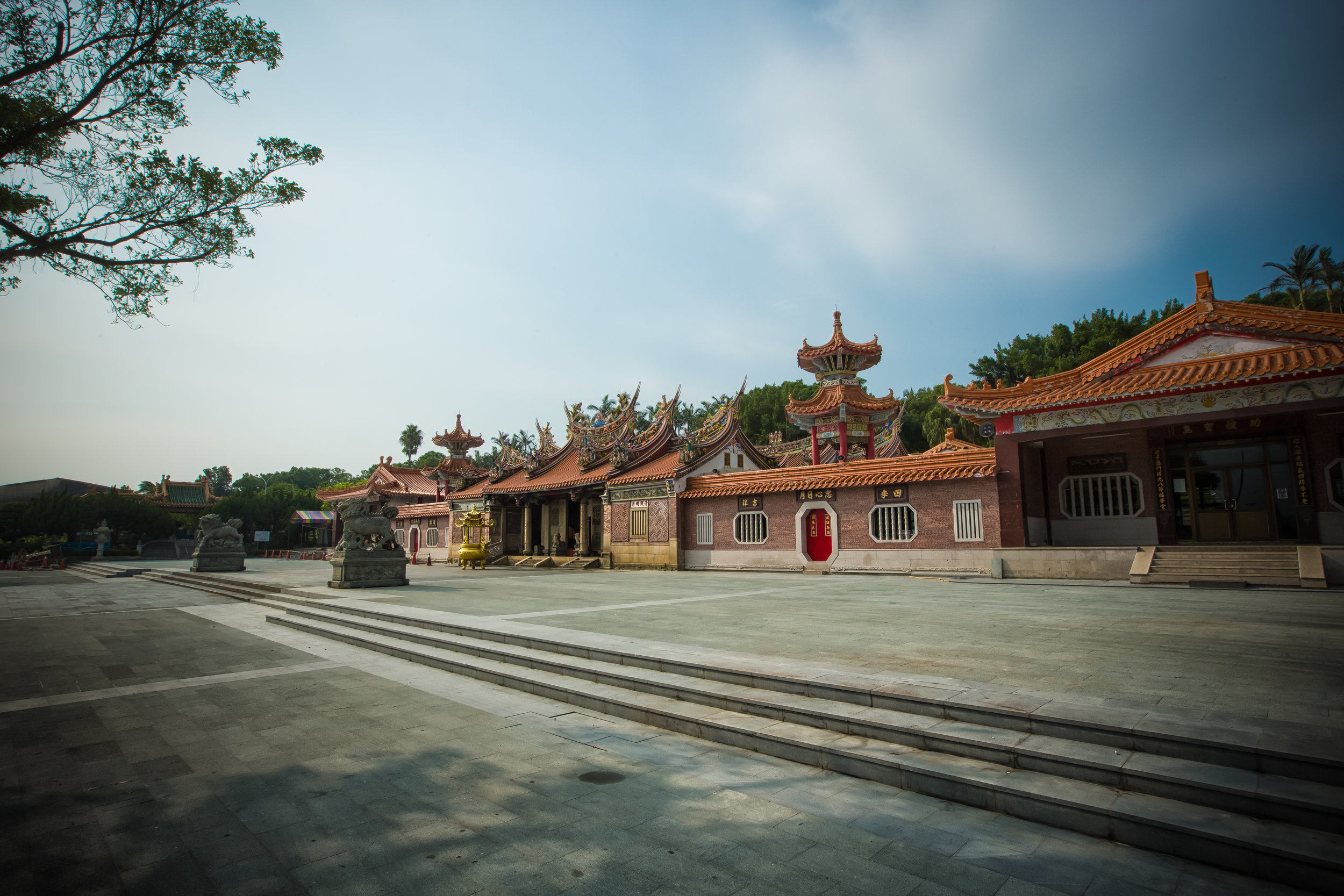
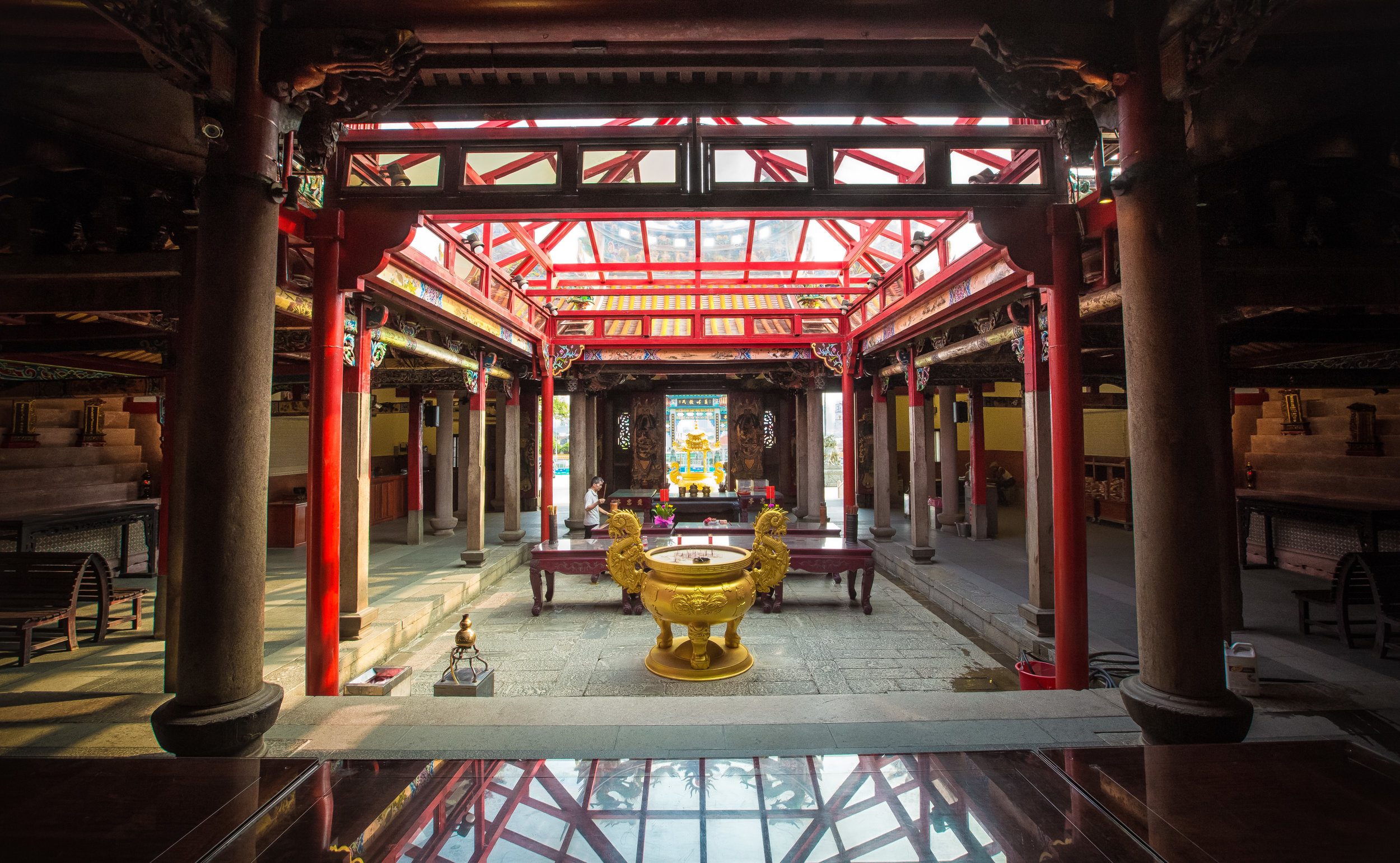
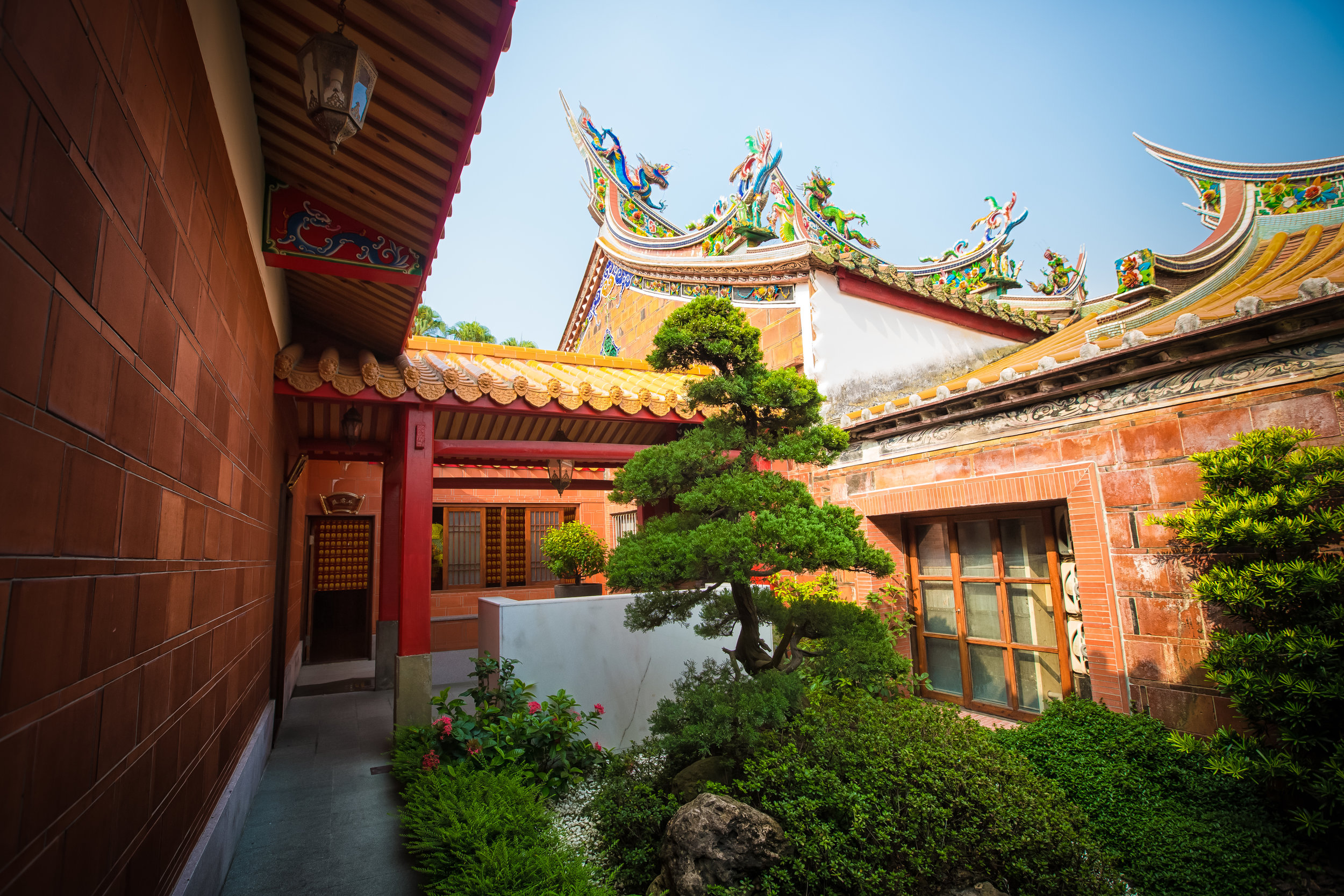
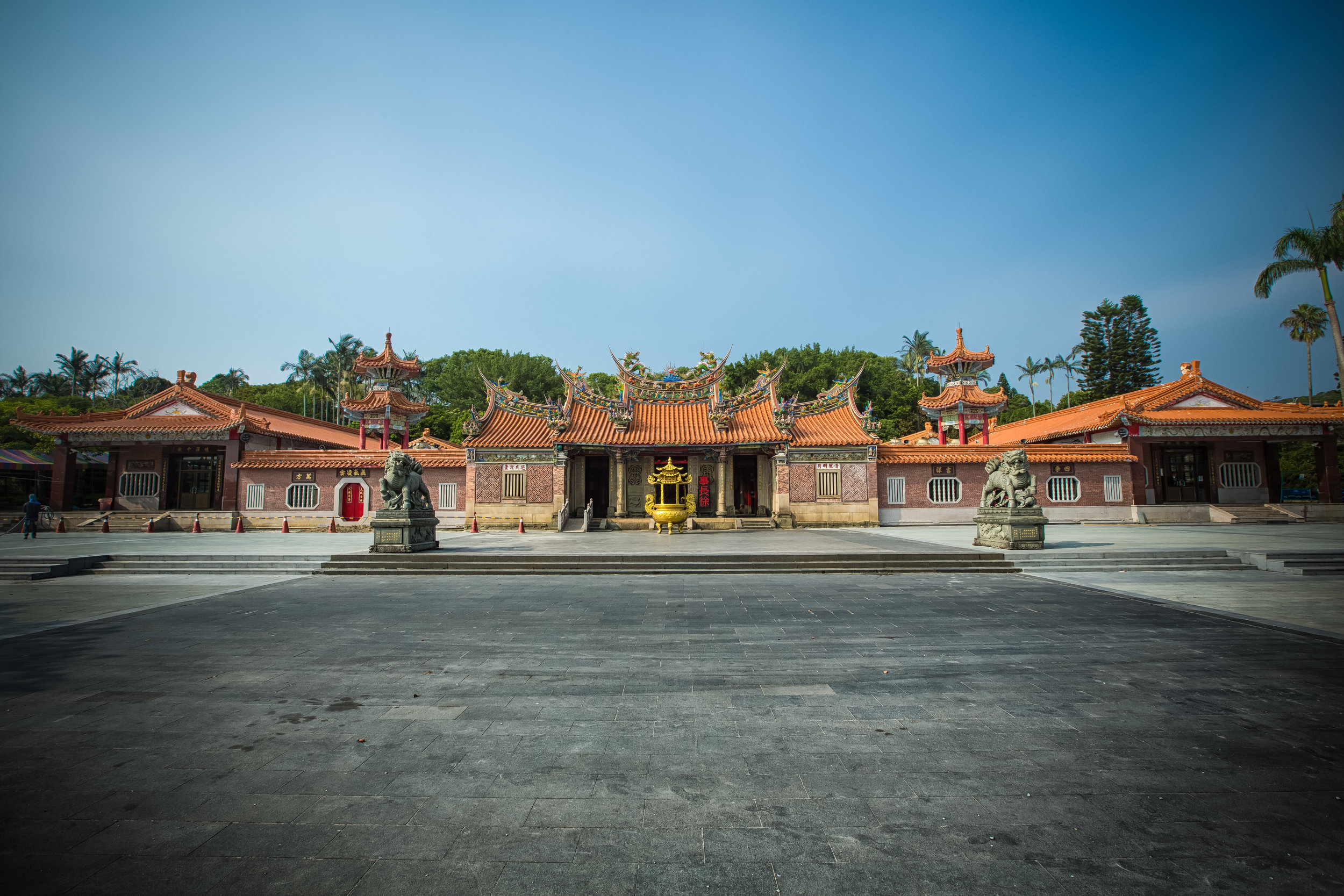
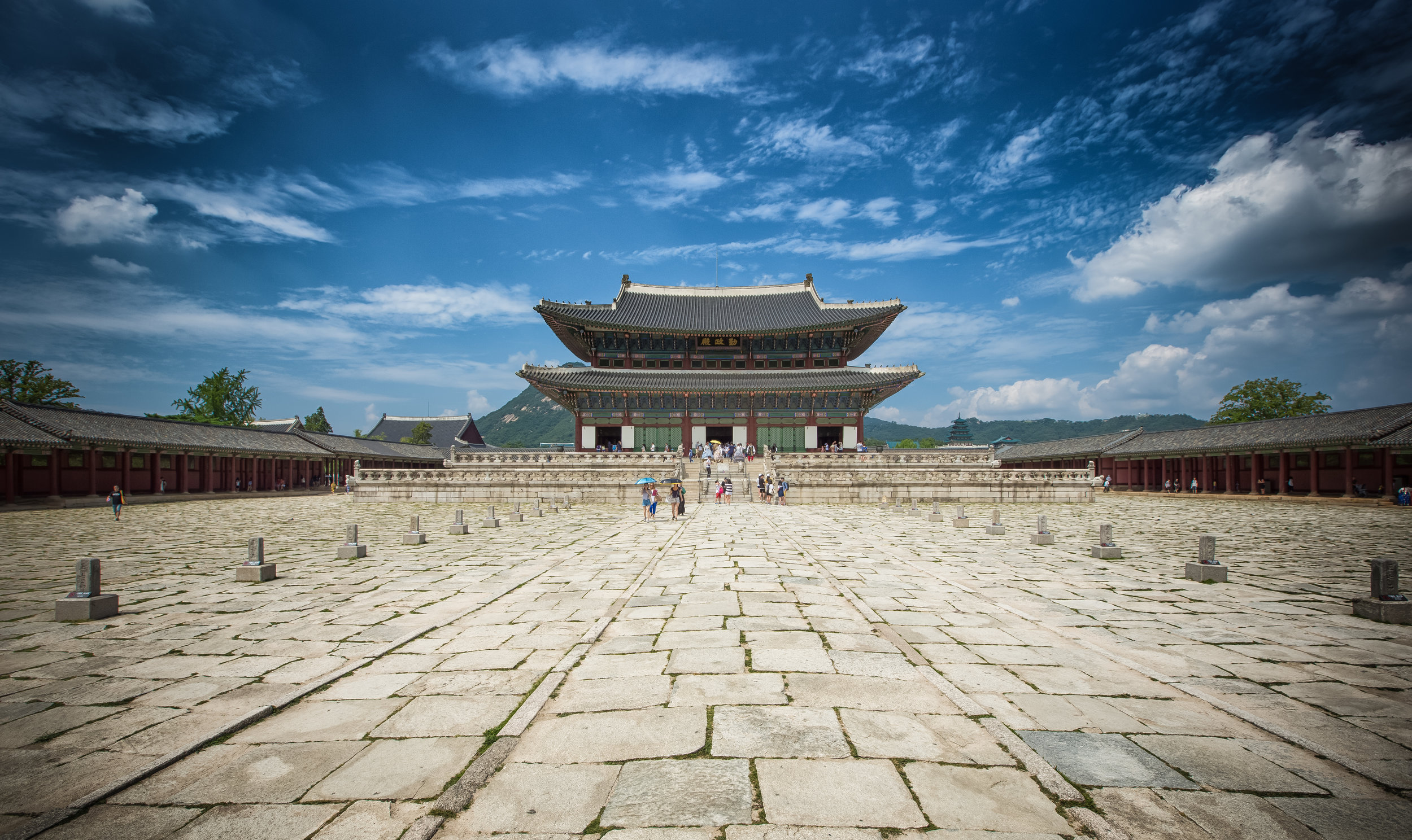
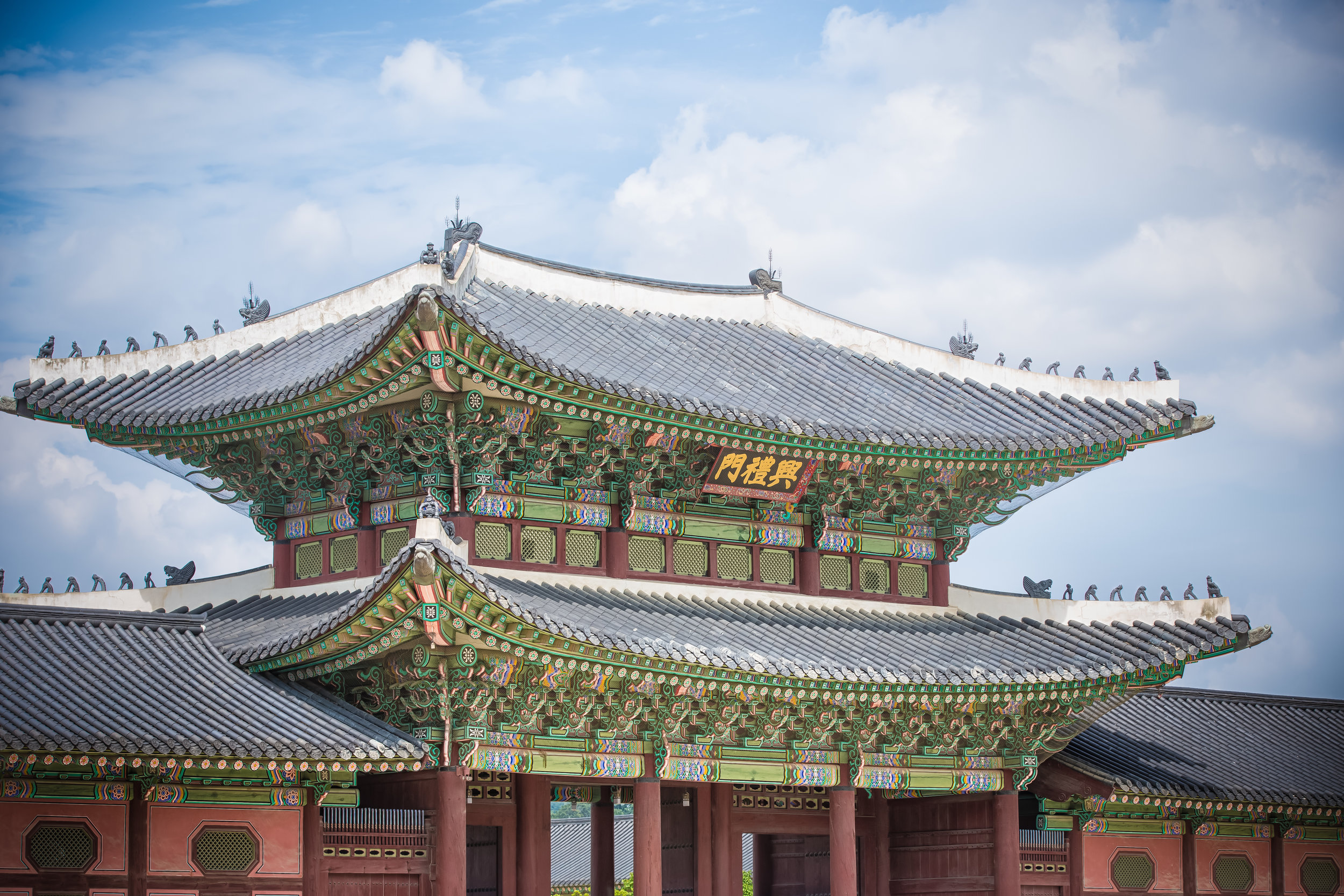
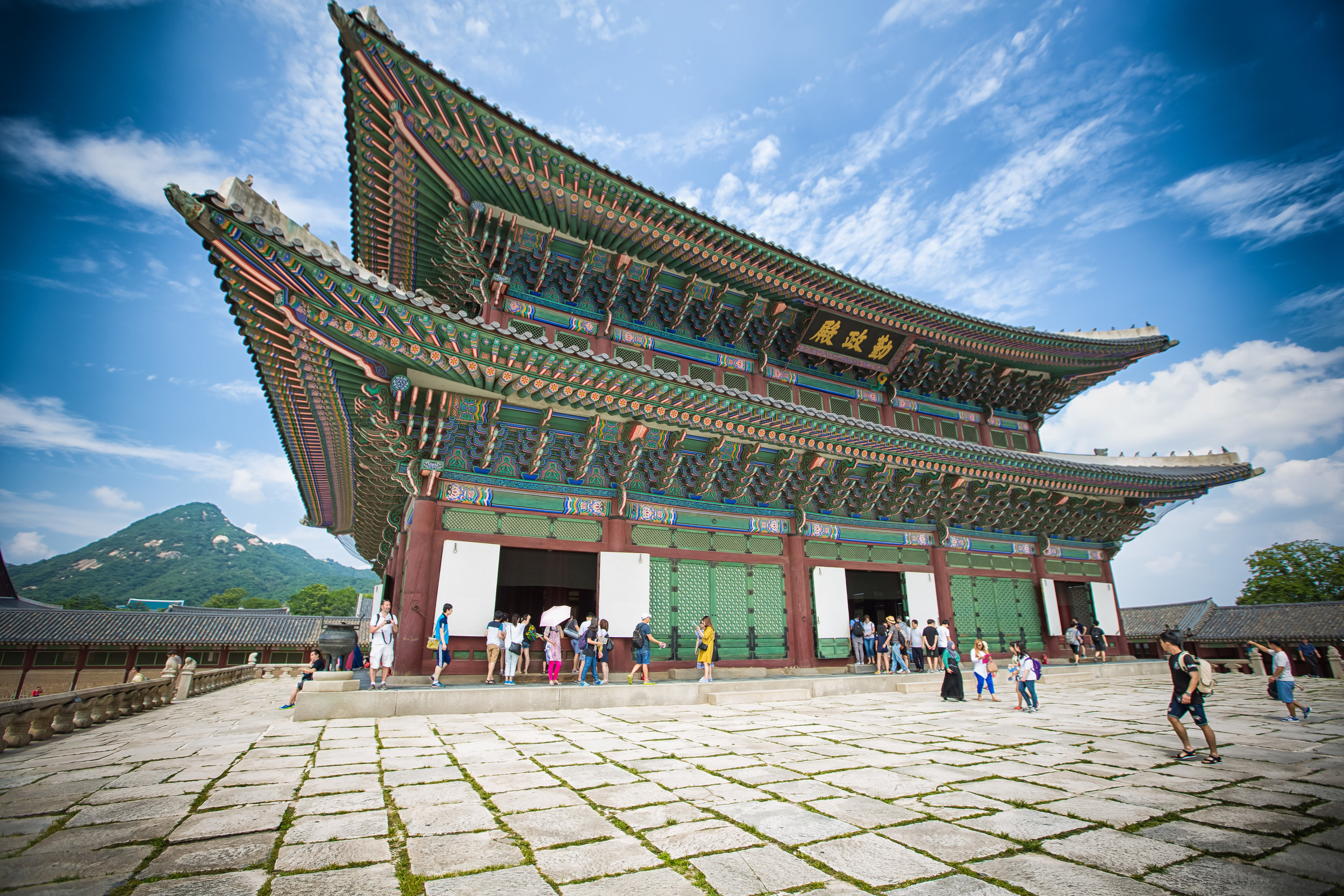
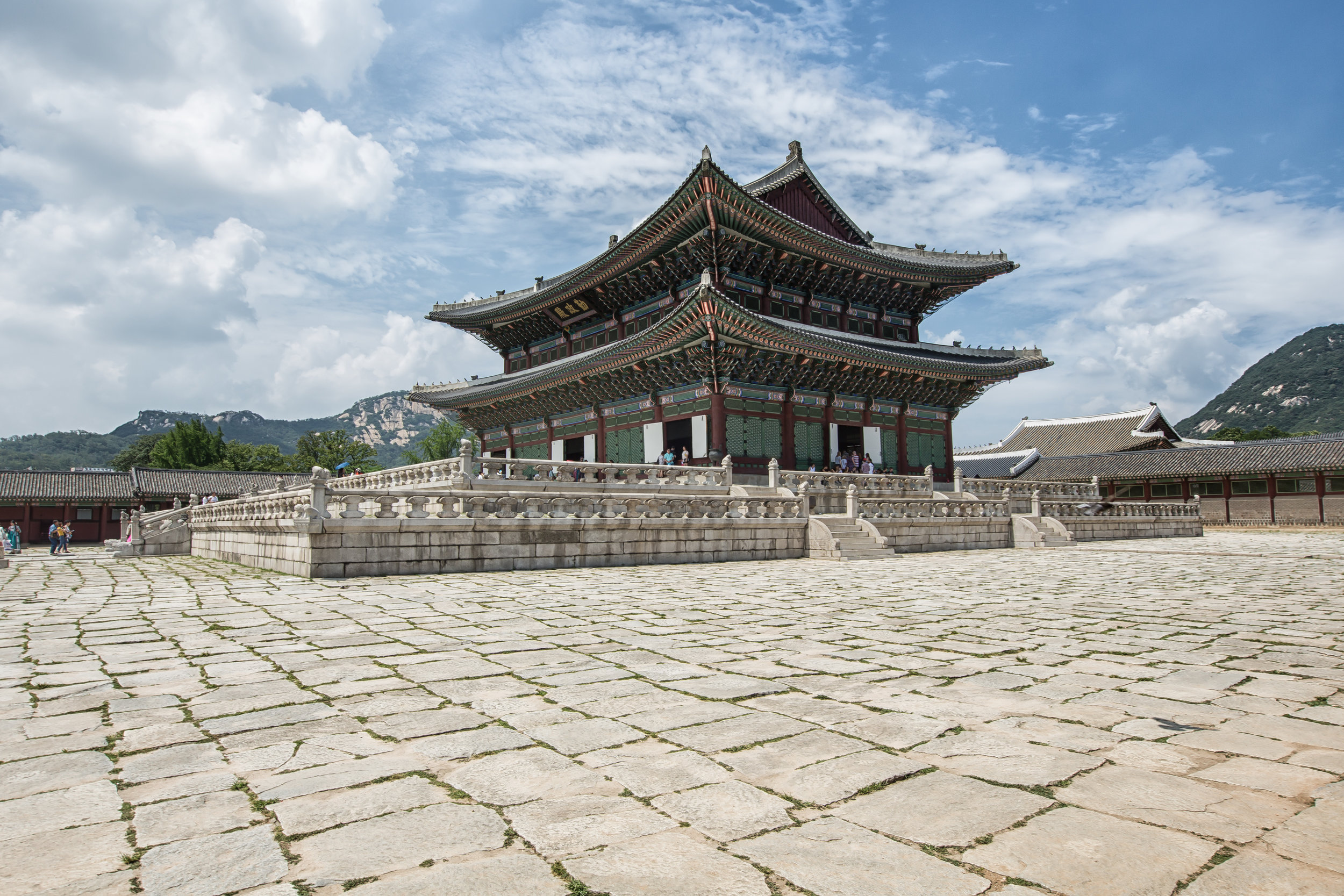
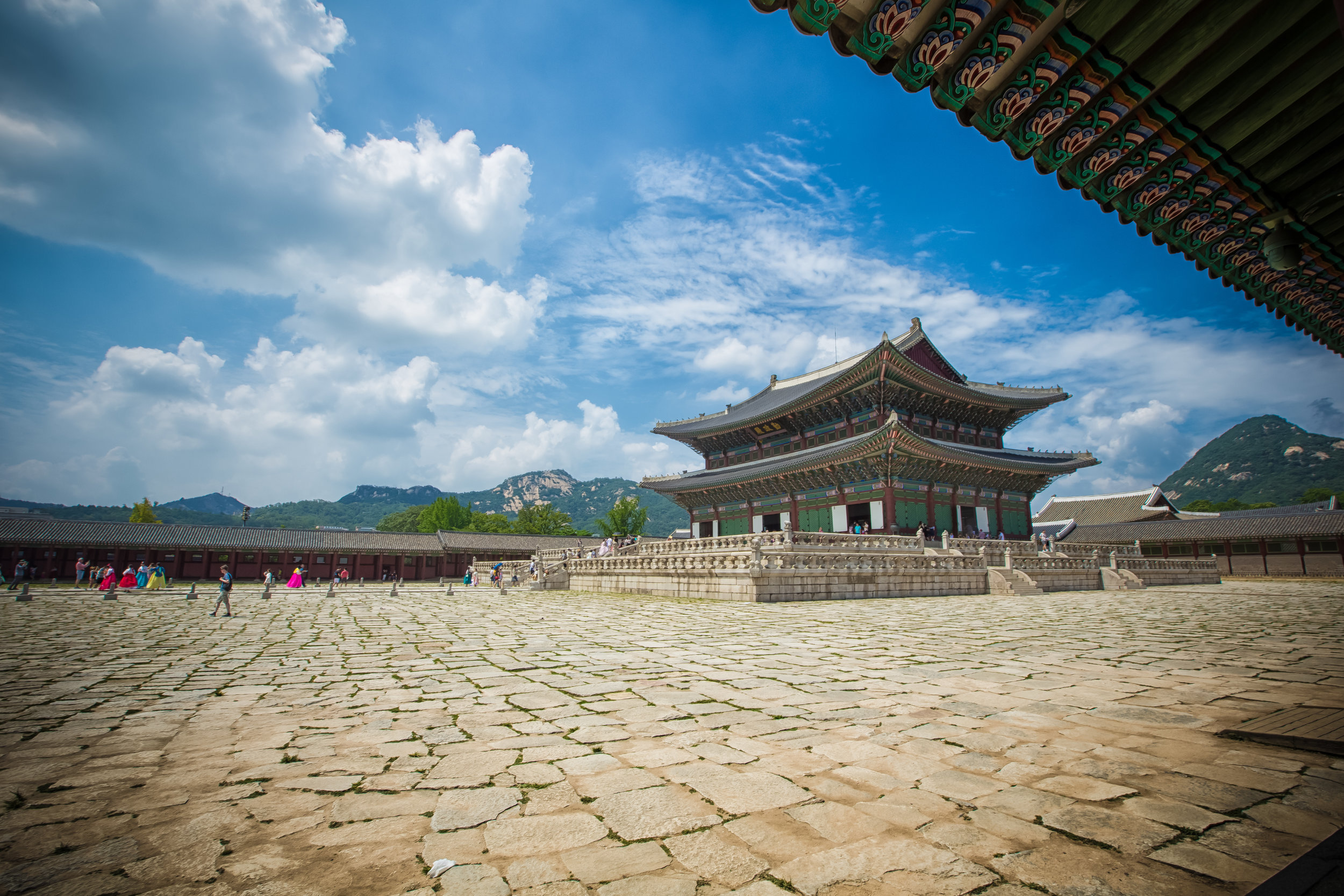
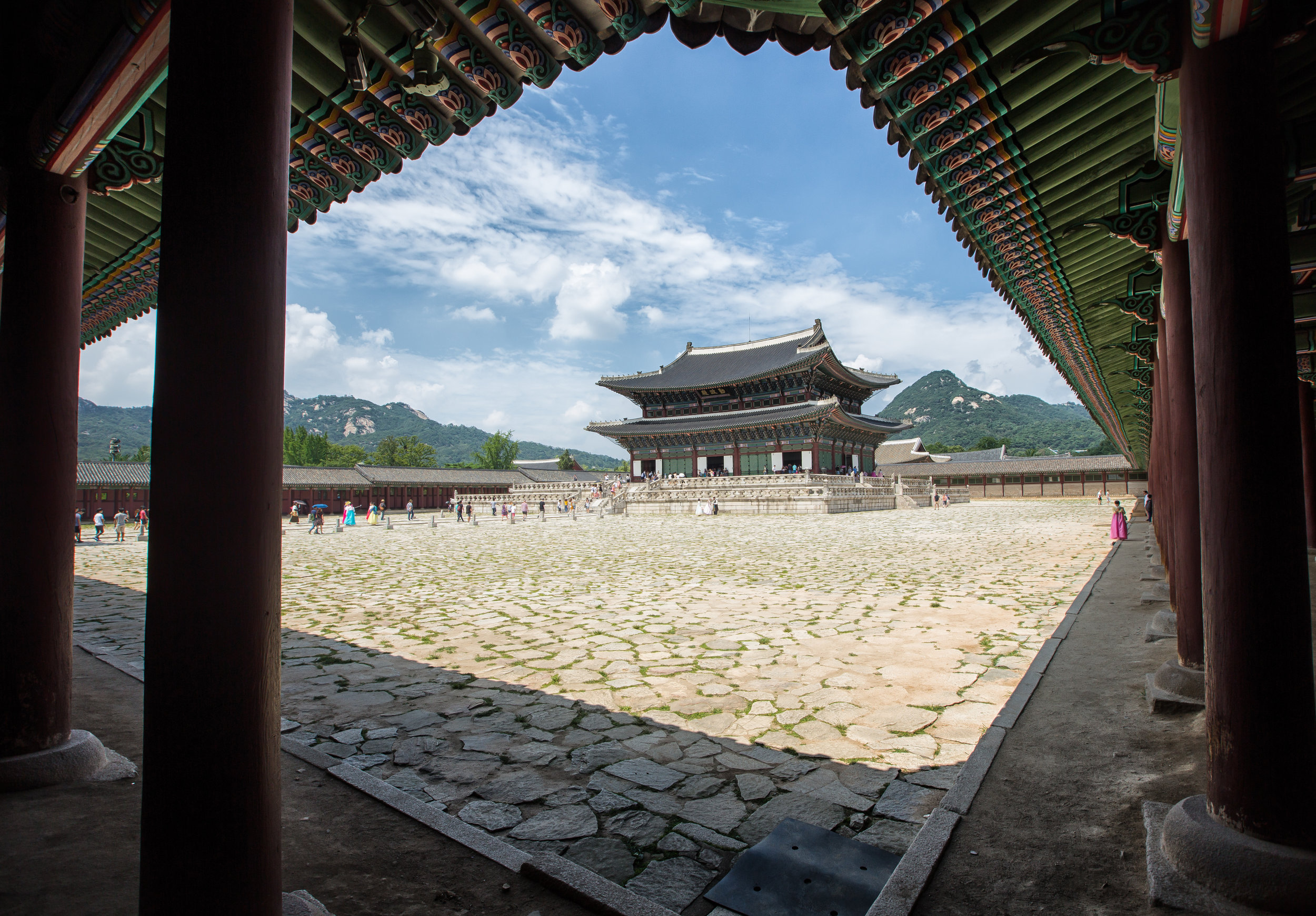
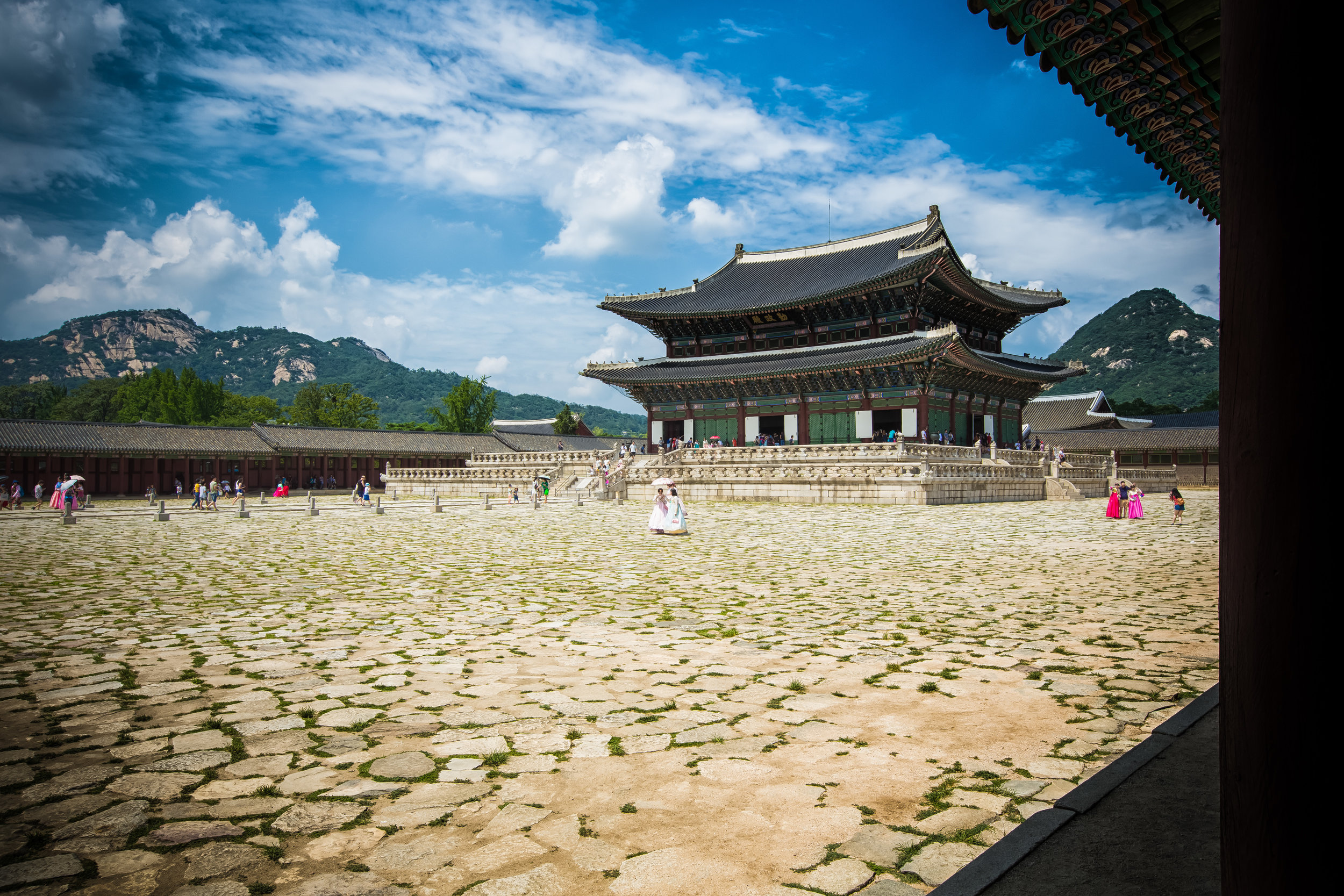
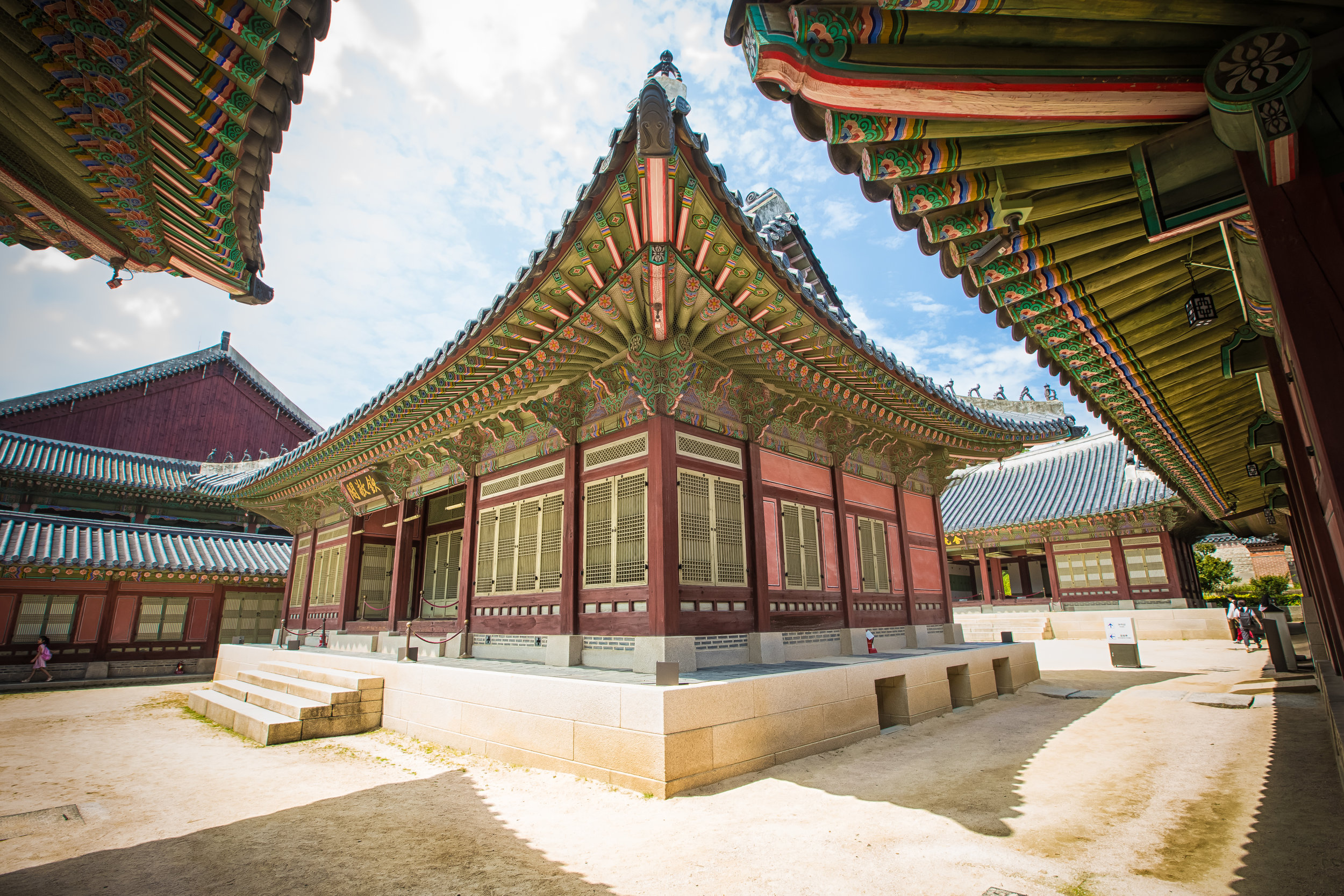
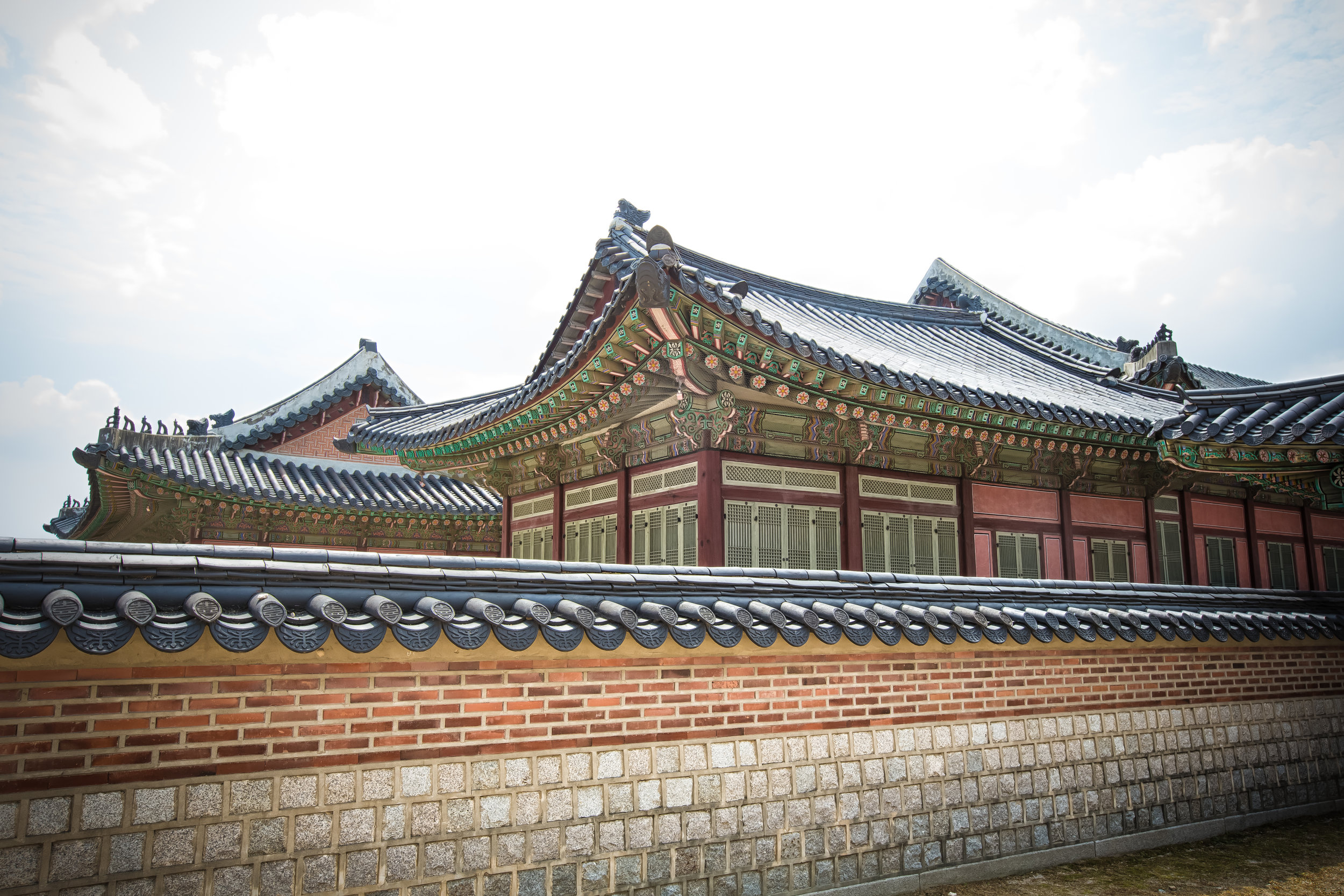
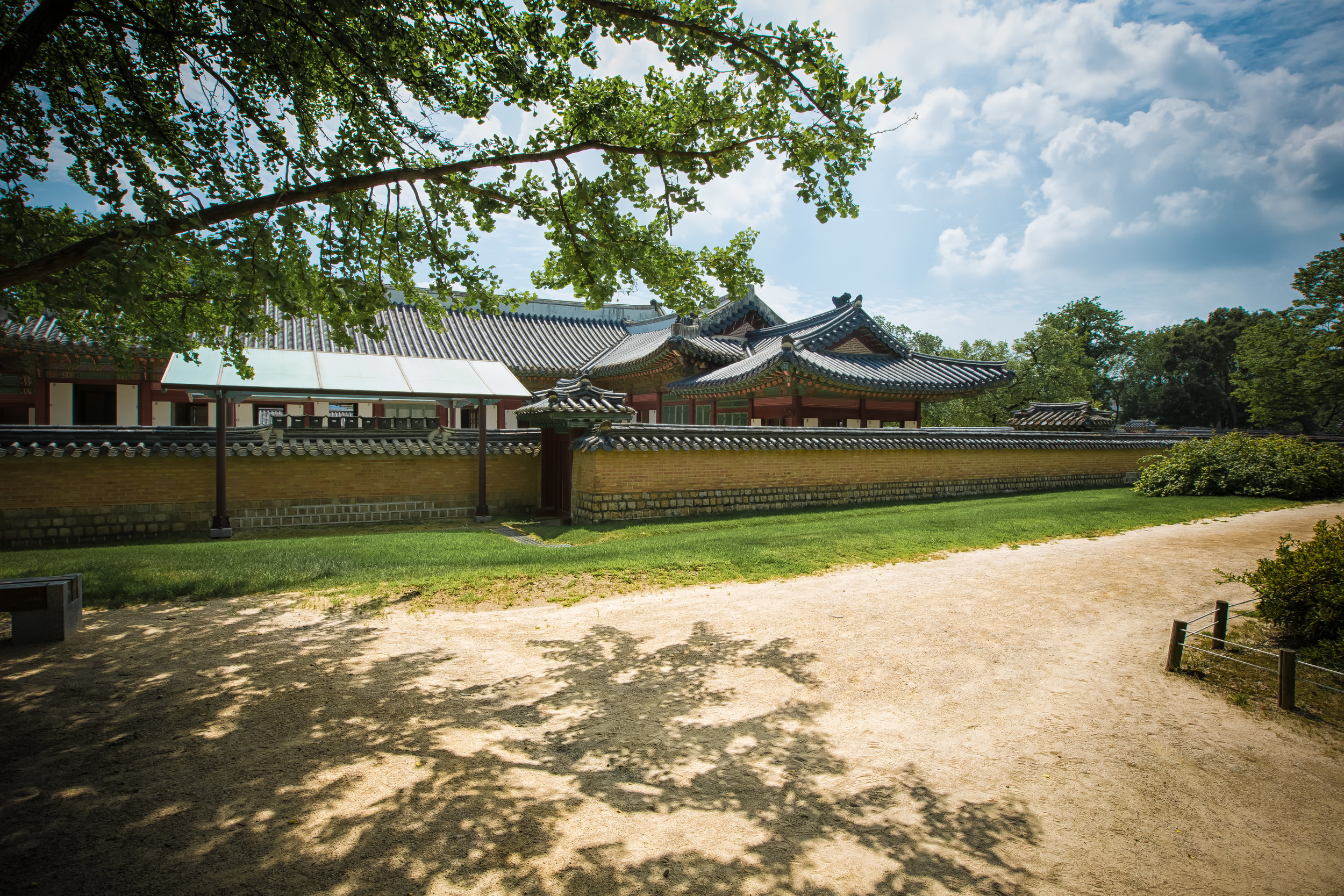
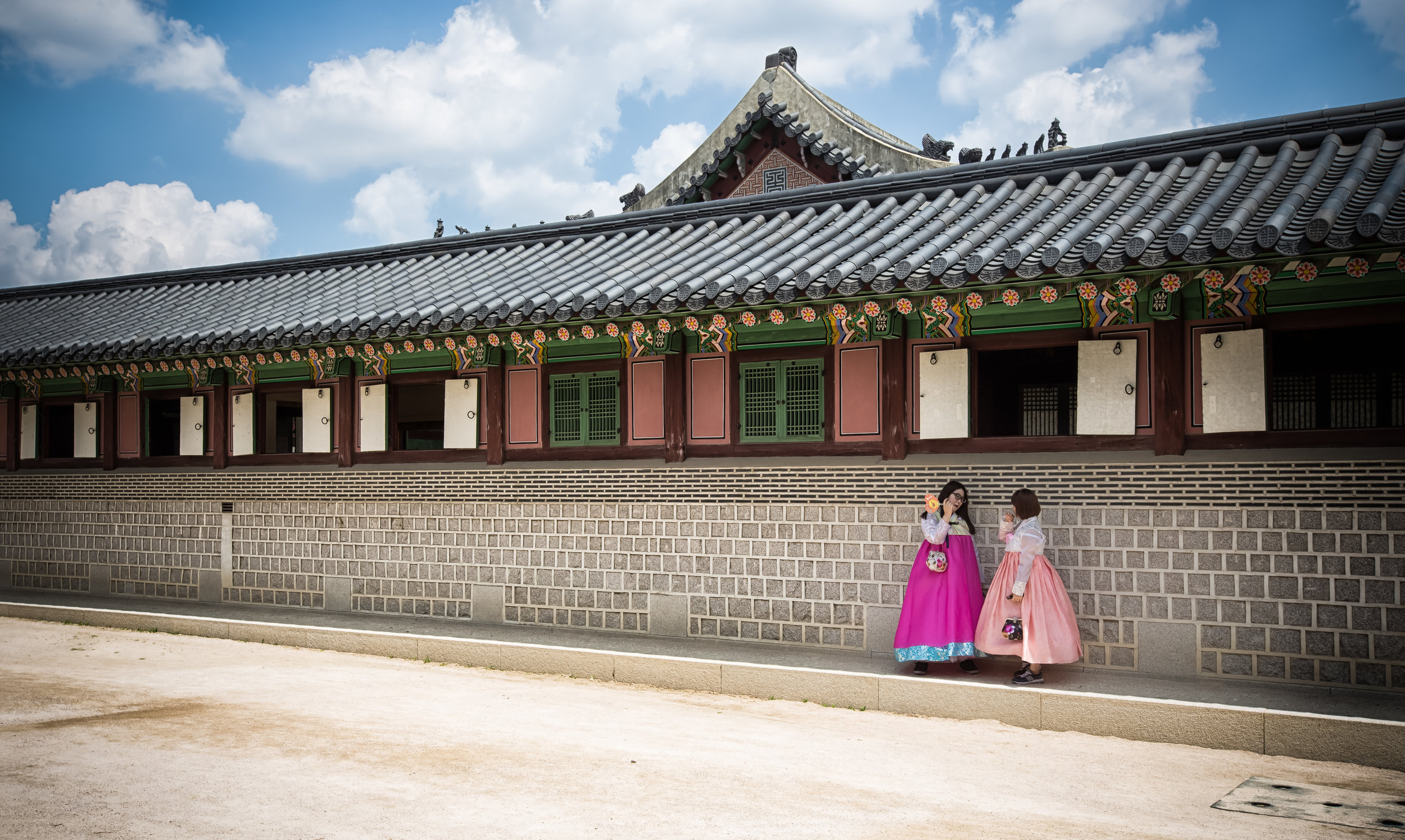
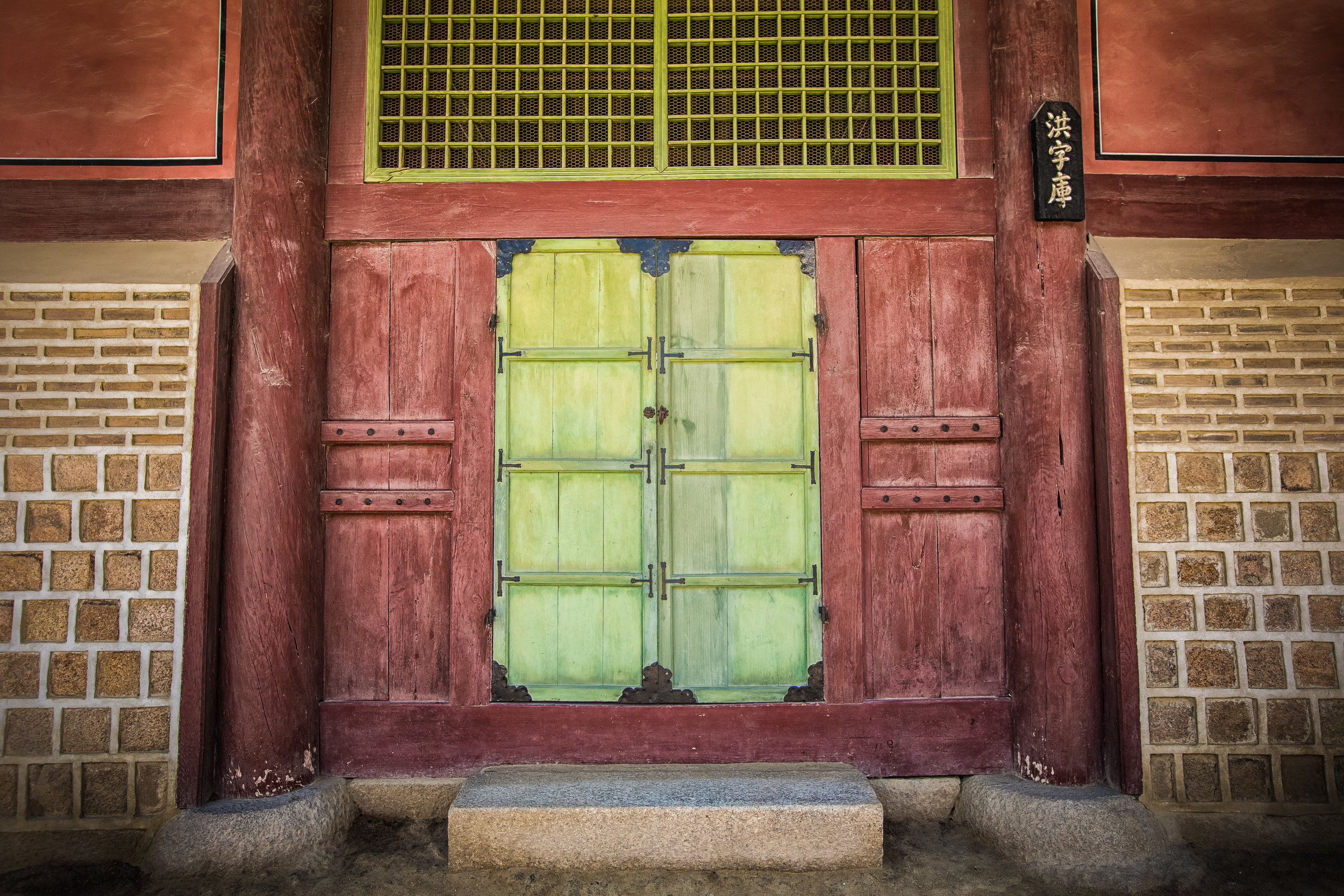
The temple takes up almost an entire city block in Taipei and is celebrated for its traditional Chinese-style architecture. If you walk into this temple having visited other Taoist temples before, the simplicity will be a stark contrast to the amazing detail of some of Taiwan's other places of worship. While it is a young temple and a simple one at that, it doesn't mean that there aren't minor details in the design that you shouldn't pay attention to and appreciate.
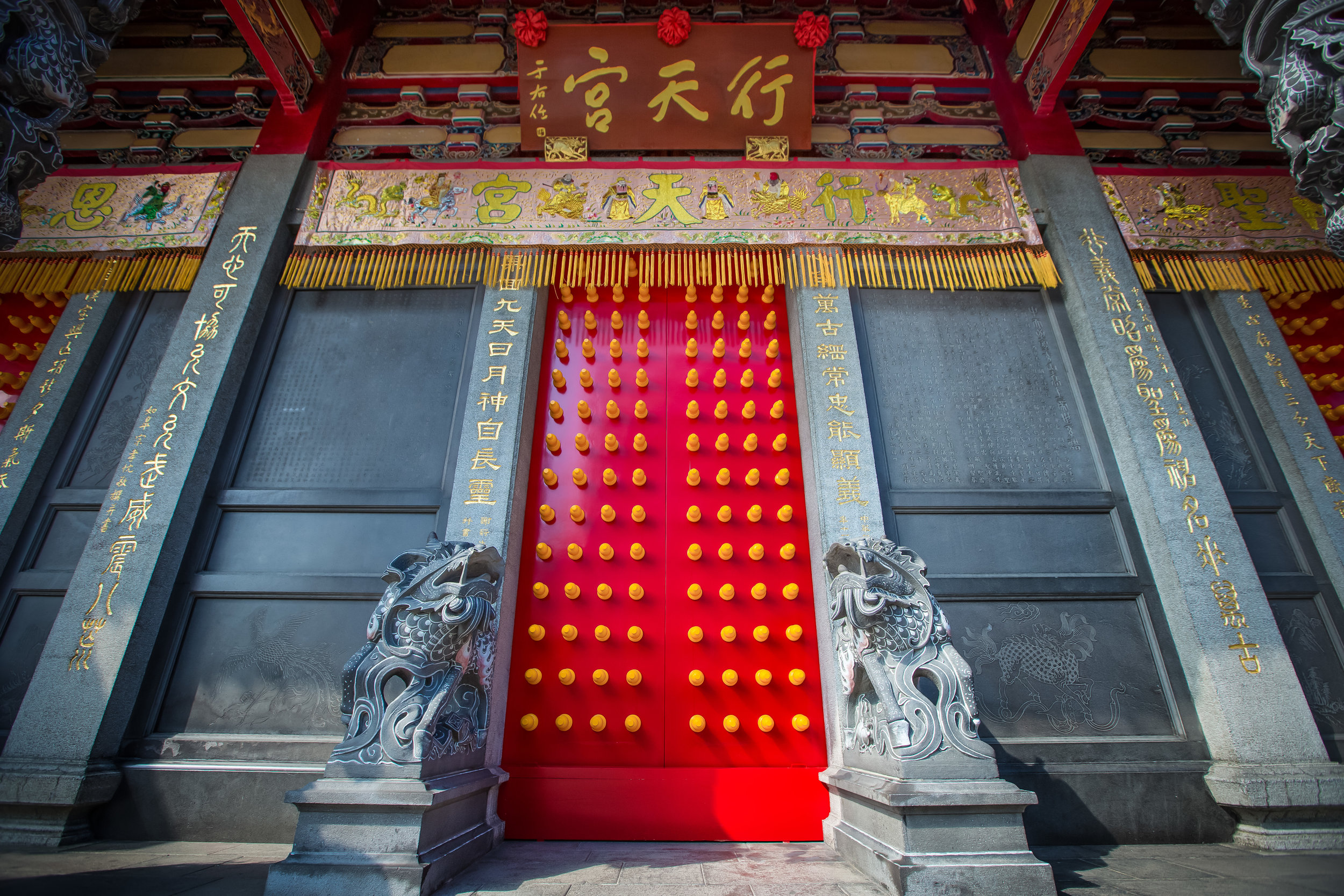
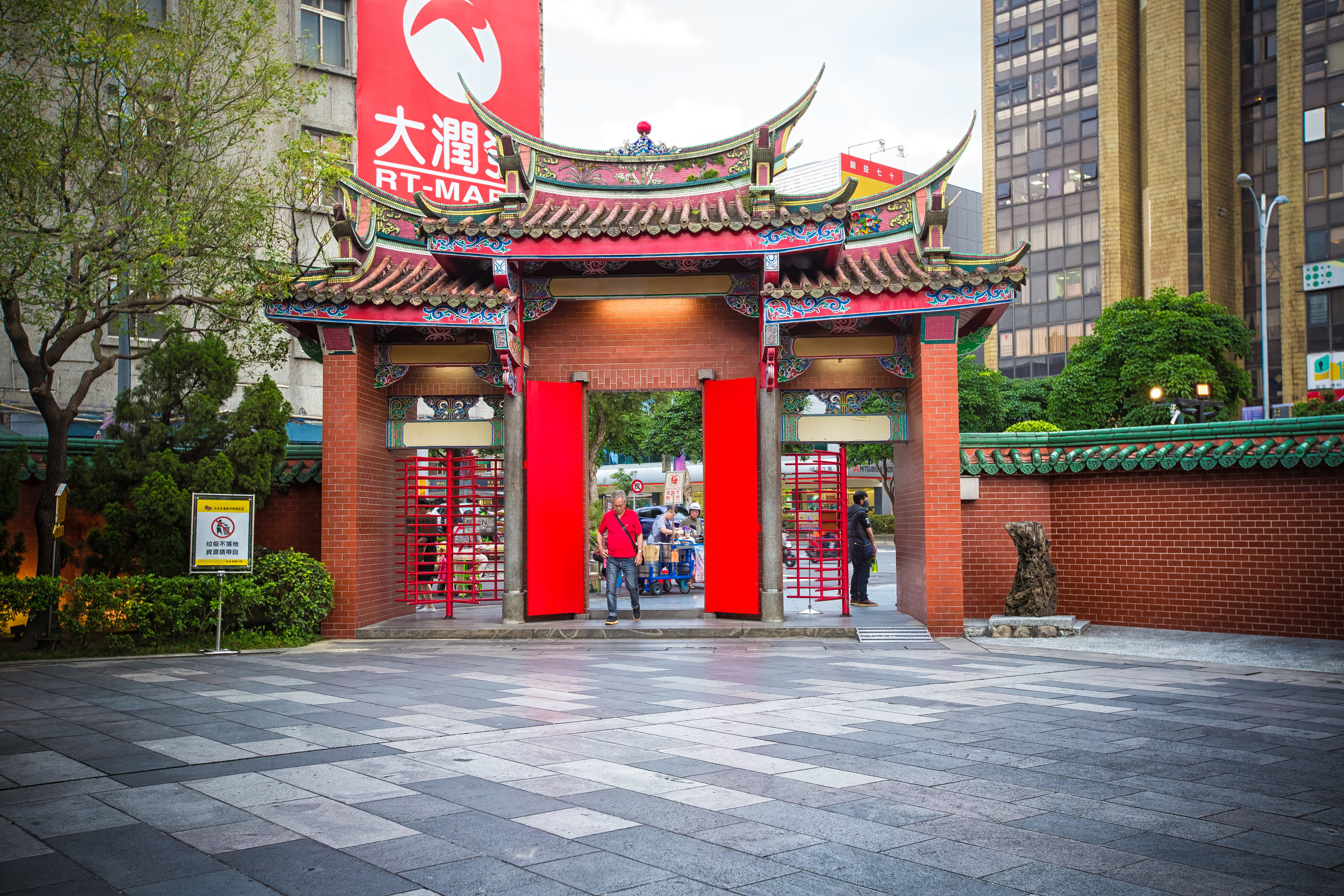
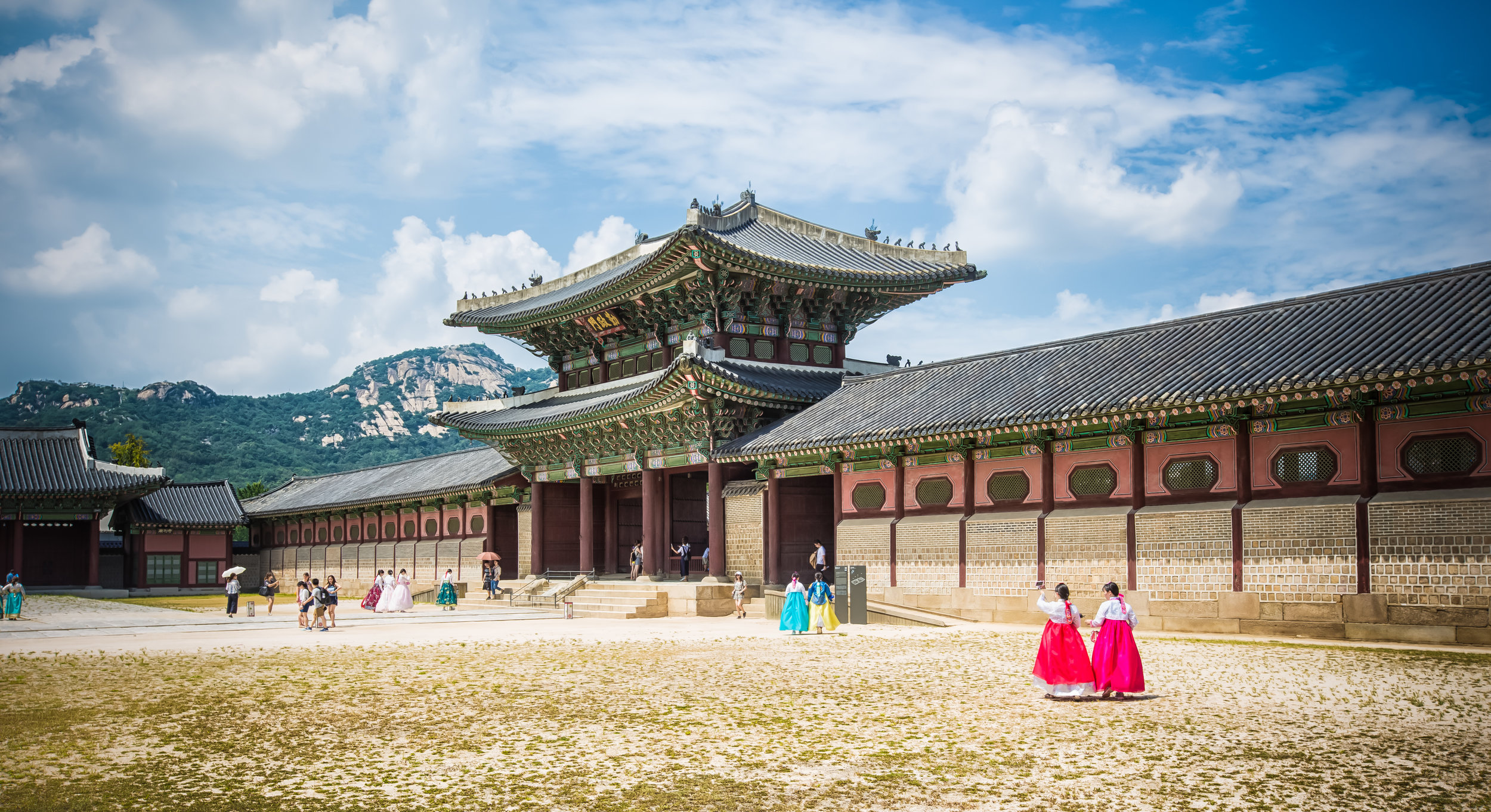
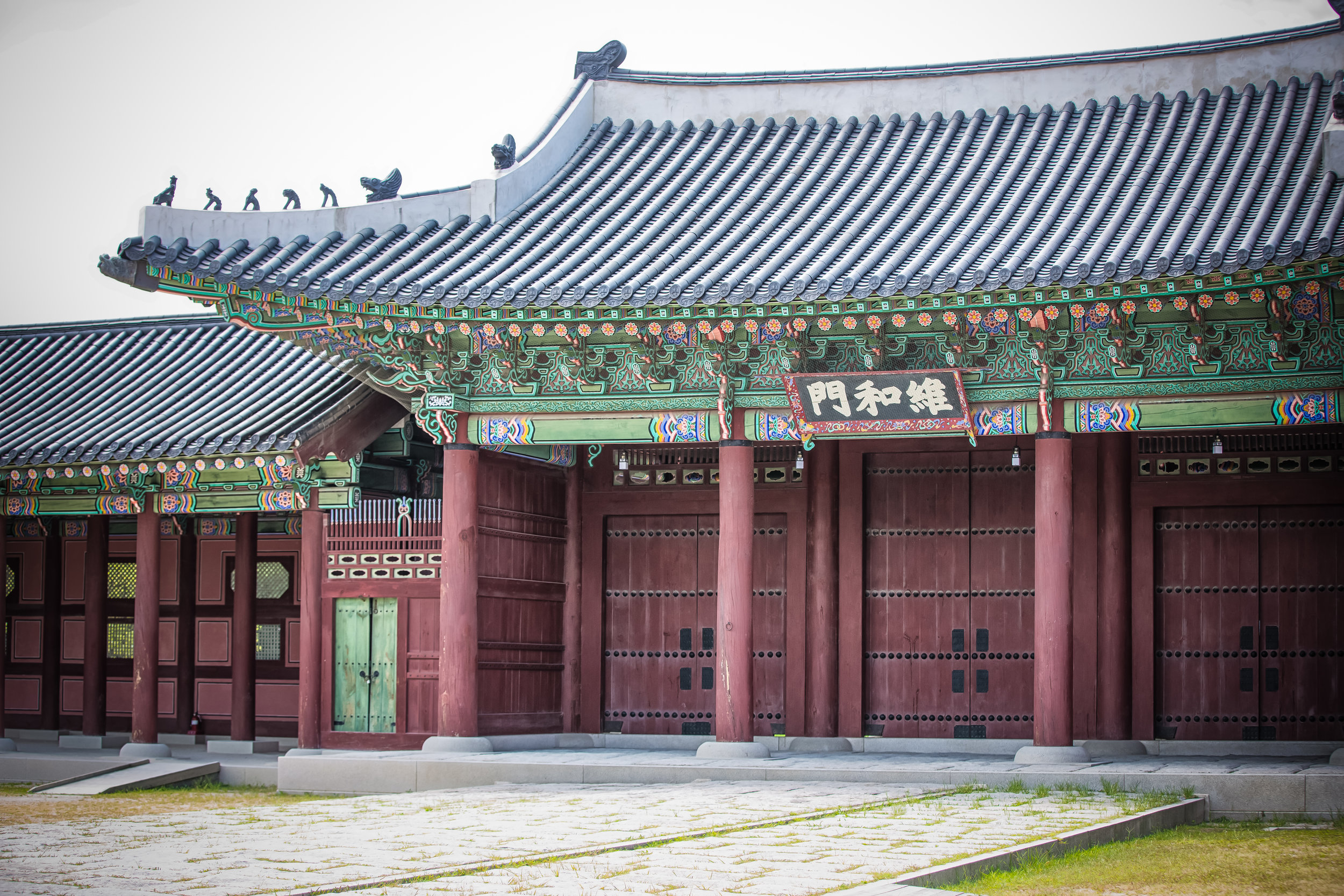
When you walk into the temple the first thing you'll notice is one of the two gates. The gates are known as the "Xun Gate" (巽門) and "Kun Gate" (坤門) or the Wind and Earth gates. The gates each have inscriptions on the inside which read "Hehe" (赫赫) and “Yanyan” (巖巖) which are reminders to the faithful to practice virtue and and act accordingly and respectfully after leaving the temple.
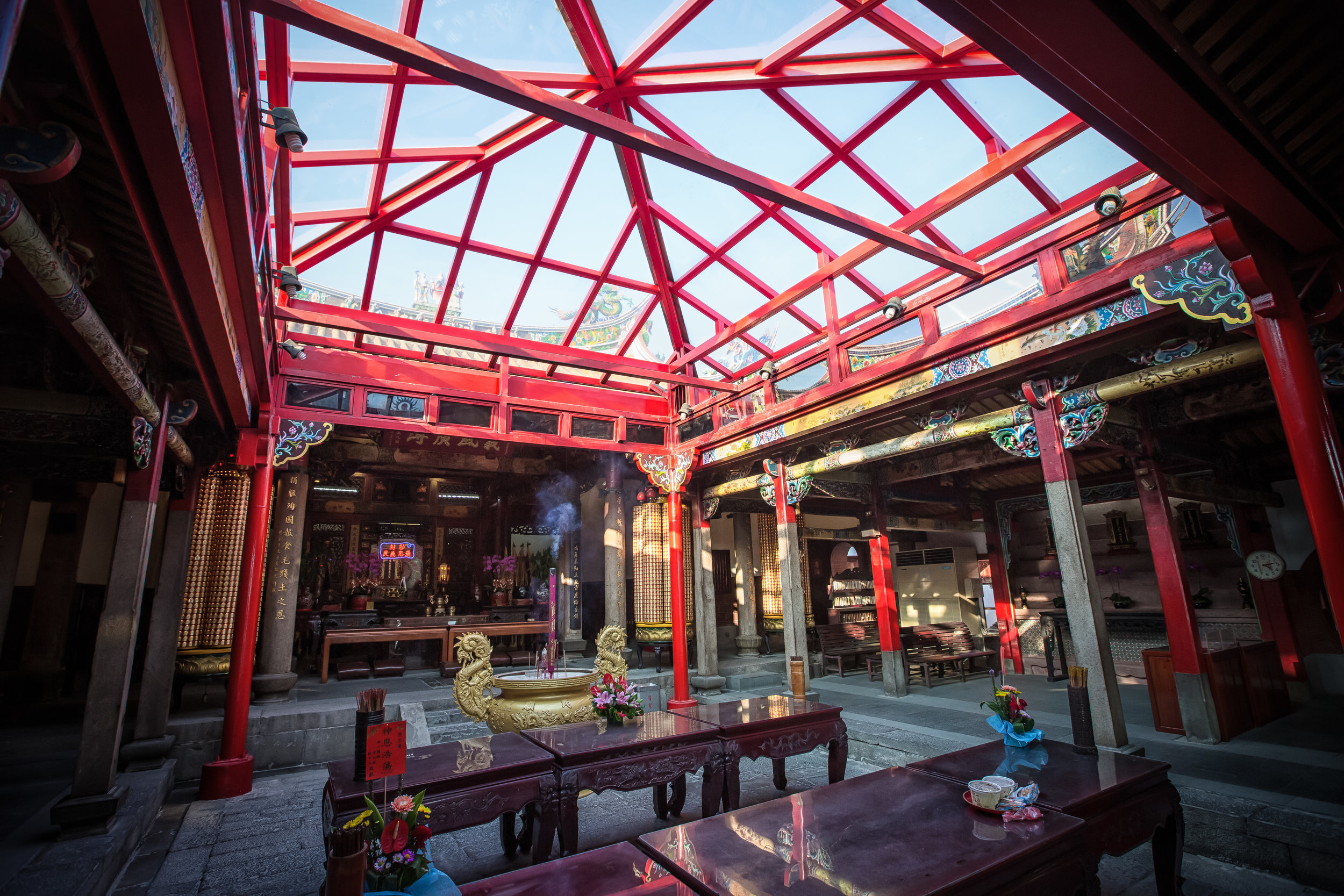
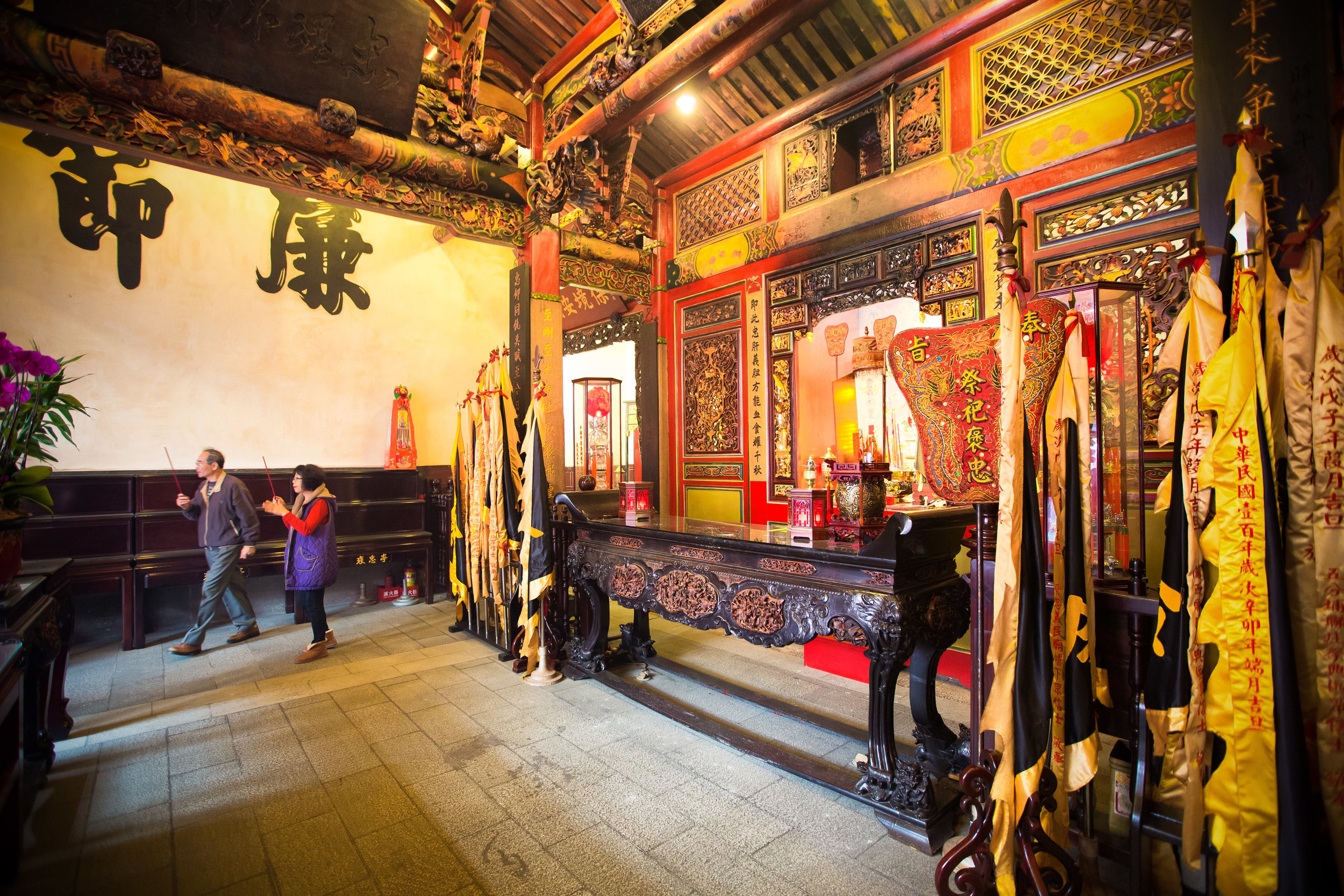
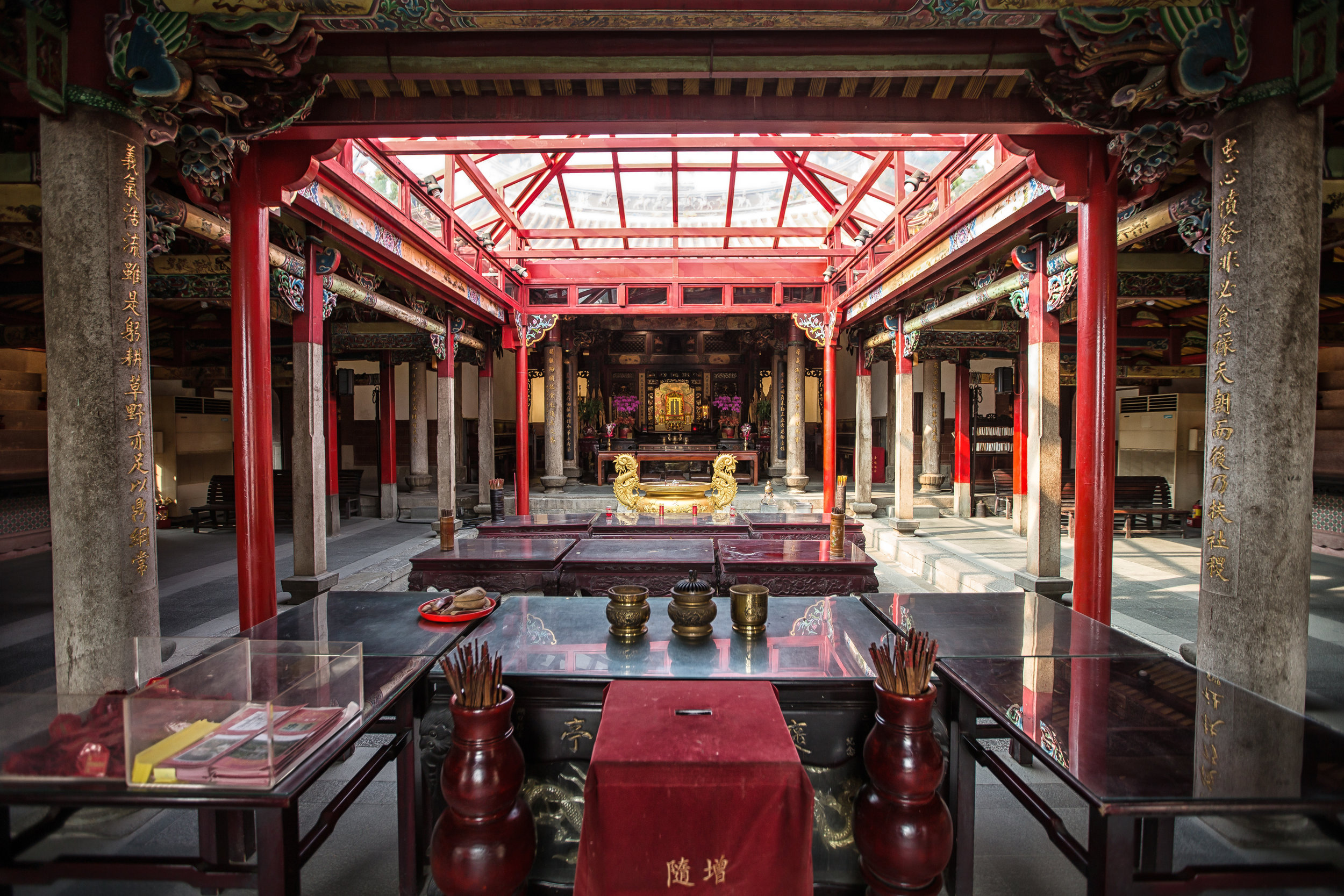
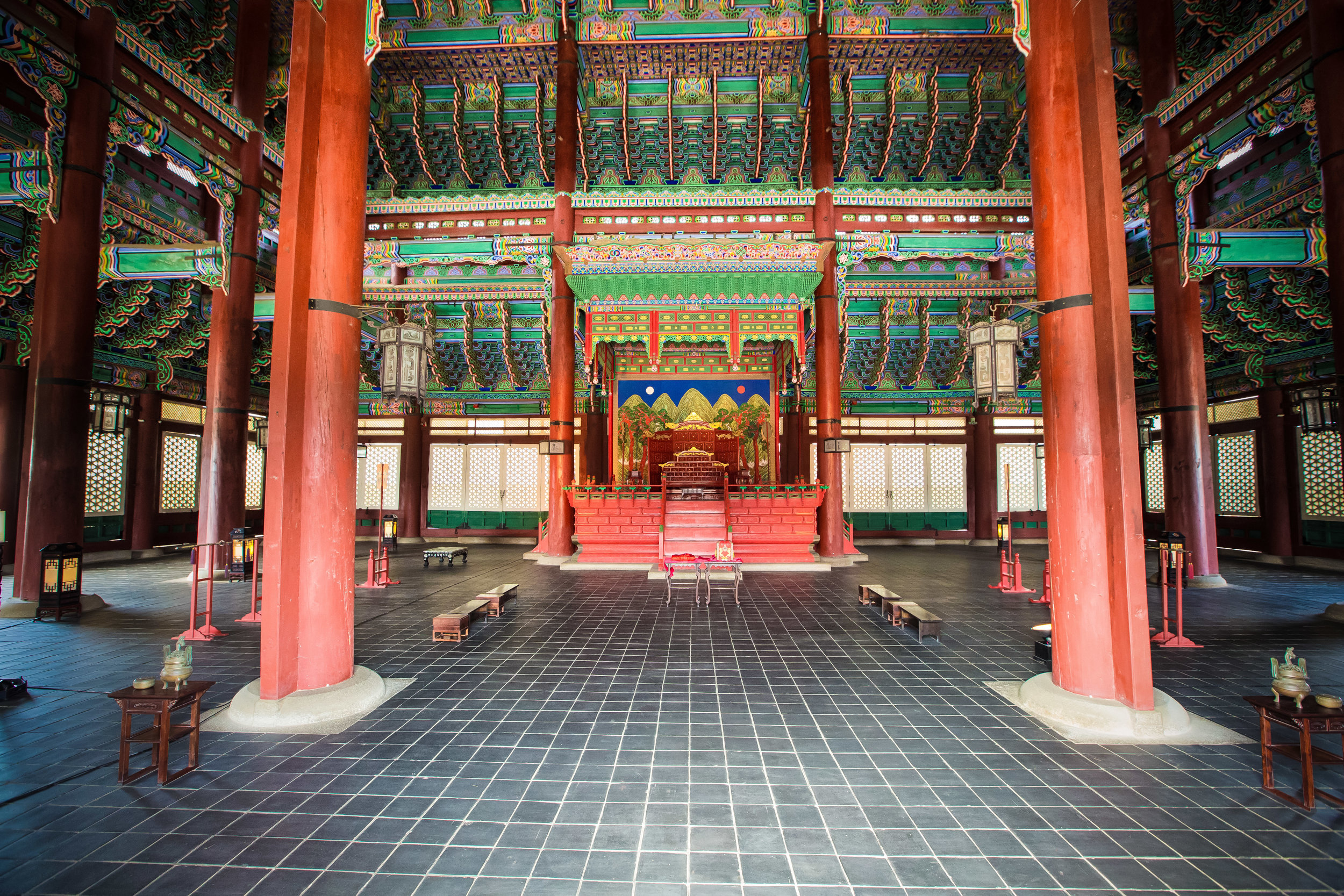
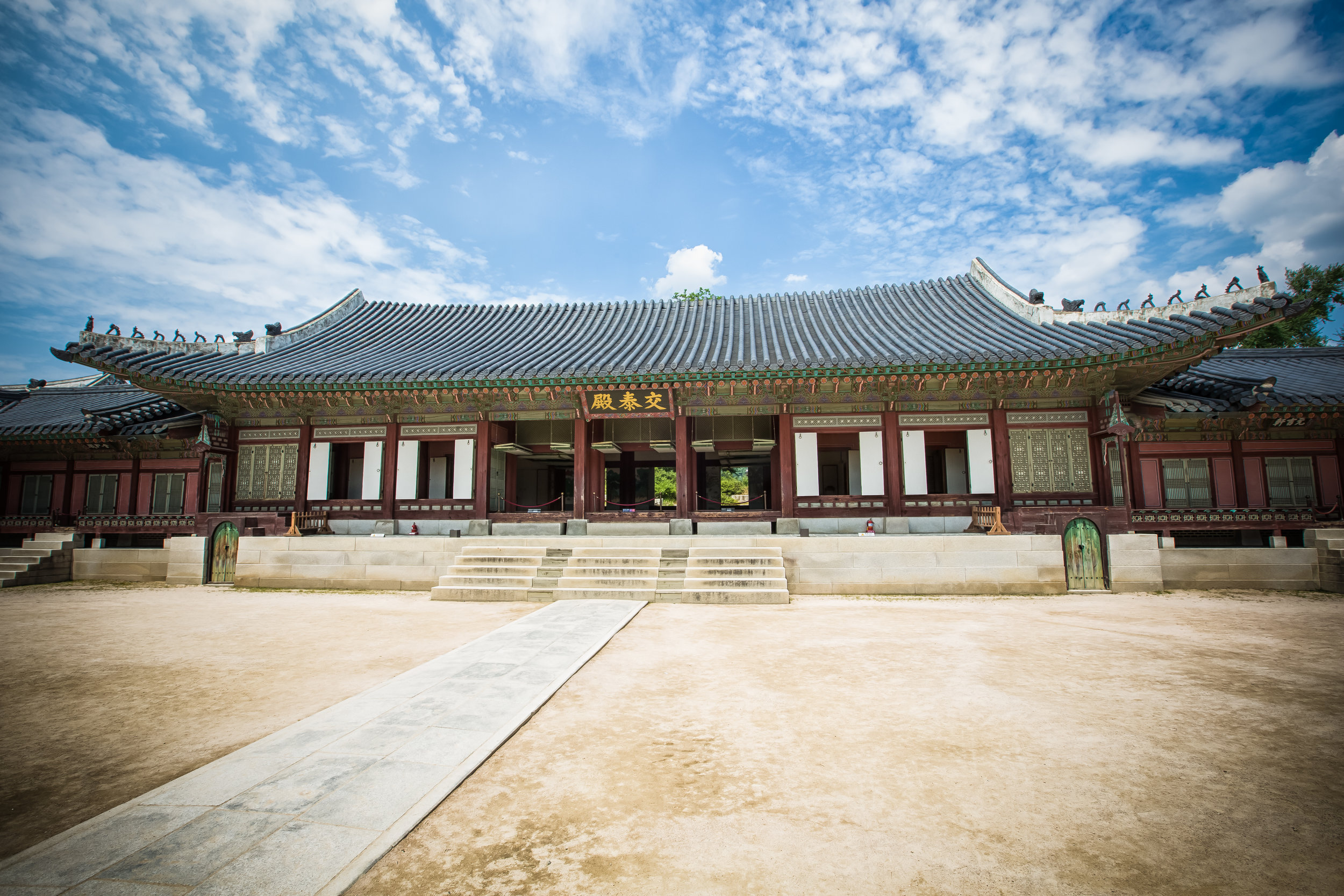
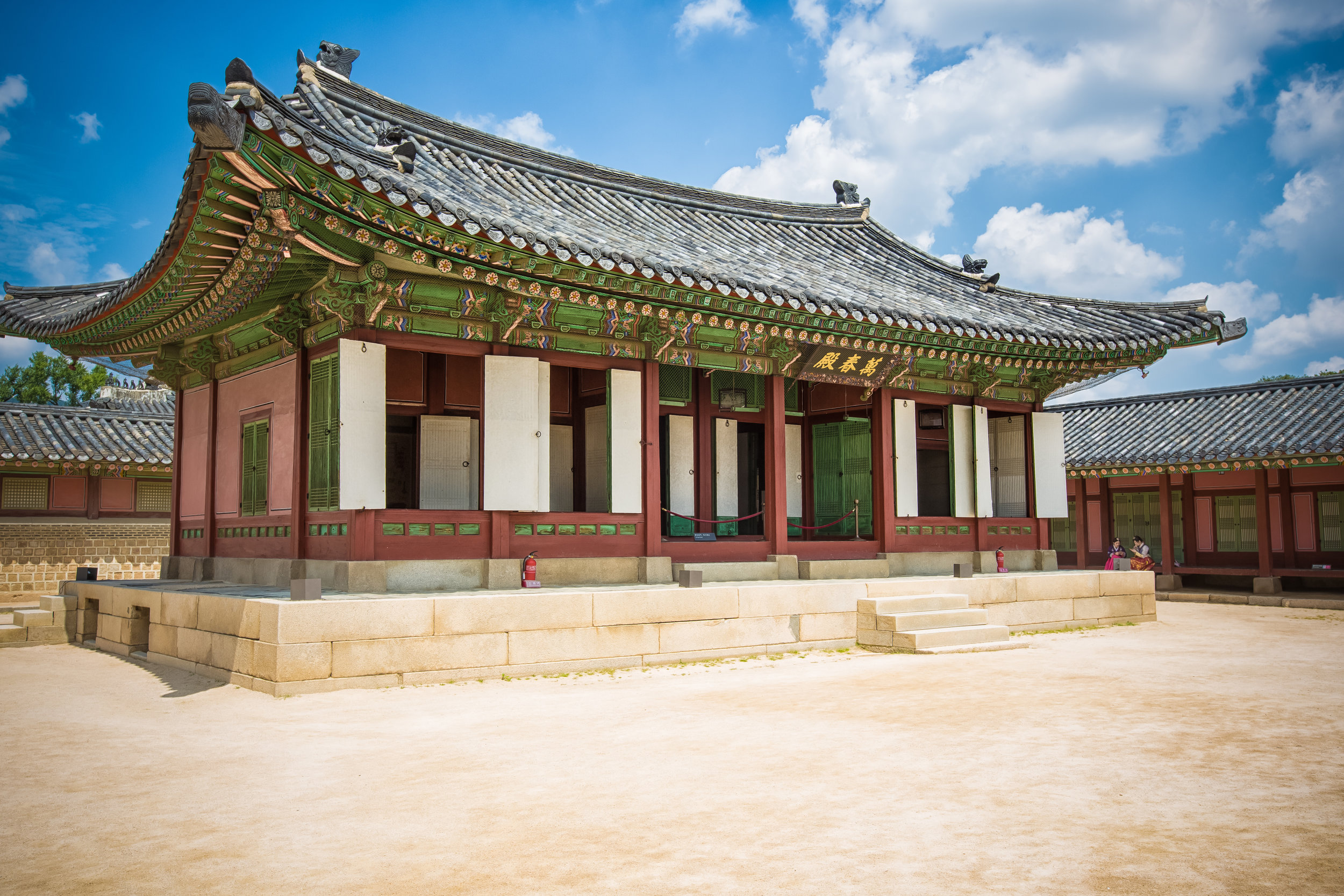
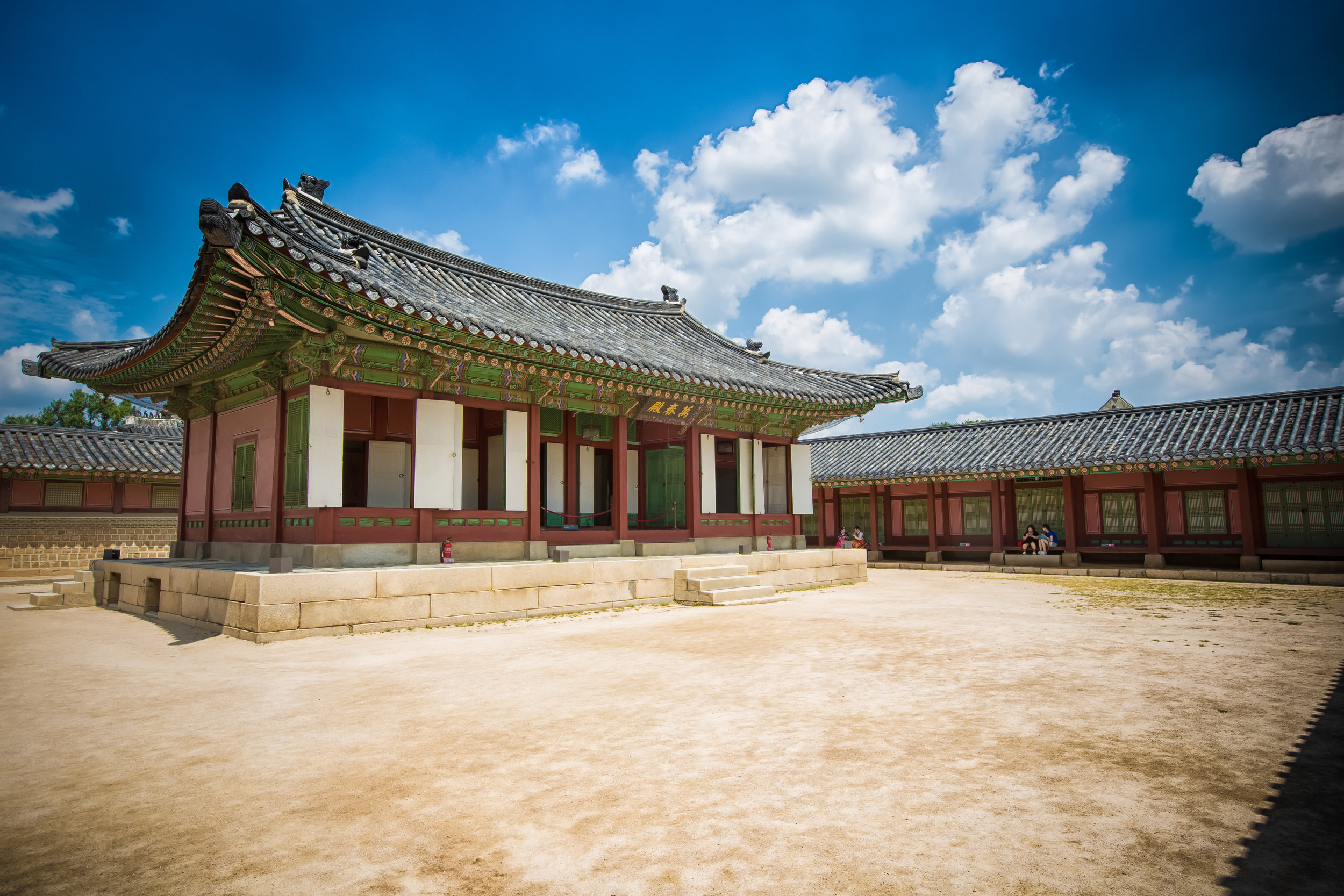
The temple itself is designed in a traditional way with a front hall (前殿) and a main hall (正殿) which are joined by two long corridors which are known as the "guardian dragons" (護龍) which house a sermon hall on the left side and an information centre on the right side.
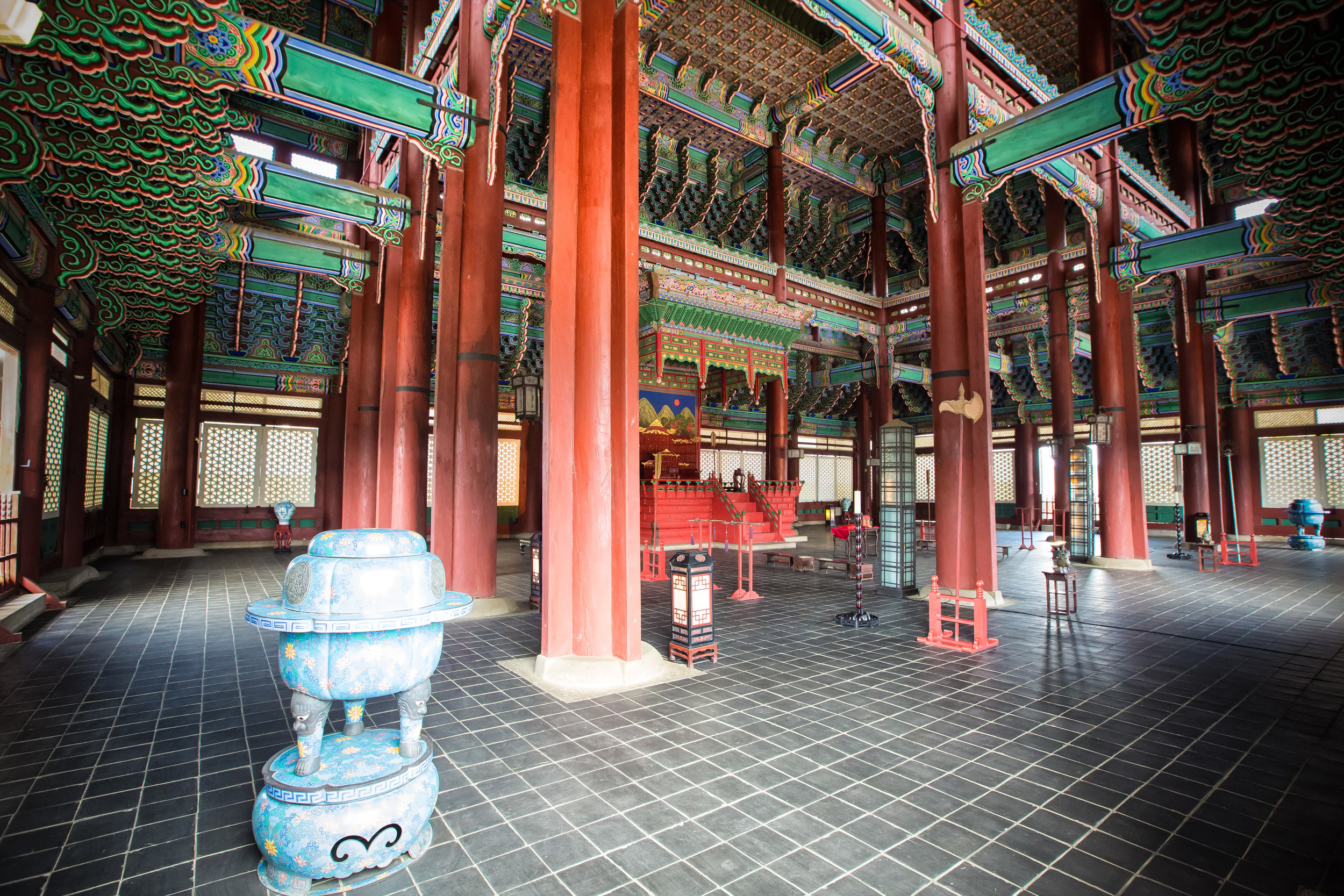
The middle of the temple which serves as the courtyard is where people will go to pray.
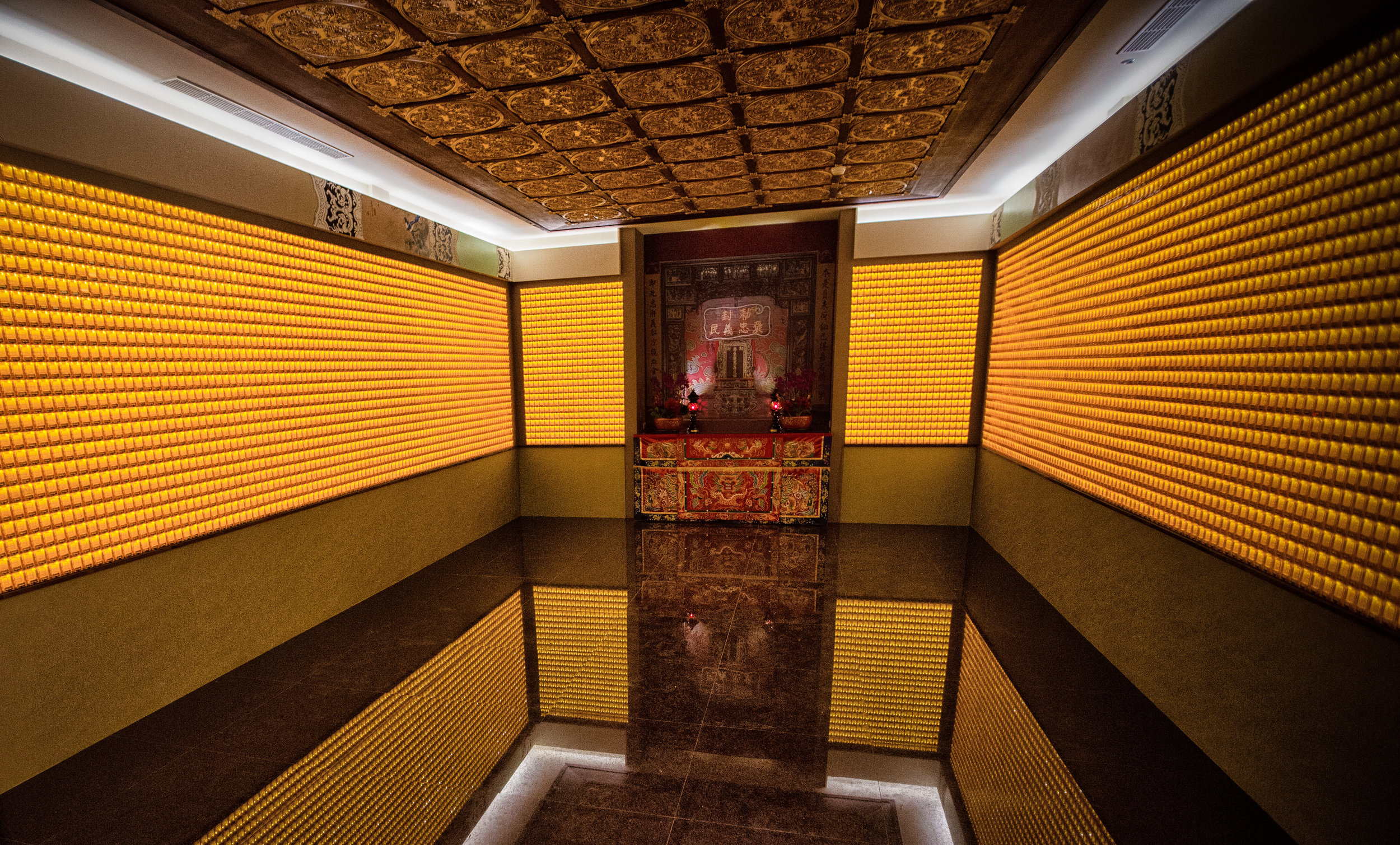
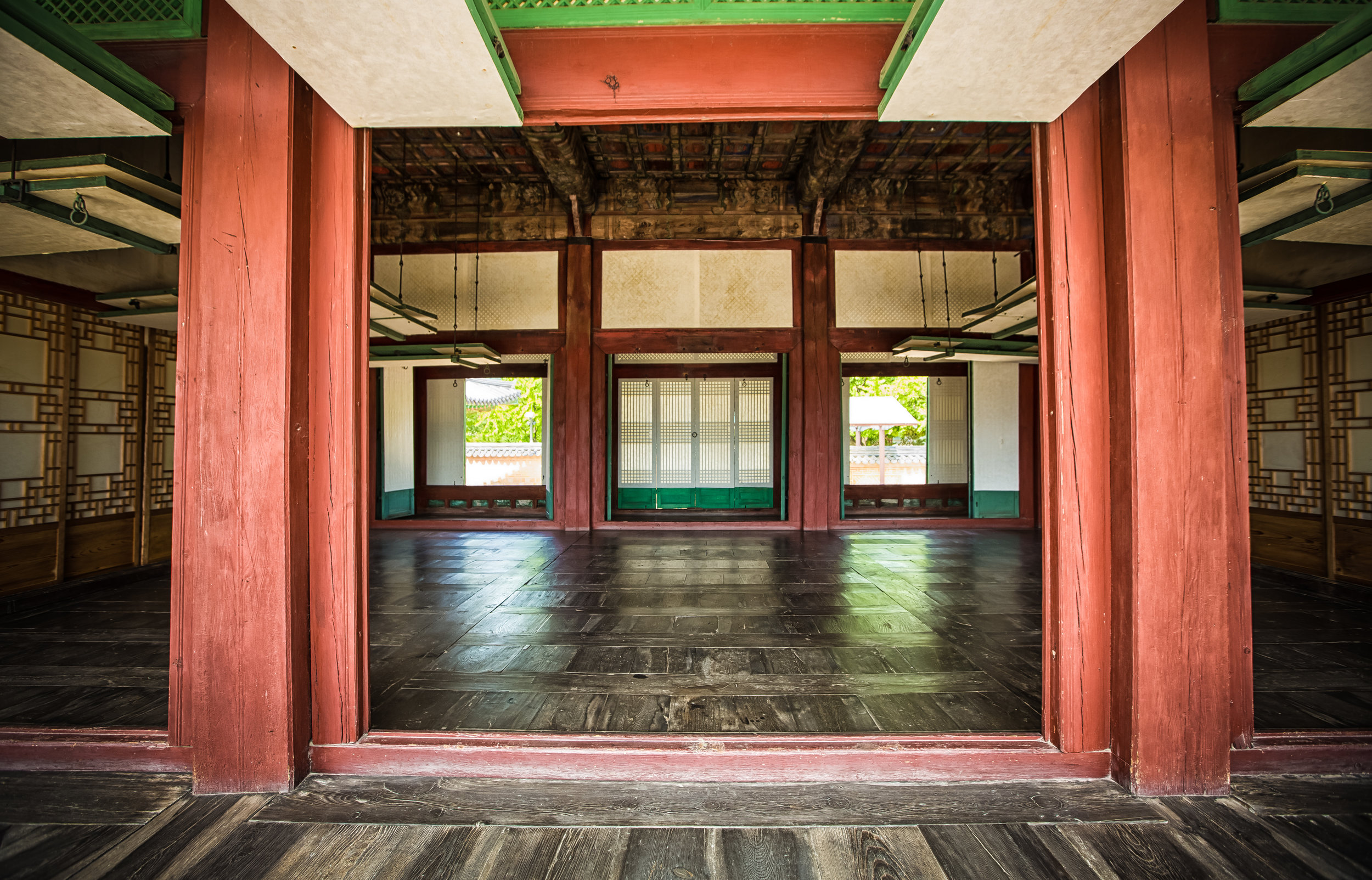
The main hall of the temple is off-limits to guests, so if you want to see the main shrine you are going to have to peer in from the courtyard. This is why I actually have very few photos of the shrine room. I had to use a telephoto lens to get shots of it.
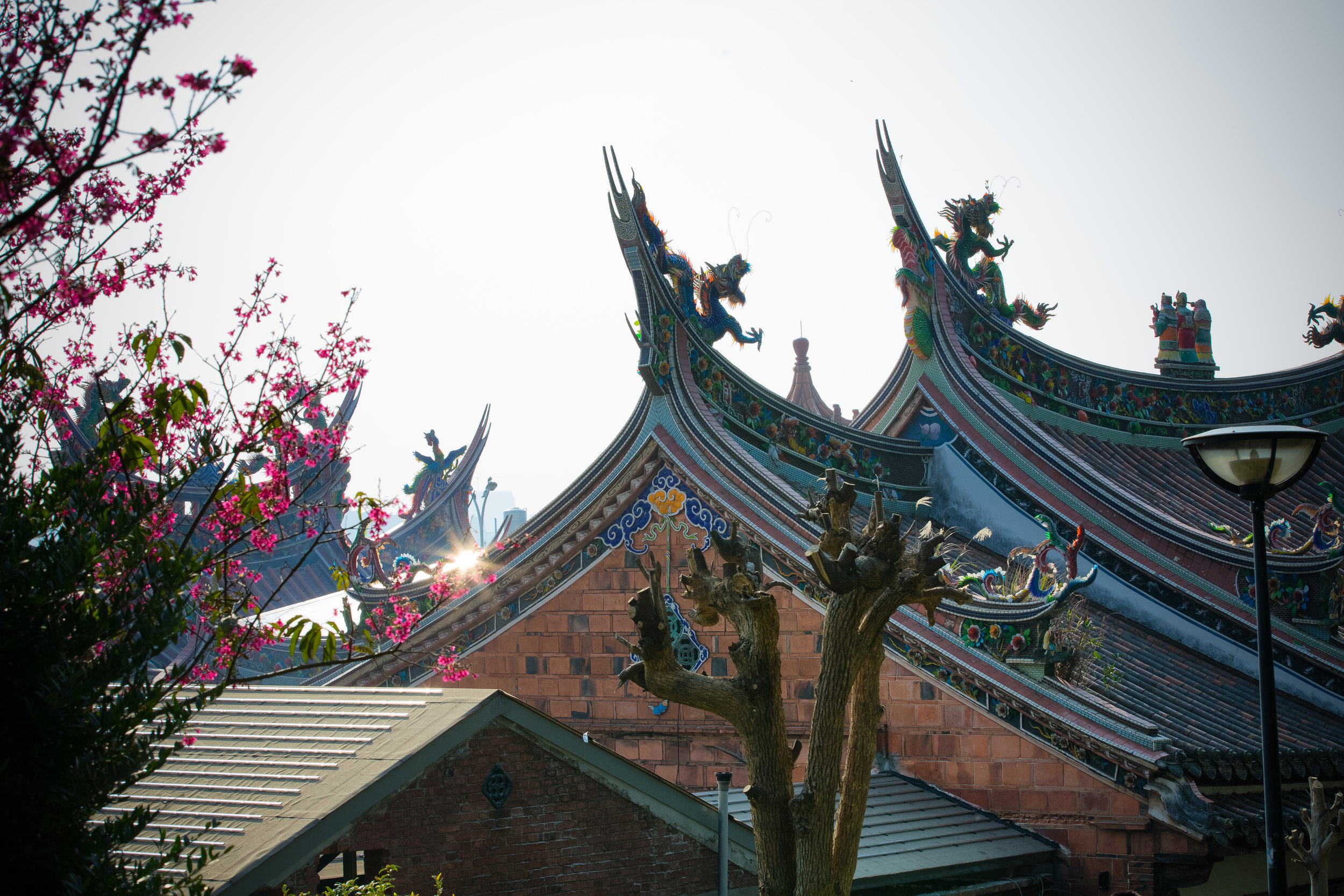
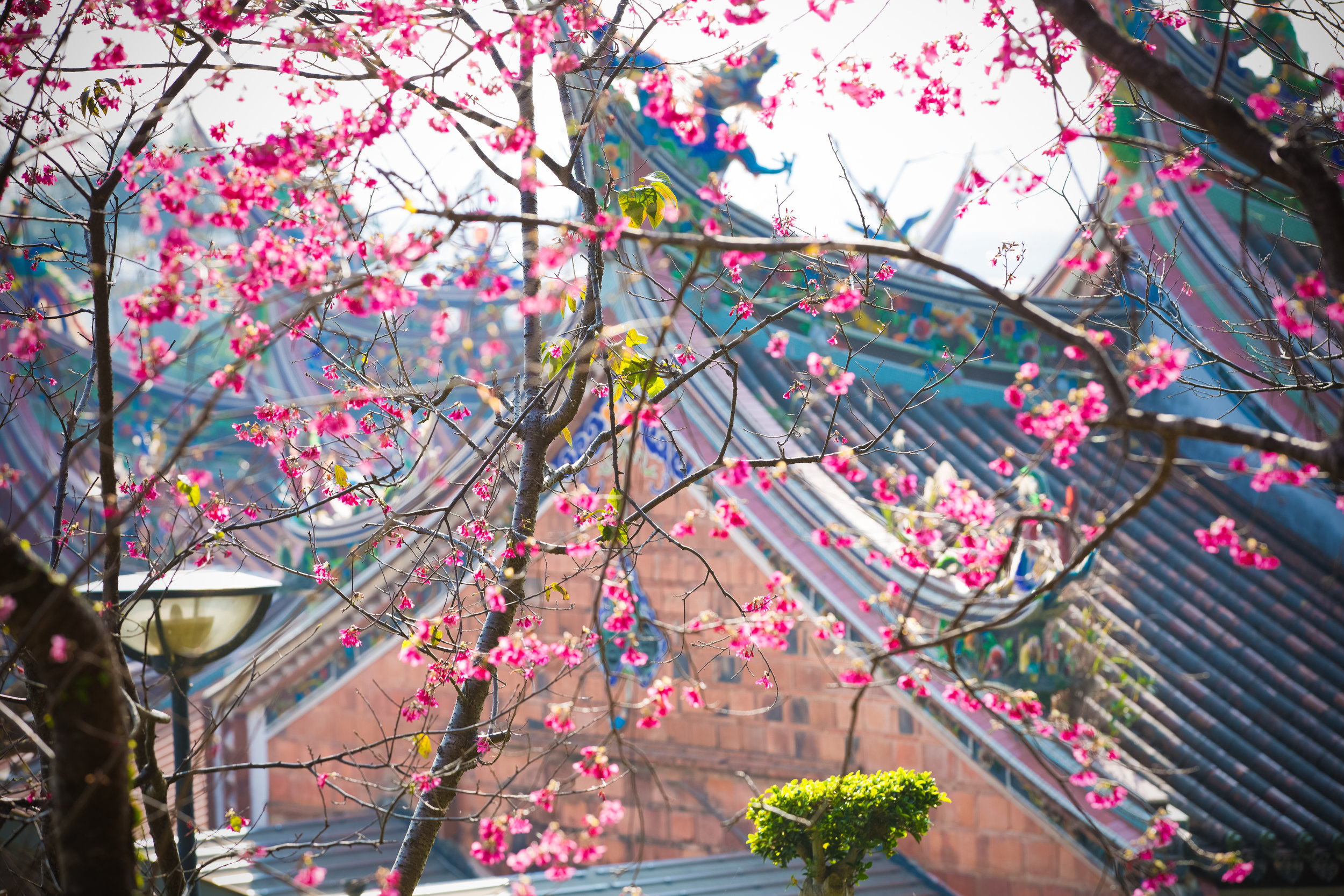
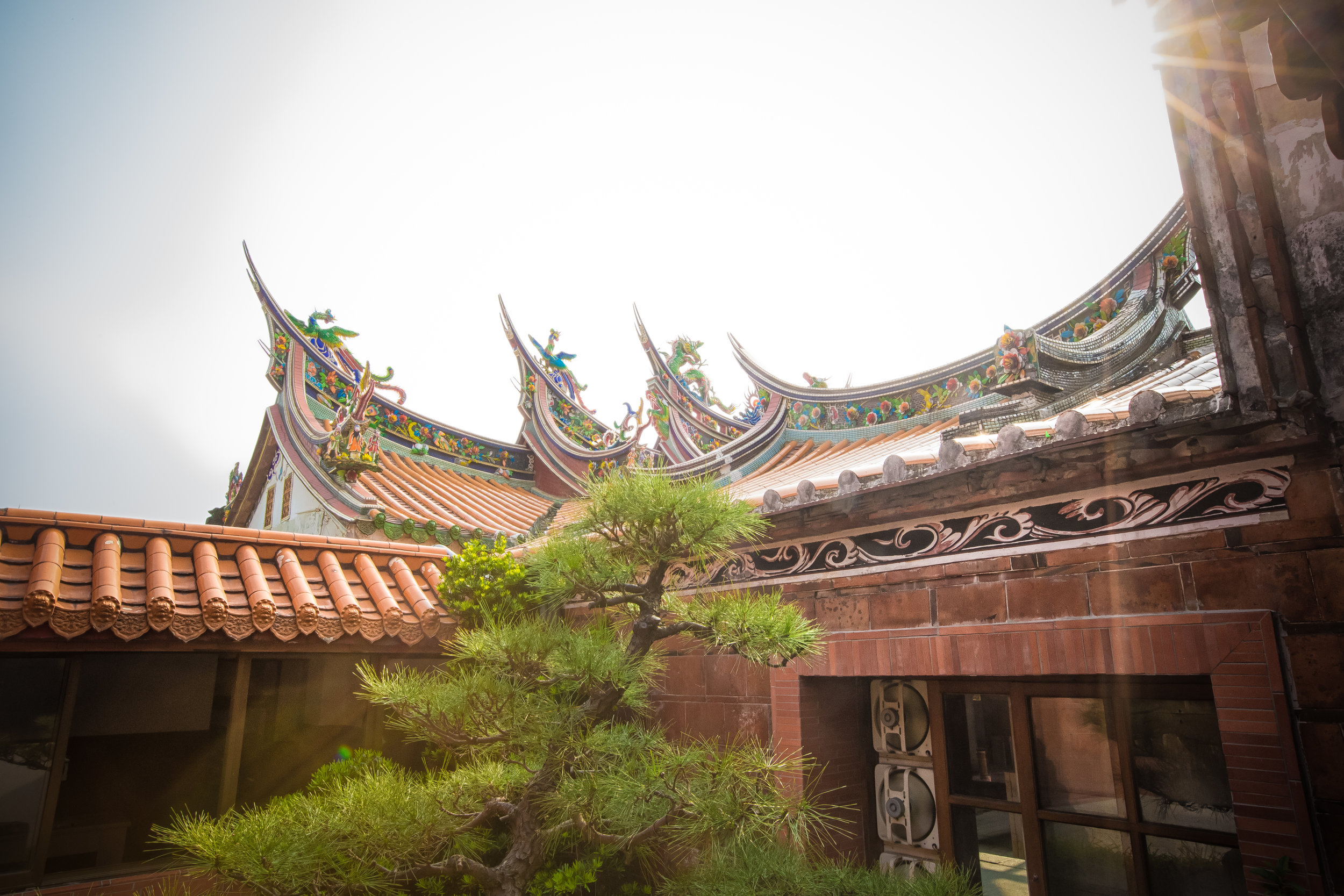
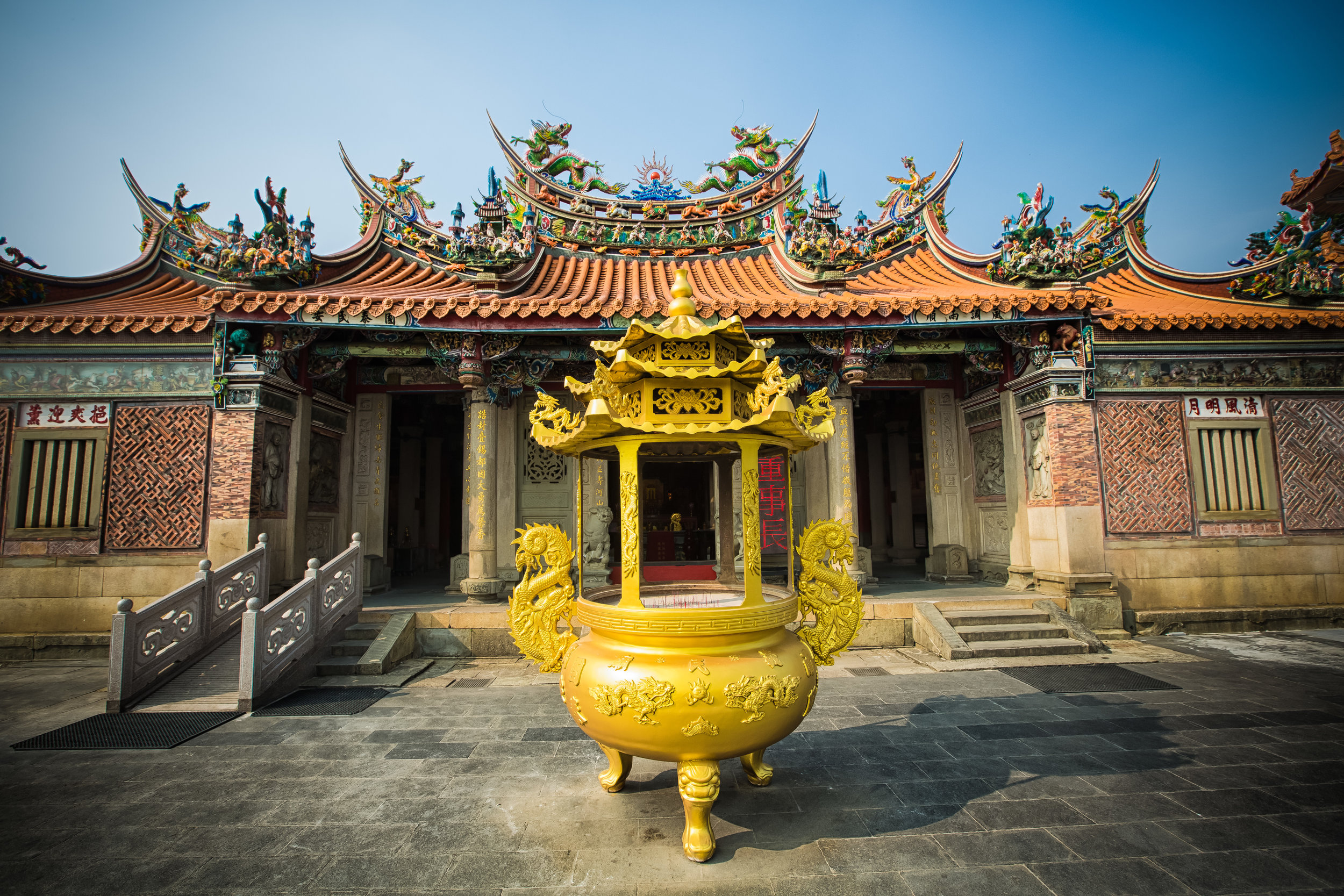
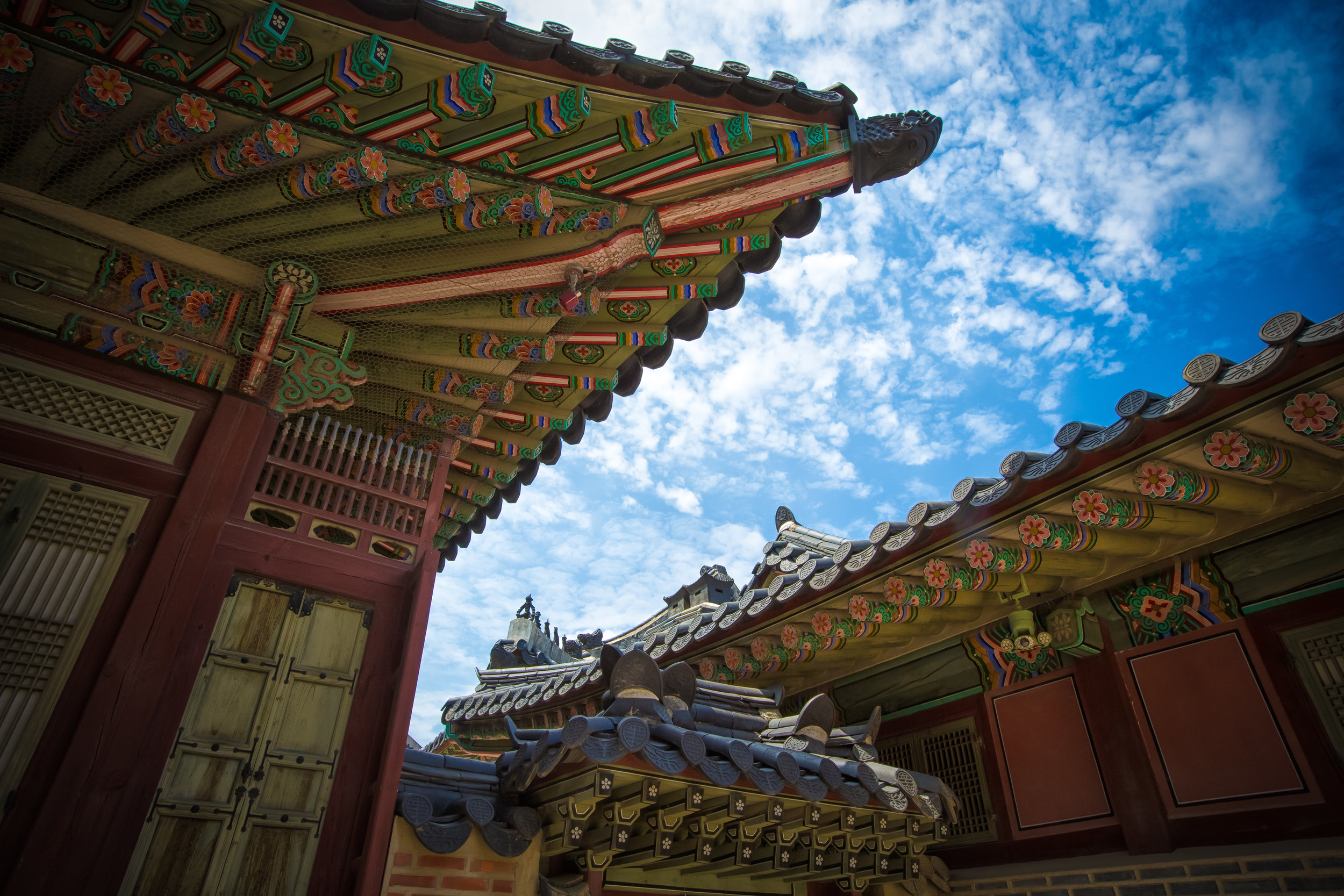
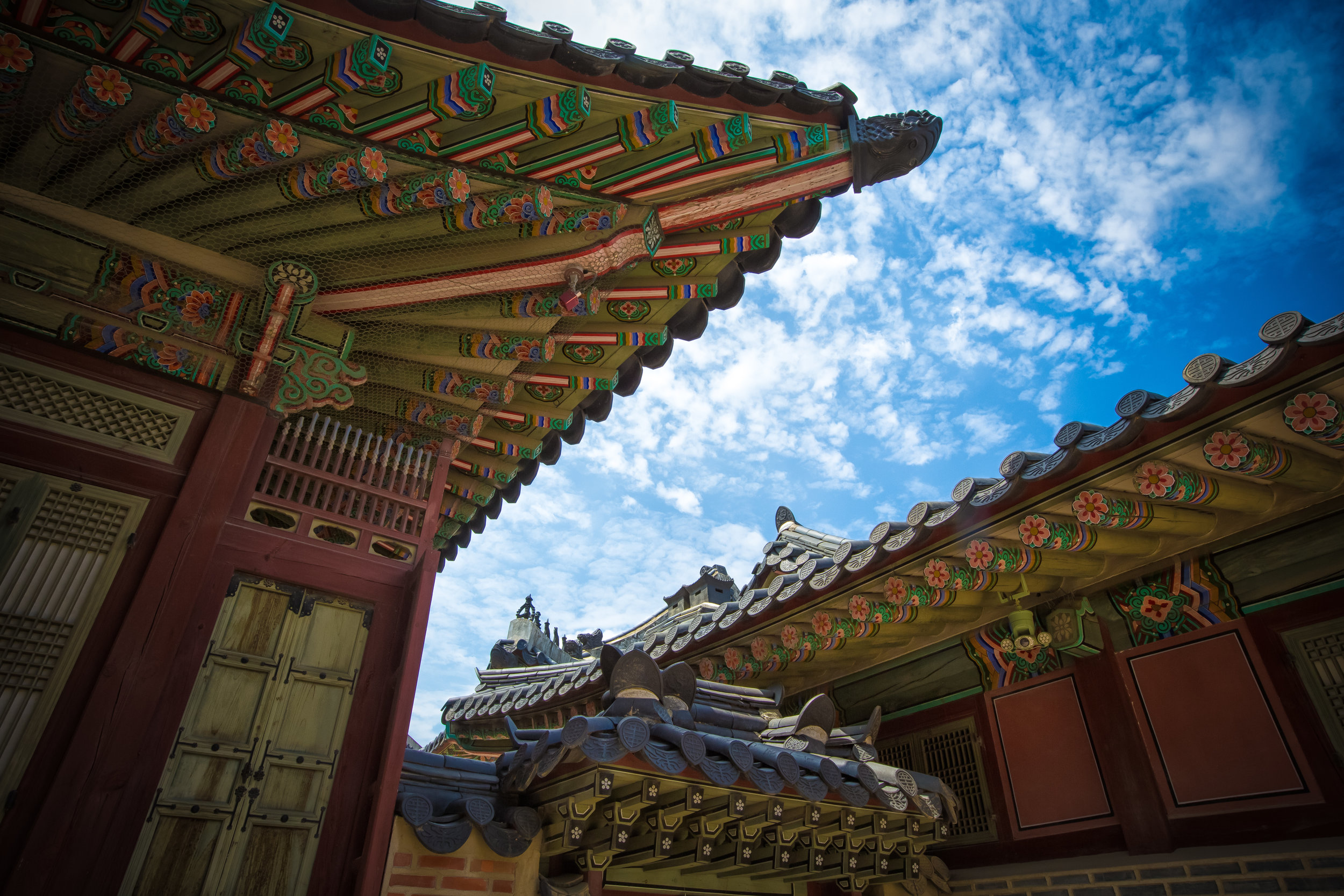
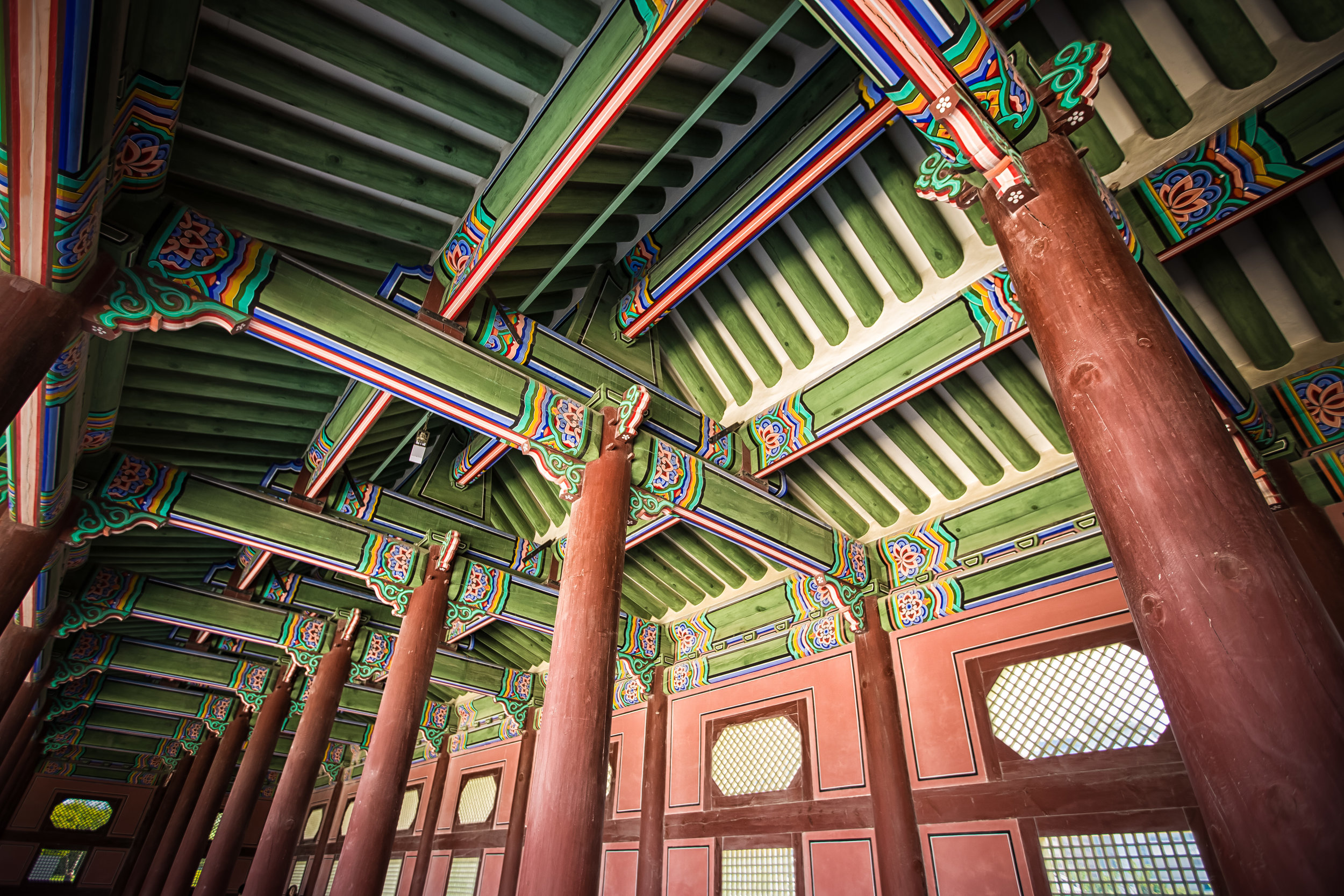
While the temple is quite plain, the things to notice within would be the dragons and phoenixes on the roof which act as guardians which ward off evil. Dragons specifically help to prevent fires and pray for rain while phoenixes appear when the earth is at peace and have long been considered auspicious symbols within traditional Chinese culture.
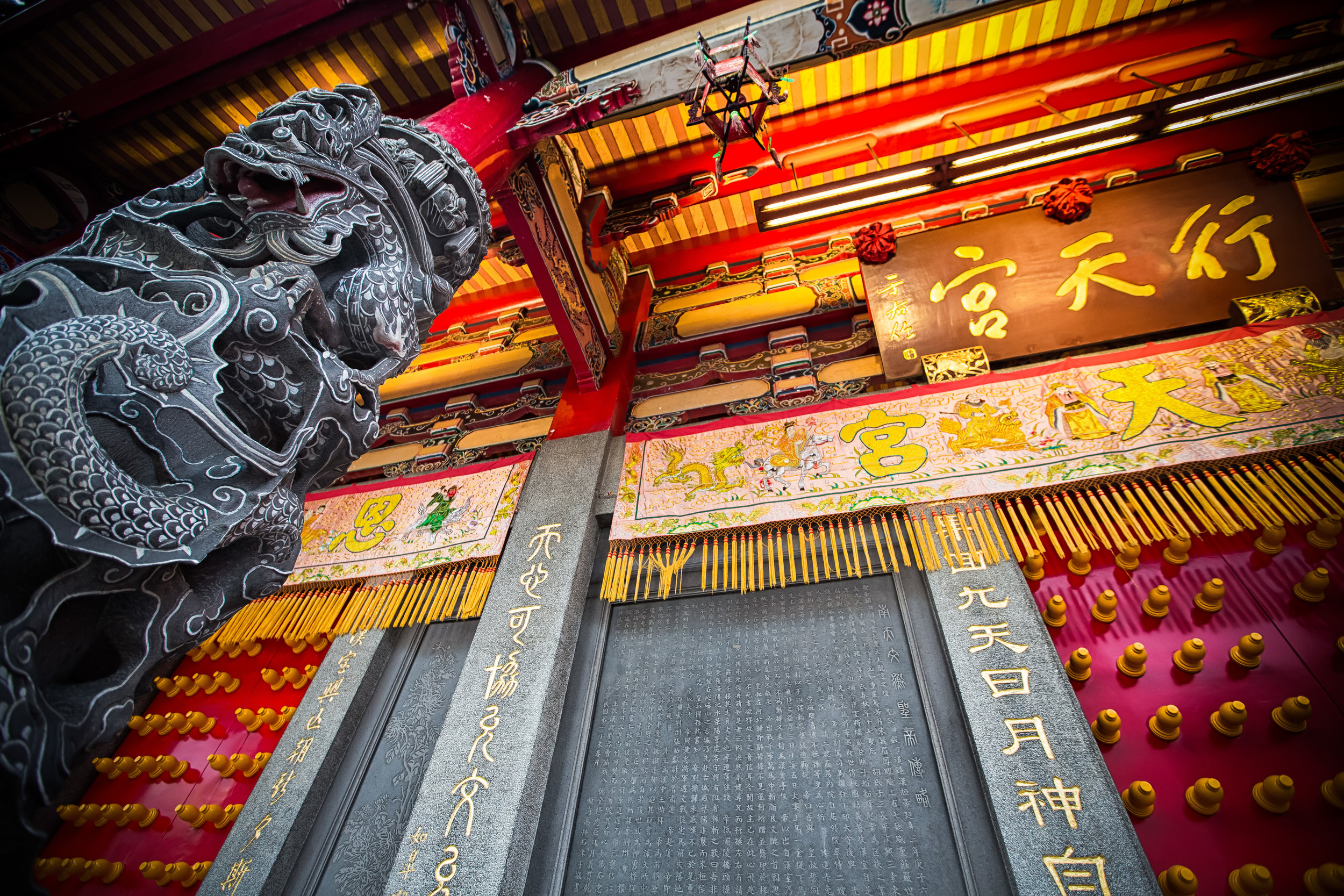
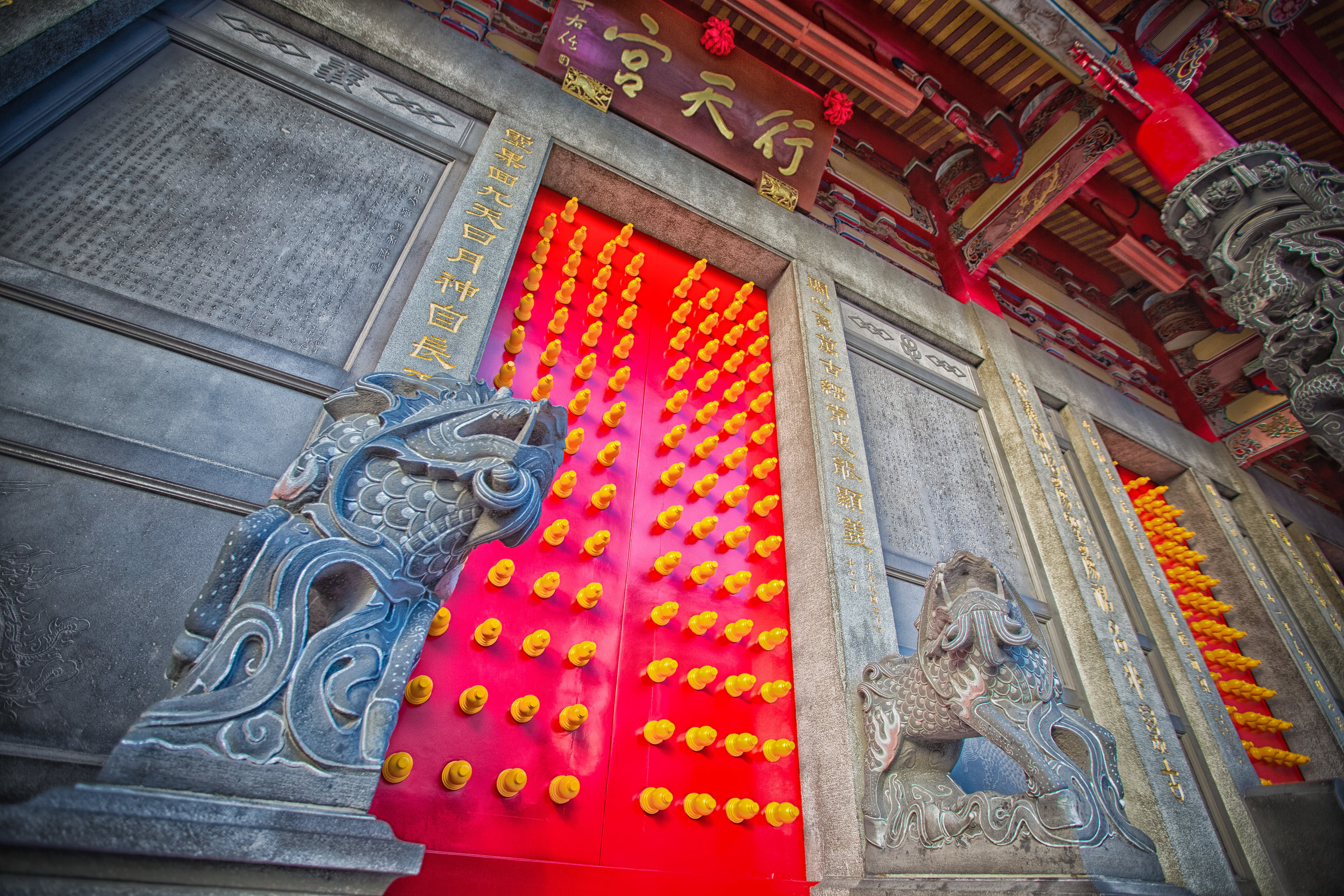
When it comes to stone work, Taiwanese temples spare no expense and Xingtian Temple is no different. The temple boasts twenty-seven beautiful stone columns in the front hall which have beautiful calligraphy poems carved into them by various Taiwanese artists. The poems on the pillars are meant to glorify Lord Guan and are an important addition to the design of the temple.
Apart from the columns, you'll find two stone Qilin (麒麟) at the main entrance to the front hall. Taiwanese temples are typically protected by stone lions but this one is a bit different - Qilin which are also known as 'Chinese unicorns' are mythical Chinese creatures that have the head of a dragon and the body of either an ox, deer, or horse with scales and hooves. While extremely cool-looking, Qilin symbolize prosperity, serenity and that the nation is at peace which I think fit in well with this temple.
As I mentioned above with the temple disciples, this temple is a bit more organized that your average Taiwanese temple and is part of a much larger Taoist organization. The Xingtian Temple organization which formed in 1956 under the leadership of Master Hsuan Kung (玄空師父) has since expanded to three temples, one in New Taipei City's Beitou district (北投分宮) and another in Sanxia district (三峽行修宮) and includes four libraries and a fully functional hospital. The group is dedicated not only to the promotion of Taoism but also to education, culture, medical care and charity and is quick to mobilize in the event of disaster.
Despite having three temples, this specific one which sits in the heart of Taipei is one of the city's largest tourist attractions with thousands of people visiting each day and a new subway stop which makes visiting the temple much easier.
Tourists who visit are likely to include a trip to the nearby Taipei Fish Market (上引水產) for fresh sushi with quality that rivals that of the Tsukiji market (築地市場) in Tokyo.
Xingtian Temple may not have the historical importance of Longshan Temple (龍山寺) or Bao-An Temple (保安宮) but it has molded itself into one of the most important places of worship in the city and rivals the others in the hearts of Taiwanese people.
If you are in Taipei for a short time, a visit to this peaceful temple should definitely be on your itinerary.
Gallery / Flickr (High Res Shots)