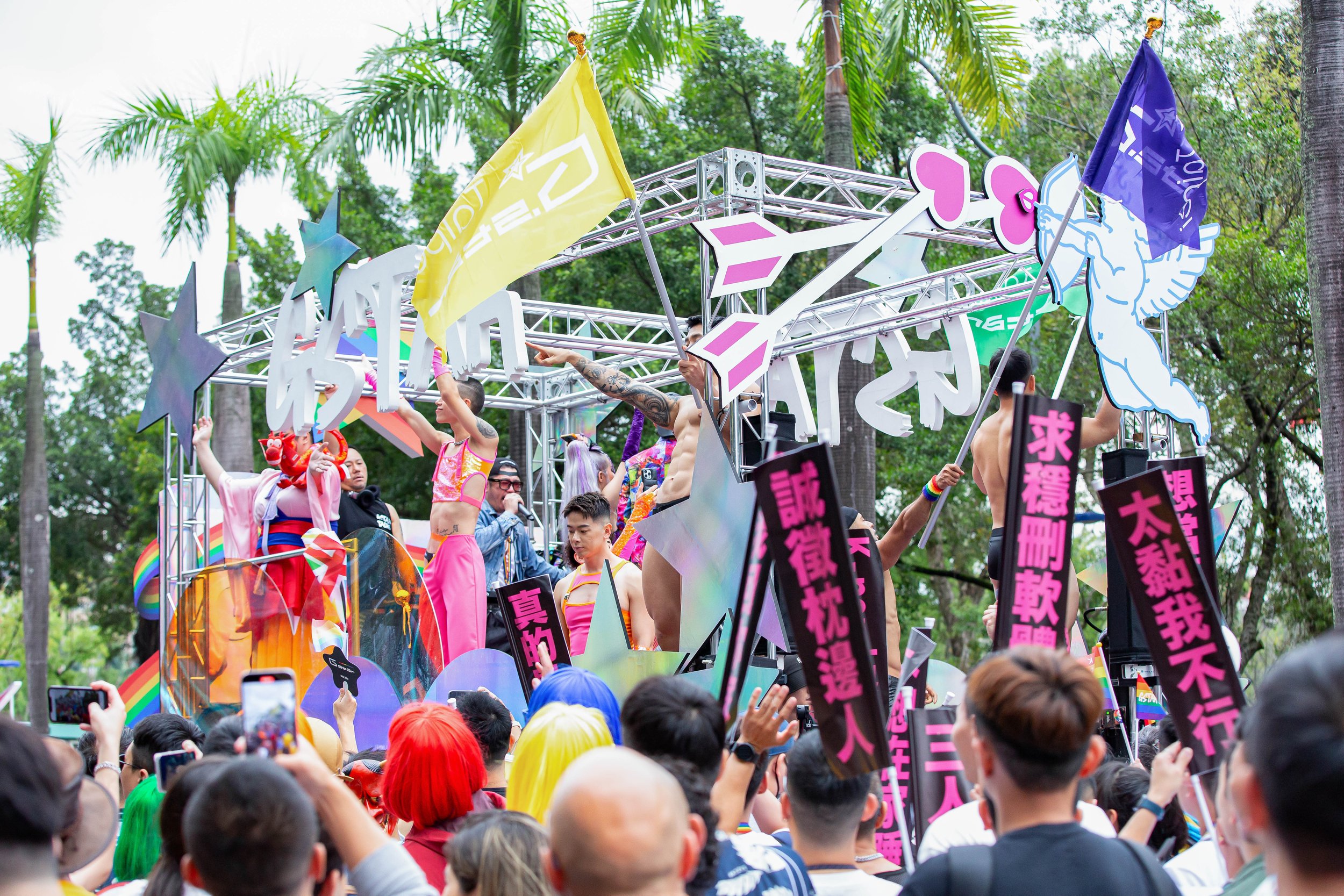
Every year, at least for the past two decades, the last Saturday of October in Taiwan doubles as a time to celebrate Halloween, and the nation’s annual Pride Parade. This year, the 21st ‘Taiwan LGBT Pride Parade’ was held on October 28th, attracting nearly two-hundred thousand participants!
Long known as Asia’s largest Pride Parade, the past few years have been quite subdued due to the COVID-19 pandemic, but this year, thankfully, everything was back to normal and the parade was once again a resounding success. This year’s theme was ‘Stand With Diversity’ (與多元同行), which aimed to "recognize the diversity of every person, and respecting and accepting different gender identities,” participants came from all walks of life, and included people from neighboring nations that have yet to reach Taiwan’s level of acceptance when it comes to LGBTQ issues.
The morning of the parade, the weather wasn’t looking like it was going to cooperate, but in the afternoon, the cloudy skies cleared up, and participants were able to enjoy their time as the sun came out and the weather cooperated. Starting from the rear of Taipei City Hall, the Pride Parade made its way through some of the busiest streets in the Taiwanese capital, but everything went smoothly thanks to the traffic control offered by the city government and the local police, who took part.
Links: Taiwan LGBT Pride | Facebook Page
As Taiwan is in the early stages of an election season, members of several different political parties took part in the festivities, including the ruling Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), New Power Party, Taiwan Green Party, Taiwan State-building Party, Taiwan Solidarity Union, and others. Most notably, in a first in the 21 year history of the parade, the Vice President William Lai (賴清德), who is currently running for president as the Democratic Progressive Party’s candidate, made an appearance.
Link: Taiwan Pride (Wiki)
In 2019, thanks to the leadership of President Tsai Ying-wen (蔡英文), Taiwan became the first country in Asia to pass same-sex marriage legislation, which was a milestone not only for Taiwan, but for LGBTQ rights across Asia, proving to nations across the region that progressive and inclusive policies are beneficial for nations and their citizens.
Link: Asia's First Mass Same-Sex Wedding (凱道同婚宴)
That being said, while Taiwan remains one of the most progressive countries in Asia on these issues, there is still a considerable amount of work to do in improving gender equality and LBGTQ+ rights. Parade organizers are quick to point out that while things have improved, ‘there are still many issues continue to influence and affect Taiwan’s LGBTQ+ community, such as immigration, adoption, and inclusion in Taiwan’s Artificial Reproduction Act, which currently prohibits support for surrogacy, which many same-sex couples may depend upon.’
Link: In pictures: Taiwan’s first mass gay wedding (Goldthread)
With an estimated 176,000 people in attendance this year, there is a considerable amount of acceptance for the LGBTQ community in Taiwan with allies of all ages coming out to show their support.
Today, I’ll save you from the typical long-winded article that I typically write and allow the photos to do the talking for me.
If you’re interested in learning more about the day’s events, I highly recommend you check out the report from New Bloom below. Similarly, I’ll offer a number of links from both local and international news outlets that covered the parade.
Link: Annual Pride Parade Draws Estimated 176,000 in Taipei (New Bloom)
I’d probably lose points as a blogger if I didn’t write something about my own experience, so let me tell you a bit about my day.
I arrived at the Taipei City Hall Station at around 1:30 in the afternoon, and the amount of people in and around the station was incredible. There were so many people that the walking pace was really slow, and MRT staff were all quite busy helping to assist with crowd control. It was pretty easy to tell by that point that this year’s event was attracting far more participants than the year before. When I emerged on ground level, there were happy, fabulous people everywhere, and although the weather wasn’t perfect, it was really quite comfortable!
Making my way through the massive crowds of people, I took some time to find a spot near where the parade started to take photos of all the people walking by. I ended up being fortunate enough to meet a friend who had arrived before me, so I grabbed a spot next to him, and we chatted and took photos together while the parade passed us by.
One of the great things about the Pride Parade, especially here in Taiwan, is that it is always a learning experience with the celebrity appearances. Some of the participants that passed by forced me to take out my cell phone to figure out why the crowd was getting so excited for certain people. There were celebrities and local ‘internet’ famous people all over the place, but I didn’t know who any of them were. I’m probably more familiar with all of the politicians who walked by, including the US Ambassador, former Mayor of Kaohsiung Chen Chu (陳菊), and lots of other local politicians.
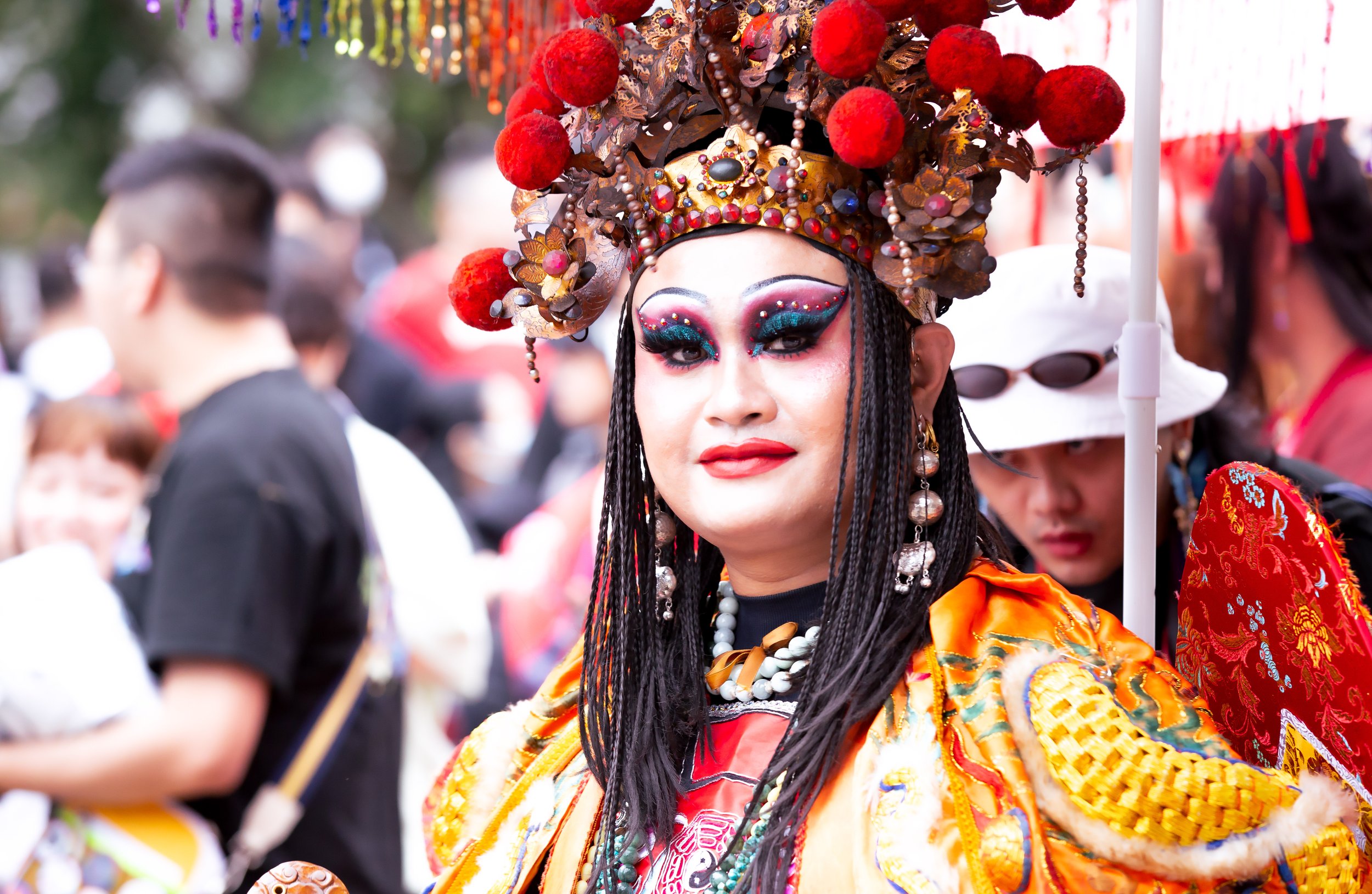
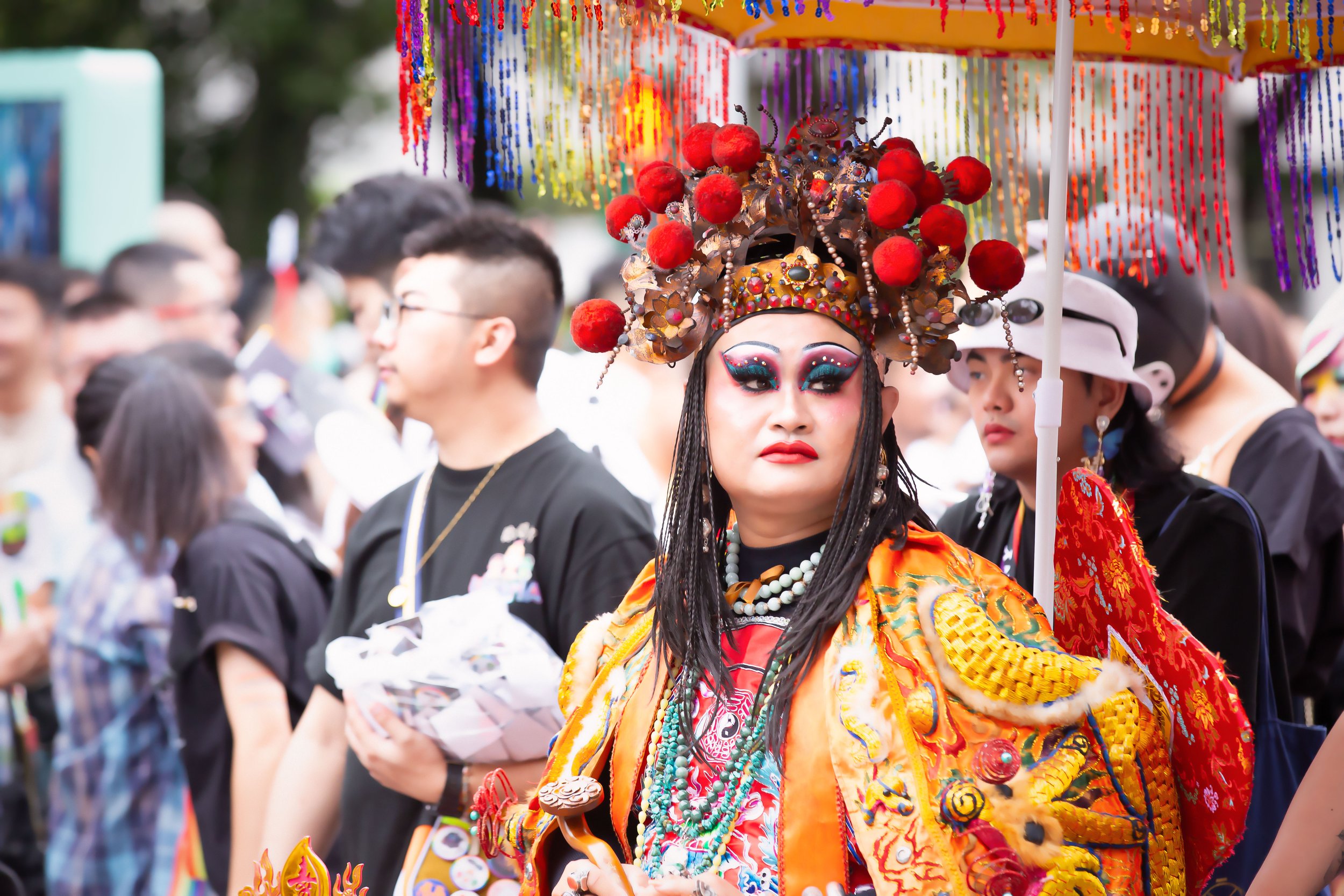
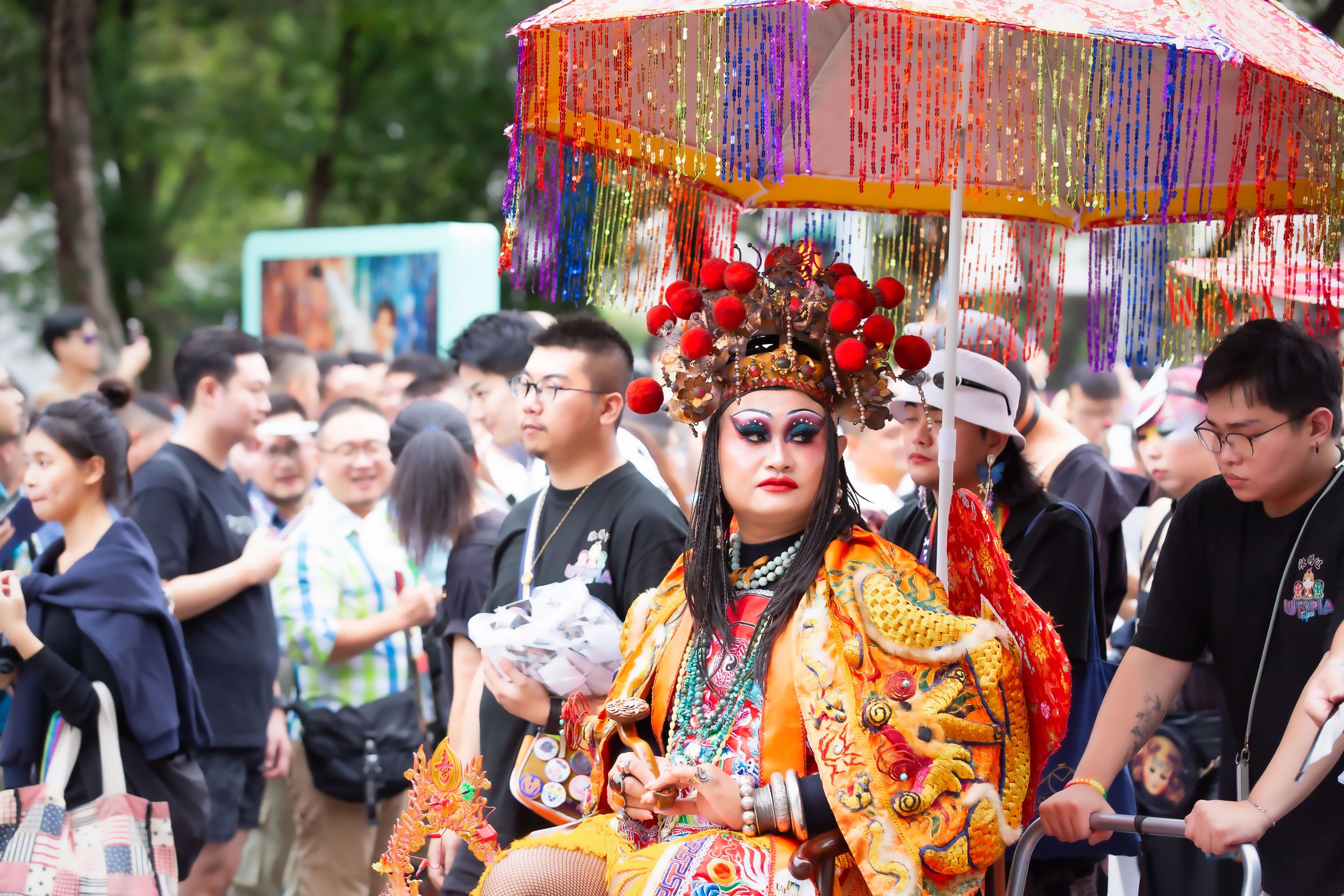
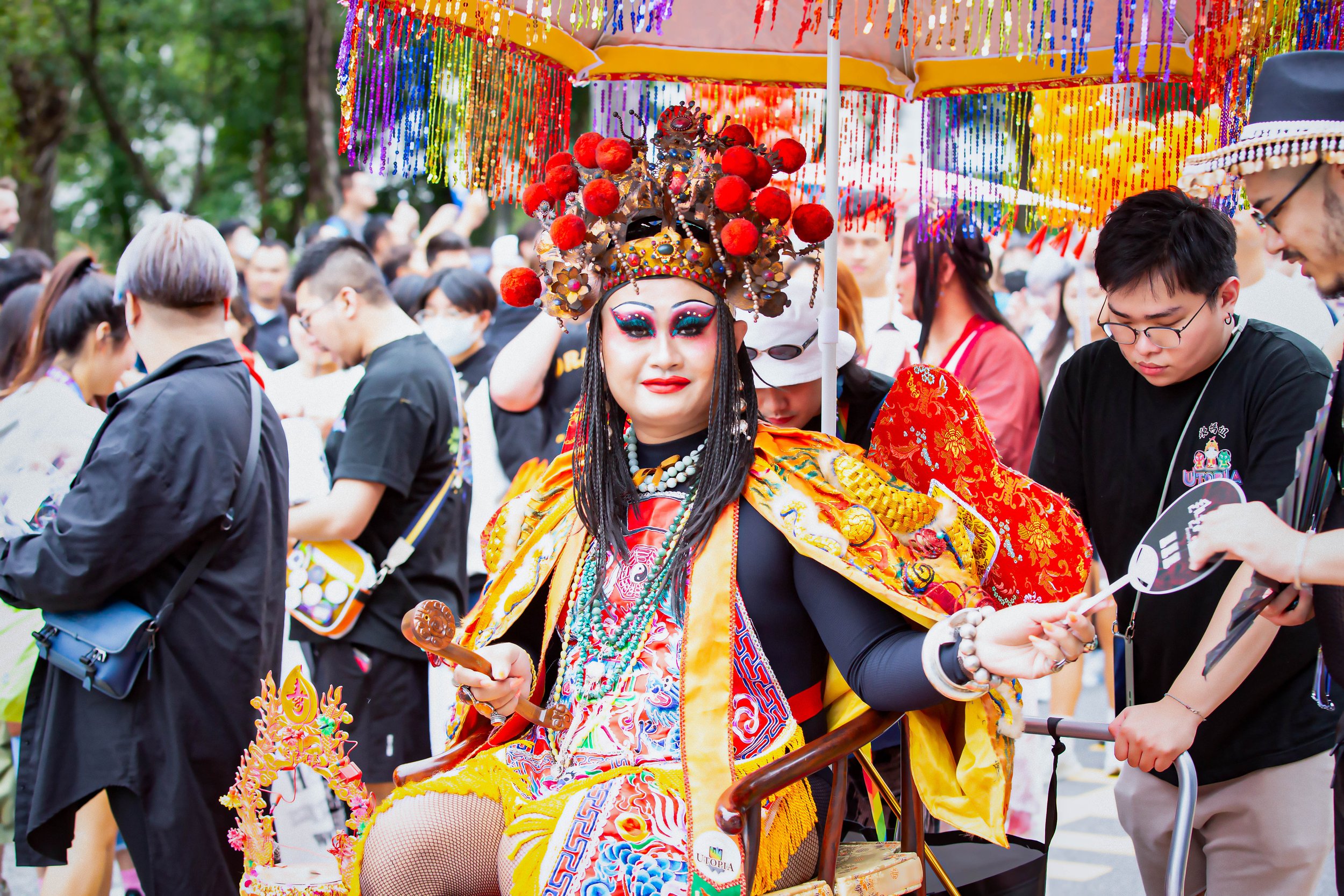
One of my favorite aspects of the parade, though, which is something that I look forward to every year, are the Queens that take part. Taiwan has a really vibrant Drag Queen scene, and every year they go out of their way to come up with something new, and it is always something that is very artistic. Given that the parade coincides with Halloween weekend, the costumes that they come up with for the event are always really cool, and they also work really hard to incorporate Taiwanese culture and history into whatever they’re doing.
Also, the after parties that they put on are apparently quite epic.
I’ll leave you with some shots of one of my favorite performances during this year’s parade, which brilliantly incorporated Taiwanese temple culture into the Pride parade.
If you’d like to know more about this year’s parade, check out some of the links below from local and international media that covered the event.
Hopefully you enjoyed the photos!
Media Coverage and Further Reading:
LGBTQ RIGHTS/Taiwan celebrates diversity, inclusion in Pride parade (Focus Taiwan)
Taiwan celebrates east Asia’s largest Pride march (Taipei Times)
Taiwan holds Asia's largest Pride after gay rights milestone (DW)
Taiwan’s 21st pride parade celebration to be the largest to date (Reuter)
Taiwan draws hundreds of thousands in East Asia’s largest Pride march (Pink News)
Photo Story: Taiwan LGBT+ Pride 2023: Celebrating Love Across Boundaries (The News Lens)