I’ve been criss-crossing the country over the past year in search of the sites related to the Japanese-era railway. As one the research projects I started this year, I’ve tried my best to visit as many of the historic railway factories, offices, dormitories, and historic stations as I could in order to document what many people believe to be one of the most important aspects of Taiwan’s modern development. Having authored close to a dozen articles this year, I’ve only covered a small percentage of what actually remains, so this is one of those projects that will continue for the foreseeable future.
The ironic thing is that while I’ve been traveling across the country in search of these historic buildings, the one that was actually the closest to me, a station that I must have passed by hundreds of times remained at the back of my long list of places to visit. Located just a few stops away from home, Shanjia Station in New Taipei’s Shulin District (樹林區) is one of those beautiful Japanese-era stations that has been recently restored and re-opened to the public as a cultural attraction, while the modern station to the rear continues service.
Every time I passed by the station on my way to Taipei, I’d say to myself “I should really stop by some day soon to get some photos” as I enjoyed the view of the station from the window of the train. It started to become a bit of a running joke that I would repeatedly say the same thing every time we passed by.
I realize this probably isn’t a huge selling point for anyone thinking of visiting, but one of the main reasons why I never actually got off the train to check out the station is that there isn’t very much else to see in the area.
For reasons I’ll get into later, the station was historically an important one, but the area around it doesn’t really offer much for tourists looking for something to do, unless you’re riding a bike along the river.
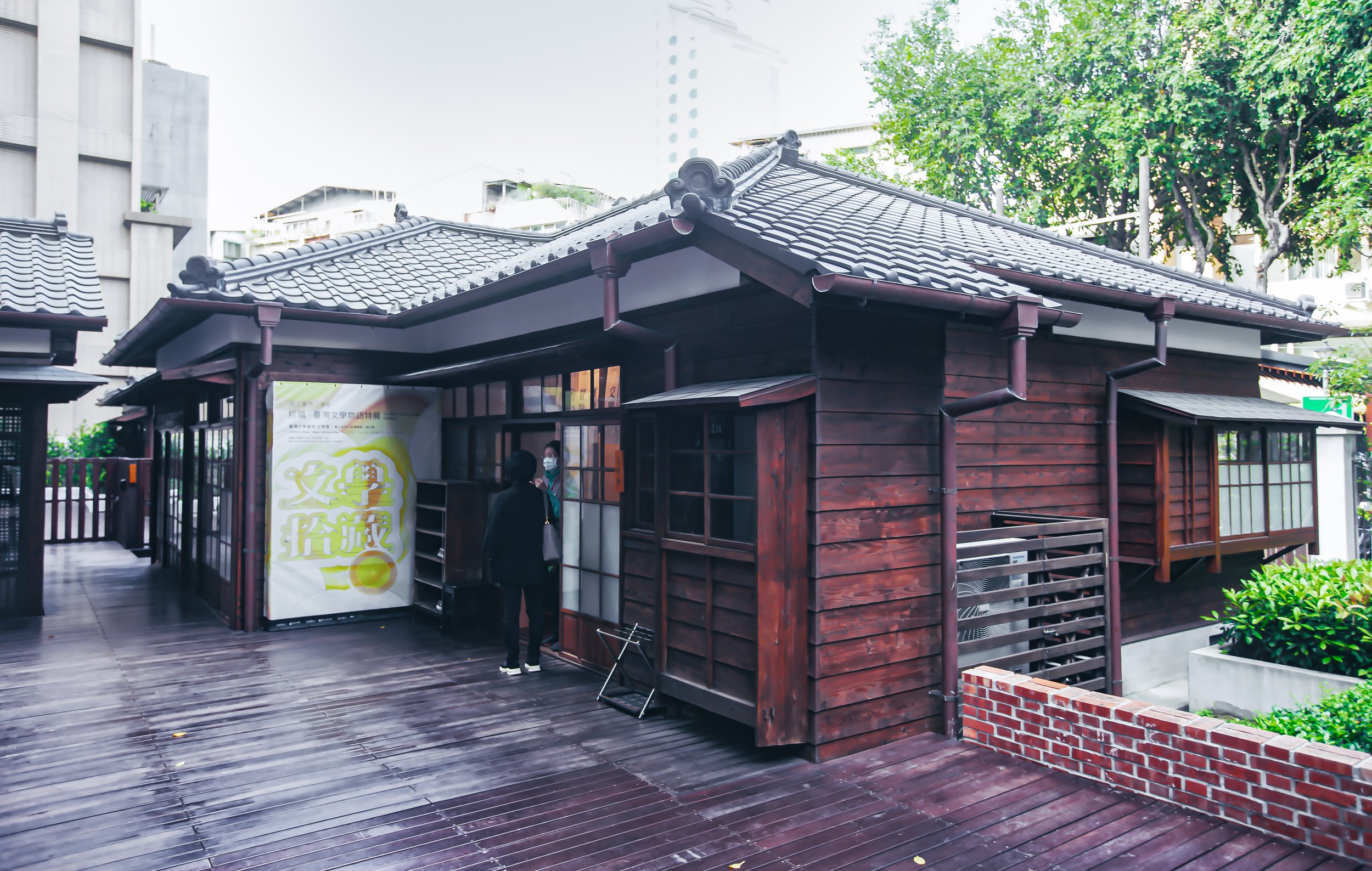
Fortunately I found myself on beautiful Autumn day with some extra time, and since I was already in the area, I decided to finally make an effort to stop by to check out this beautiful little station. That being said, unlike some of the Japanese-era stations along the Coastal Railway (海岸線) that I’ve already introduced, this one is similar to the historic Qidu Railway Station (七堵車站) in that it has been completely restored and reopened to the public, while a newly constructed modern station has taken over with regard to passenger services.
There are quite a few Japanese-era stations around the country that have been restored and continue to exist in conjunction with a modern station nearby - Shanjia Station however was the first to follow this model, so the others that we’ve seen reopening around the country as of late are simply following its excellent example.
As I move on below, I’ll introduce the history of this nearly 120 year old station, explain why it was so important for so long, and then go into detail about its architectural design, which is considerably different from many of the wooden Japanese-era stations that remain in Taiwan today.
Shanjia Train Station (山佳車站 / さんかえき)
Dating back to the early years of the Japanese Colonial Era, the station we refer to today as Shanjia Station (山佳車站) was constructed in 1903 (明治36年) as Yamakogashi Station (山仔脚駅 / やまご あしえき) along the Jukan Tetsudo (ゅうかんてつどう ), otherwise known either as the ‘Taiwan Trunk Railway’ (縱貫鐵道), or the West Coast Railway.
Within a few short years of Japanese control, railway stations started opening for service around the island thanks to the over four hundred kilometer railway constructed between Keelung and Kaohsiung. For the first time in the island’s history, population centers were connected to a modern form of transportation and Yamakogashi Station was one of them.
Over the years, the name of the station has changed on several occasions, but essentially it was named due to its proximity to the base of Datung Mountain (大棟山), a mountain that these days is split between Taoyuan and New Taipei City, and was important to the local community involved in the mining industry.
Interestingly, the name was changed once during the colonial era, but only with regard to the Kanji (Chinese Characters) in the name, and not the actual pronunciation of the station. Originally named “Yamakagashi” (Or Yamagoashi depending on your preferred romanization) with a “仔“ (zi/ zai), a commonly used character in Taiwanese/Hokkien (台語/閩南話), it was later renamed with the character “子” (zi), in a move that was likely made for the convenience of the technology at the time as the original character was less common in Japanese.
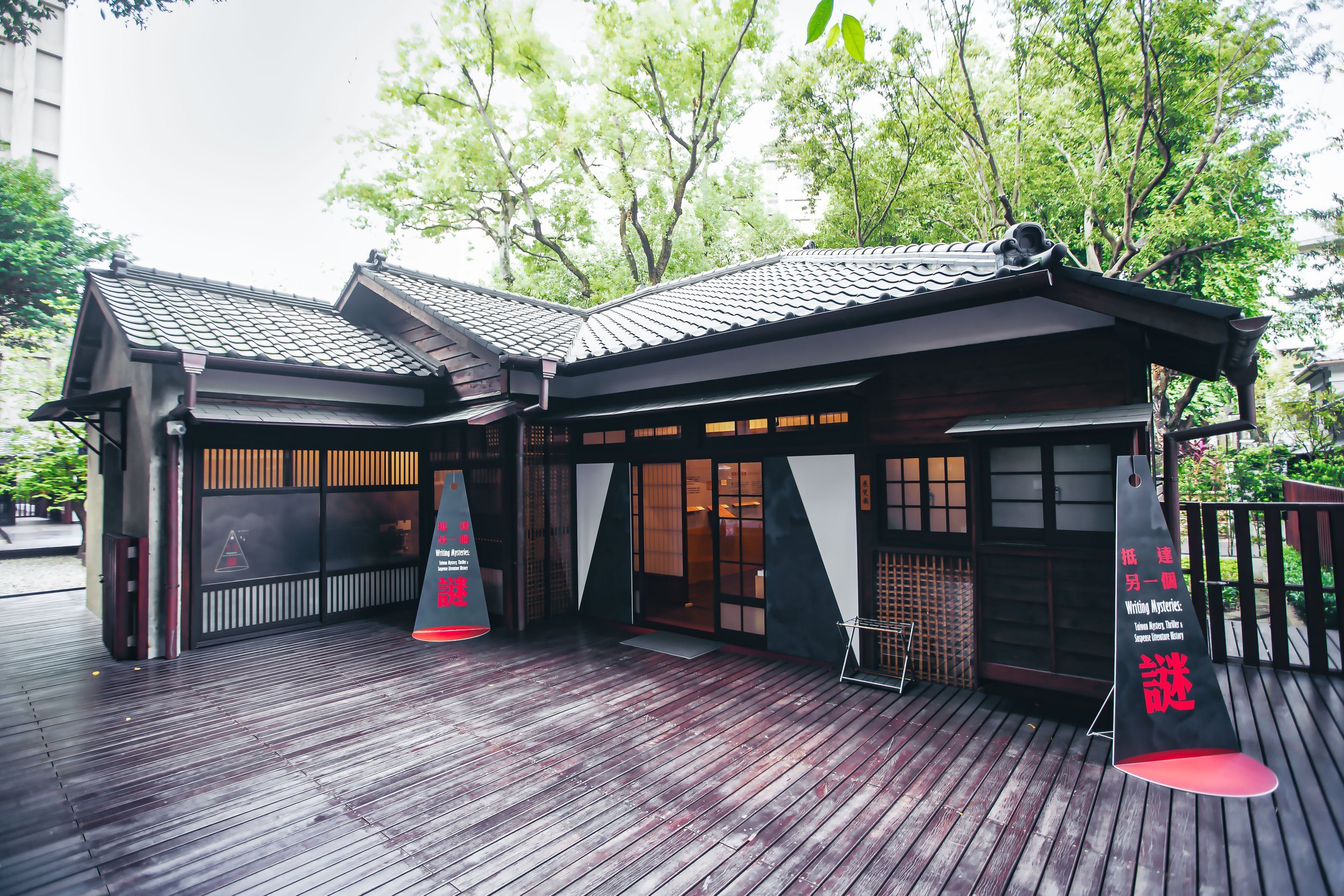
Like many of its contemporaries around Taiwan, Yamakagashi Station was originally constructed as a traditional wooden station house, but a few decades after its construction, it was torn down and replaced with the concrete building that we can see today. When you visit the station today you’ll find reference to it being a “century-old” (百年) station, but that’s not exactly true given that the building was we see today was constructed in the early years of the Showa era (昭和) when the usage of concrete was becoming more common around the island. Factually speaking, the beautiful station we can visit today is about ninety years old, but I suppose it sounds more impressive if you say it is almost 120 years old.
For a small station, in what is even much smaller community, especially since the much larger Shulin Station (樹林車站) is located nearby, the number of passengers that pass through the station on a daily basis remains quite impressive. The numbers have gone up and down over the years, but an average of half a million passengers make use of the station on an annual basis, making it a relatively busy station. That being said, historically Yamakagashi Station was known more for the important freight that was loaded at the station than the number of passengers that passed through the turnstiles.
Records from the Japanese era (1917 specifically) indicate that the area around the station accounted just around 300 households, or about 1700 people in total. The station today serves on average around 2000 passengers a day, but back then only around 5-6 people per day.
From this, I’m sure you can gather that the local community has grown quite a bit over the past century.
As mentioned above, the lack of passengers getting on the train at the station didn’t really matter all that much given that it was the loading point for an estimated 25,000 metric tons of coal on an annual basis during the heyday of the mining industry. Similarly, the station was also a focal point for the loading of sand and gravel excavated from the nearby Dahan River in addition to locally farmed white rice.
As one of Taihoku’s (current day ‘Greater Taipei’) six mining communities, Yamakagashi was the only one located on the western side of the Dahan River (大漢溪). The mining industry in the area flourished for quite some time, outlasting the Japanese-era, but at some point in the early 1980s, the area more or less dried up, and it became far too dangerous to continue mining, having a detrimental effect on the local community and the local economy.
Today, many of the old coal mine shafts remain open and a few of them have been restored to allow visitors to go check them out. If you’re so inclined, a visit to the station could also include a hike up the mountain nearby to see some of the mining-related sites. If you’re interested in that, I highly recommend checking out the link below where fellow blogger Tom Rook made the effort on a miserable day to go check out the old shafts.
Link: The Old Mining Village of Shanjia (Over The City)
A few years after the Japanese-era ended, the station was renamed Shanjia Station (山佳車站) and the community around the station grew and diversified around it. As the decades passed the number of passengers traveling through the station ultimately became far too many for the small station house to handle, so it was decided that a larger modern station would have to be constructed to better suit the needs of the local community.
Fortunately the Taiwan Railway Administration had the foresight not to knock the original station down to make way for the new one. So when the new iteration of the station, a gaudy structure devoid of any architectural style, opened to the public in 2011, it was made a bit more respectable by the fact that it had the original Japanese-era station in front.
Before I get into the architectural design of the station, I’ll provide a bit of a timeline of events that took place at the station over the past century.
Timeline
1903 (明治36年) - Yamakoashi Station (山仔脚駅) opens for service.
1920 (大正9年) - The station is renamed Yamakoashi Station (山子脚駅), a slight variation on the original Kanji characters given that the character “仔” is rarely used in Japanese.
1928 (昭和4年) - The original wooden station is demolished and construction on a new station begins.
1931 (昭和6年) - The new (current) cement station is completed and is reopened for service.
1962 (民國51年) - The station is renamed Shanjia Station (山佳車站).
2008 (民國97年) - The station switches primarily to the EasyCard swiping system rather than issuing tickets.
2009 (民國98年) - The original “S” shaped platform is demolished in order to allow express trains to pass through the station more easily.
2011 (民國100年) - The new cross-platform elevated Shanjia Station is opened to the public while the original station is covered in canvas and plans are drawn up to have it restored.
2014 (民國103年) - Typhoon Soudelor (強烈颱風蘇迪勒) causes a considerable amount of damage to the protective covering placed over the historic station. Afterwards, a new protective tent is installed to help preserve the station.
2015 (民國104年) - The restoration project on the original station is started, making it the first of several Japanese-era stations that is set to exist side-by-side with a modern station.
2017 (民國106年) - The restoration project on the station is completed and the historic Shanjia Station is reopened to the public with a railway culture park located along the platform, highlighting the history of the station and the mining activities that made it important.
Architectural Design
These days, when you walk into the historic Shanjia Station, one of the first things you’ll notice is a very large model of its 1903 predecessor on display in one of the rooms. The original station appears to be quite similar to many of the other small railway stations constructed around Taiwan, but it only ended up lasting about twenty years before it was replaced.
The ‘newer’ historic station, which as mentioned above was completed in 1931 was constructed during a period of the Japanese-era that tends to stand out architecturally-speaking. Having taken control of Taiwan in 1895, the Japanese spent a considerable amount of time developing the island and its infrastructure. For the first couple of decades, many of the buildings constructed were somewhat rudimentary and were thought to be almost temporary as the idea was to first get everything running smoothly before refining things.
By the time the Showa Emperor (昭和皇帝), more commonly known in the west as Emperor Hirohito, took control in 1926 (昭和元年), it was generally thought that the situation in Taiwan had stabilized to the point that the Governor General’s Office was given the go-ahead to start tearing down some of the older buildings and replacing them with newer ones. Similarly this was also when the Japanese architects of the era had started to combine modern construction techniques with traditional Japanese design resulting in an architectural fusion, replacing many of the older wooden buildings with those constructed with reinforced concrete.
Note: Obviously another important factor for some of these rebuilds was due to a number of natural disasters (earthquakes and typhoons) that devastated the island on several occasions over the first few decades of colonial rule.
Official government sources claim that one of the first railway stations to receive such treatment was Yamakoashi Station, and that its construction was something that was to be emulated in other areas around the island. Unfortunately, there is little information available with regard to the architectural design of the station, so I can’t actually confirm whether or not those claims are true, but given the period that it was constructed, its quite possible.
Regardless, there are two things we should keep in mind here - the first being that it is somewhat of a tradition that whenever a new emperor takes control in Japan, it is common to see ambitious construction projects taking place with the new ruler wanting to solidify his legacy, over those that came before. Secondly, those buildings constructed in Taiwan during the early years of the Showa era tend to stand out more because they took a modern approach to construction in that they combined western techniques with Japanese design.
Note: It is important to take note that even though the early years of a new emperor’s reign are known for construction and infrastructure projects, the Showa era (1926-1989) started out suffering from the devastating effects of the Great Kanto Earthquake (関東大地震) of 1923, and a number of other economic factors resulting in the Shōwa Financial Crisis (昭和金融恐慌) of 1927. The Governor Generals Office in Taiwan at the time would have been responsible for fund raising for any construction project, but growing militarism back in Japan and the Second World War ensured that money for development projects was modest from the 1940s onward.
Preceding Emperor Showa, the Taisho Era (大正), from 1912 until 1926, was known for the way Japanese architects fused traditional design with Western architectural design, especially when it came to Art-Deco and the usage of reinforced concrete to build larger structures. Thus, the early years of the Showa era continued along that path with the preferred method of construction involving concrete rather wood. That being said, it was during this period that fervent Japanese nationalism was promoted throughout the empire, resulting in military campaigns throughout Asia.
Note: It was during this period that the strict Kominka (皇民化運動 / こうみんかせいさく), or mandatory ‘Japanization’ policies came into effect in Taiwan, which included the “National Language Movement” (国語運動) requiring citizens of the empire to speak Japanese as well as taking Japanese names under the ‘kaiseimei’ policy (改姓名 / かいせいめい). The reason I mention this now is that this is the same time when the name of the station was slightly changed to remove a common character used in Taiwanese Hokkien.
Taking into consideration that the Showa era spanned six decades before, during, and after the war - when we talk about the architecture of the era with regard to Taiwan, we have to focus primarily on what was constructed from 1926 until the 1940s, which ultimately differs somewhat from what you would have seen back in Japan.
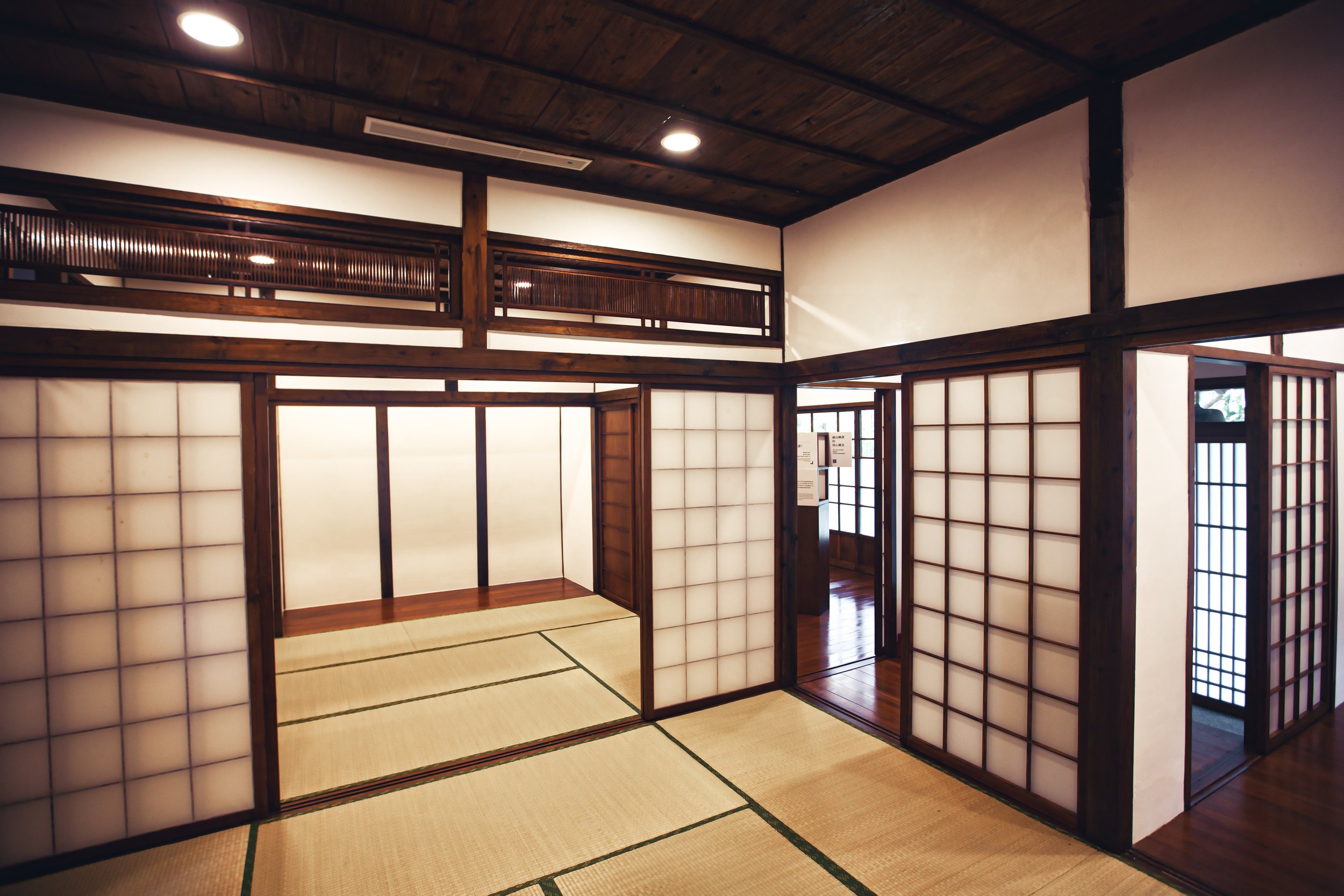
Yamakoashi Station was, as mentioned above, one of the first of Taiwan’s railway stations to receive funding for a complete rebuild and the building we can see today (albeit slightly altered from the original design) was meant to be a model for further construction projects around the country. The station maintained the traditional wooden walls within the interior, but were fortified with brick and reinforced concrete. Similarly, the traditional network of wooden beams and trusses within the building that assisted in supporting the roof were constructed of concrete rather than making use of wood, adding to the stability of the building.
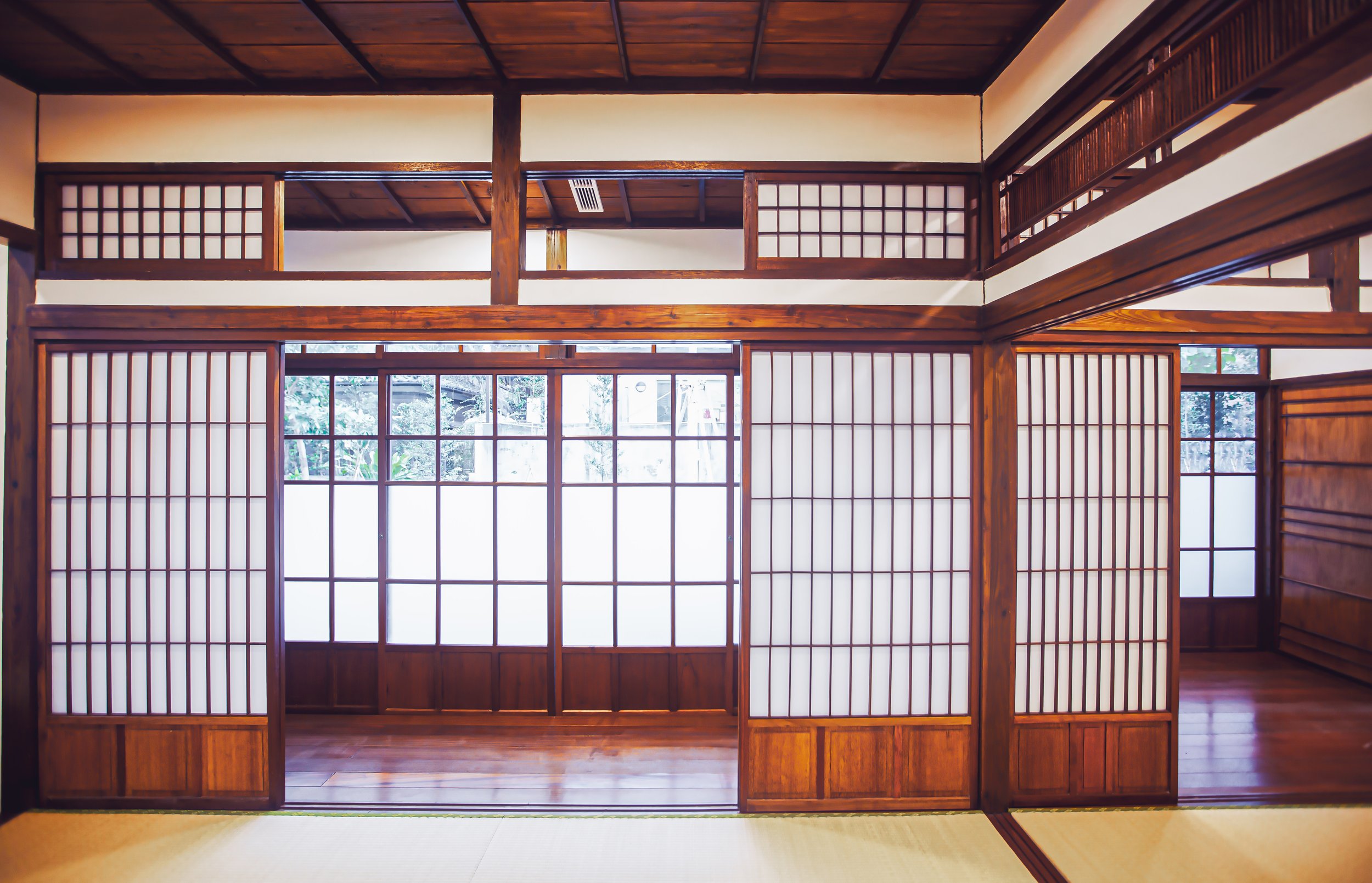
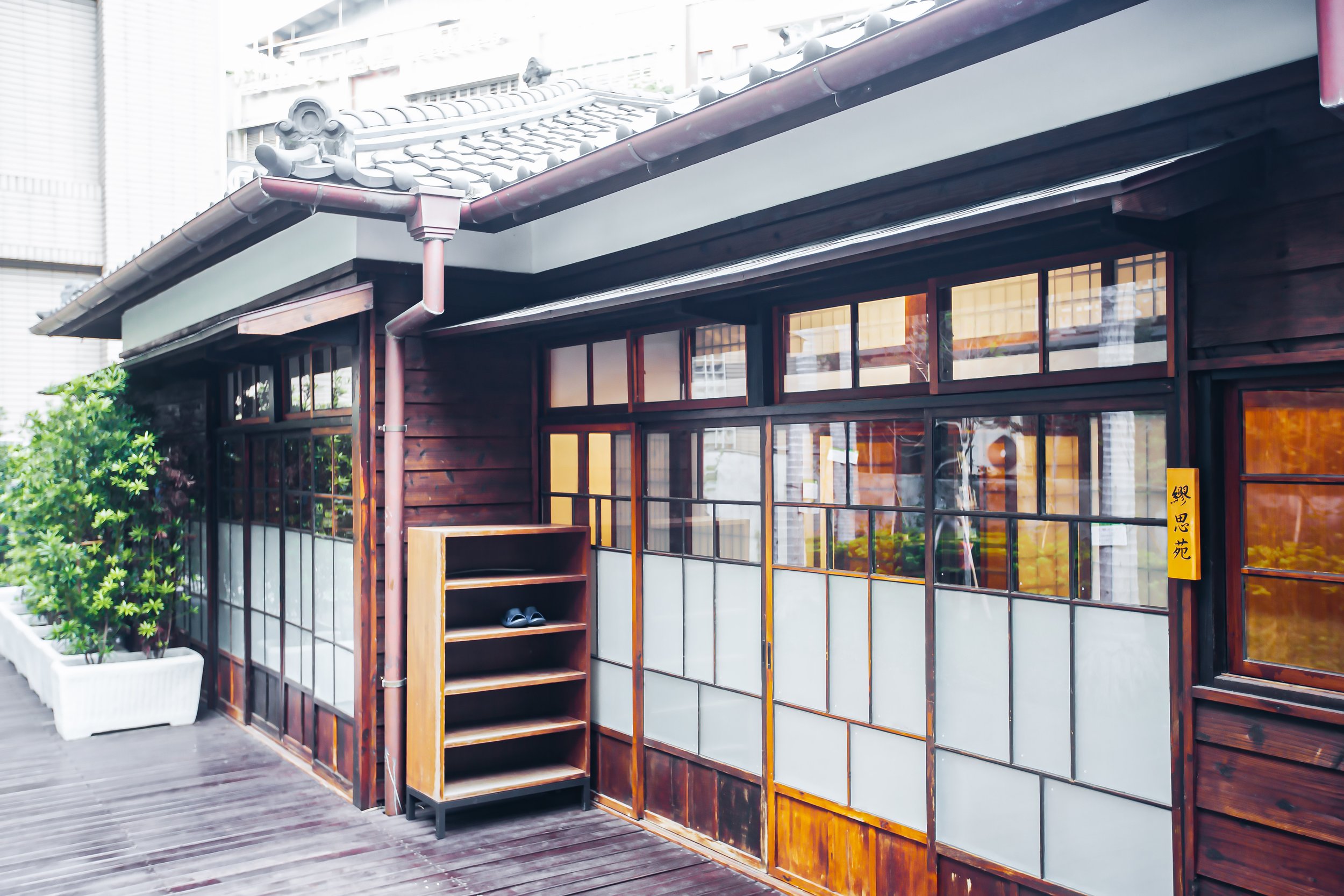
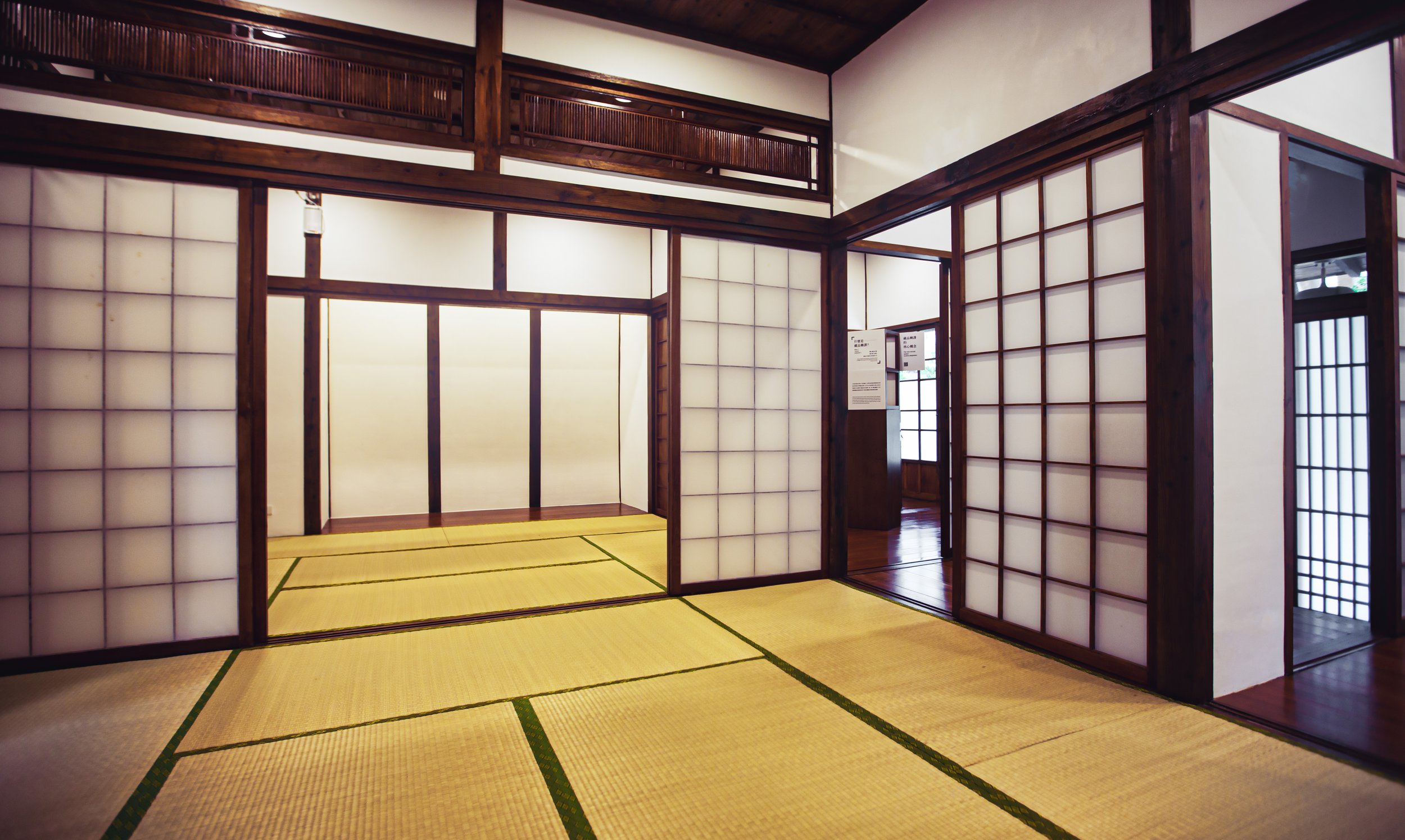
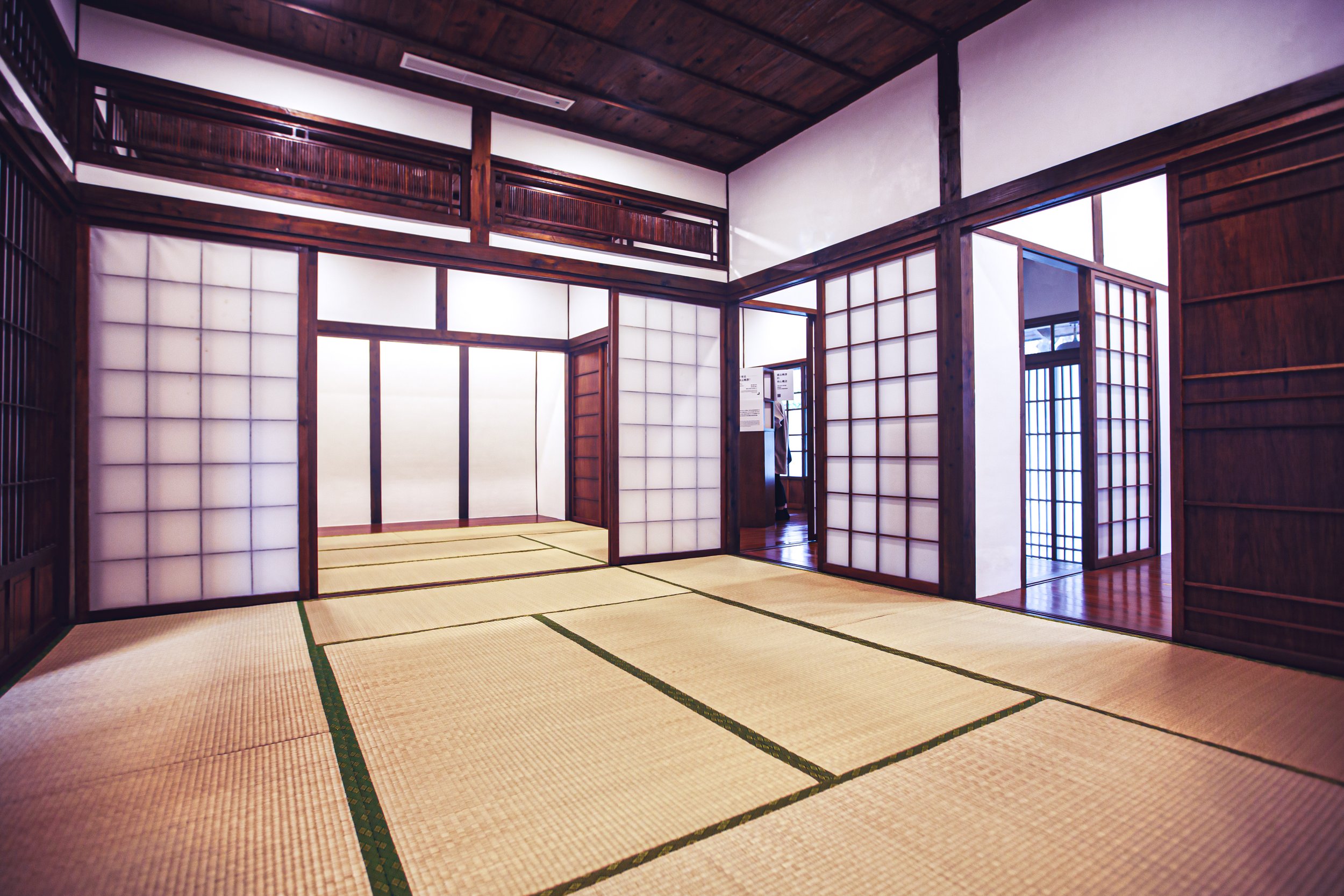
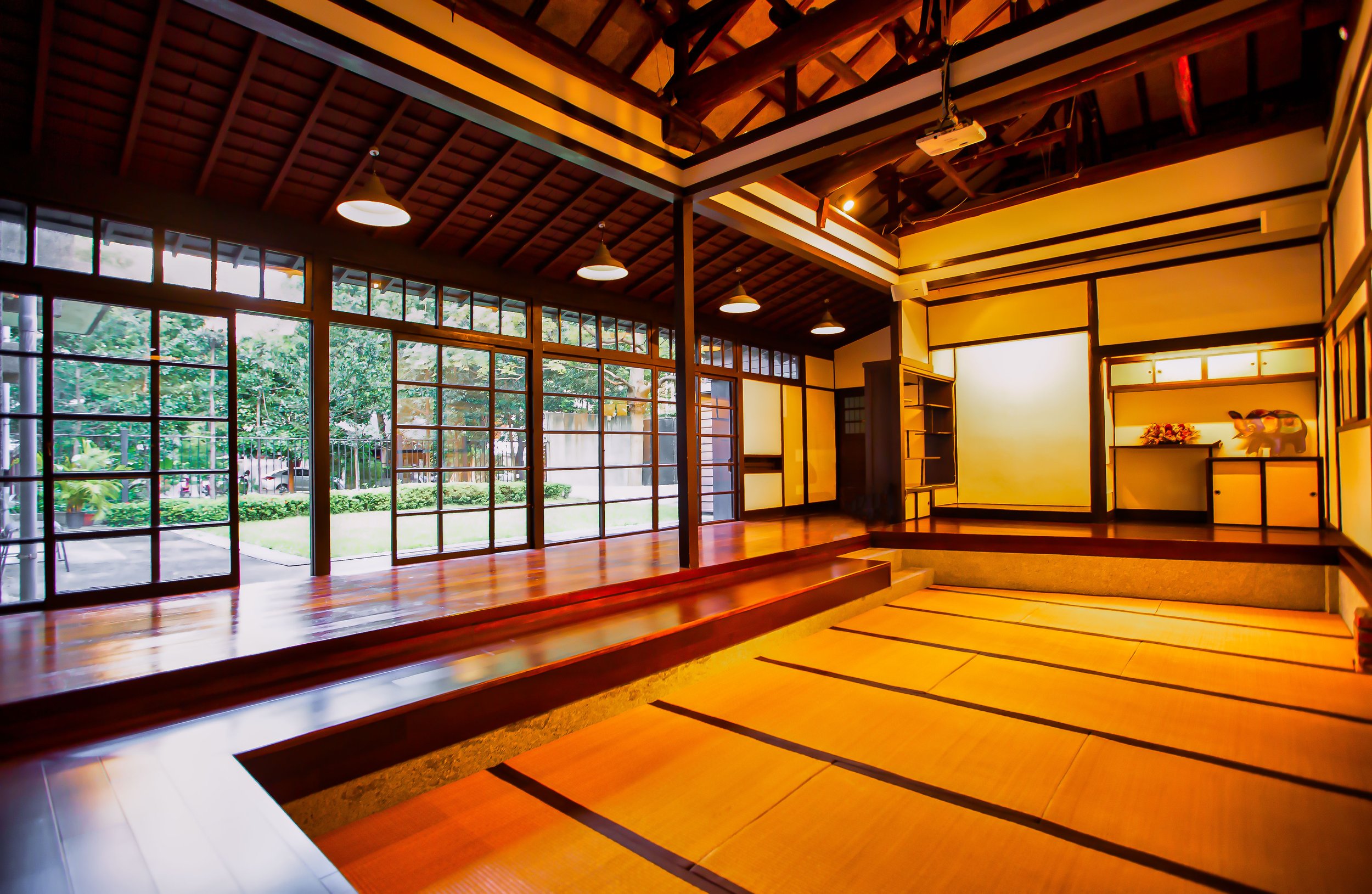
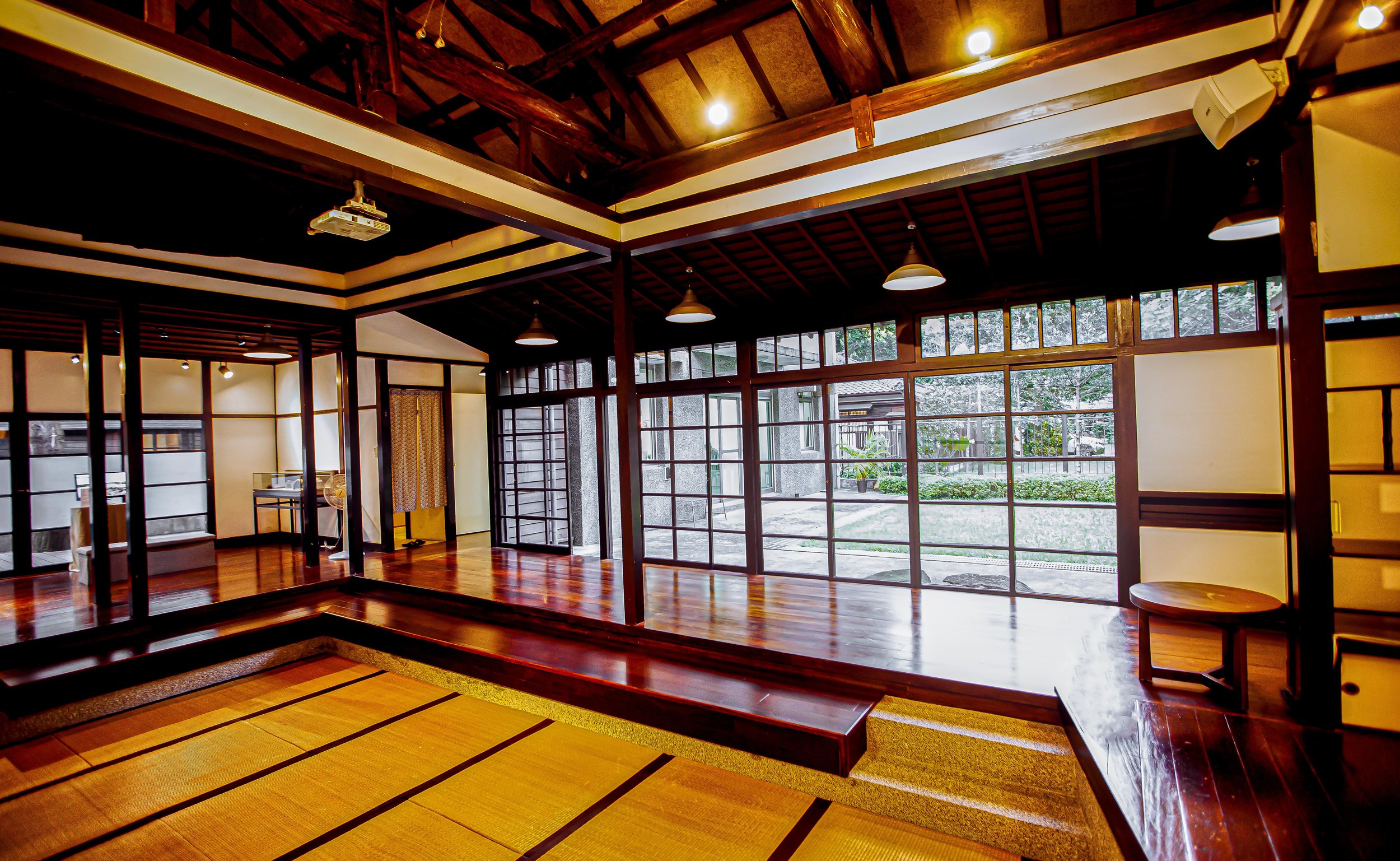
The building however does maintain a similar design to many of Taiwan’s other Japanese-era stations in that it is a one-story rectangular-shaped structure that was split in half. The western side of the building was used as the station hall while the slightly larger eastern side was used by the station master, and those in charge of maintaining the operations of the station.
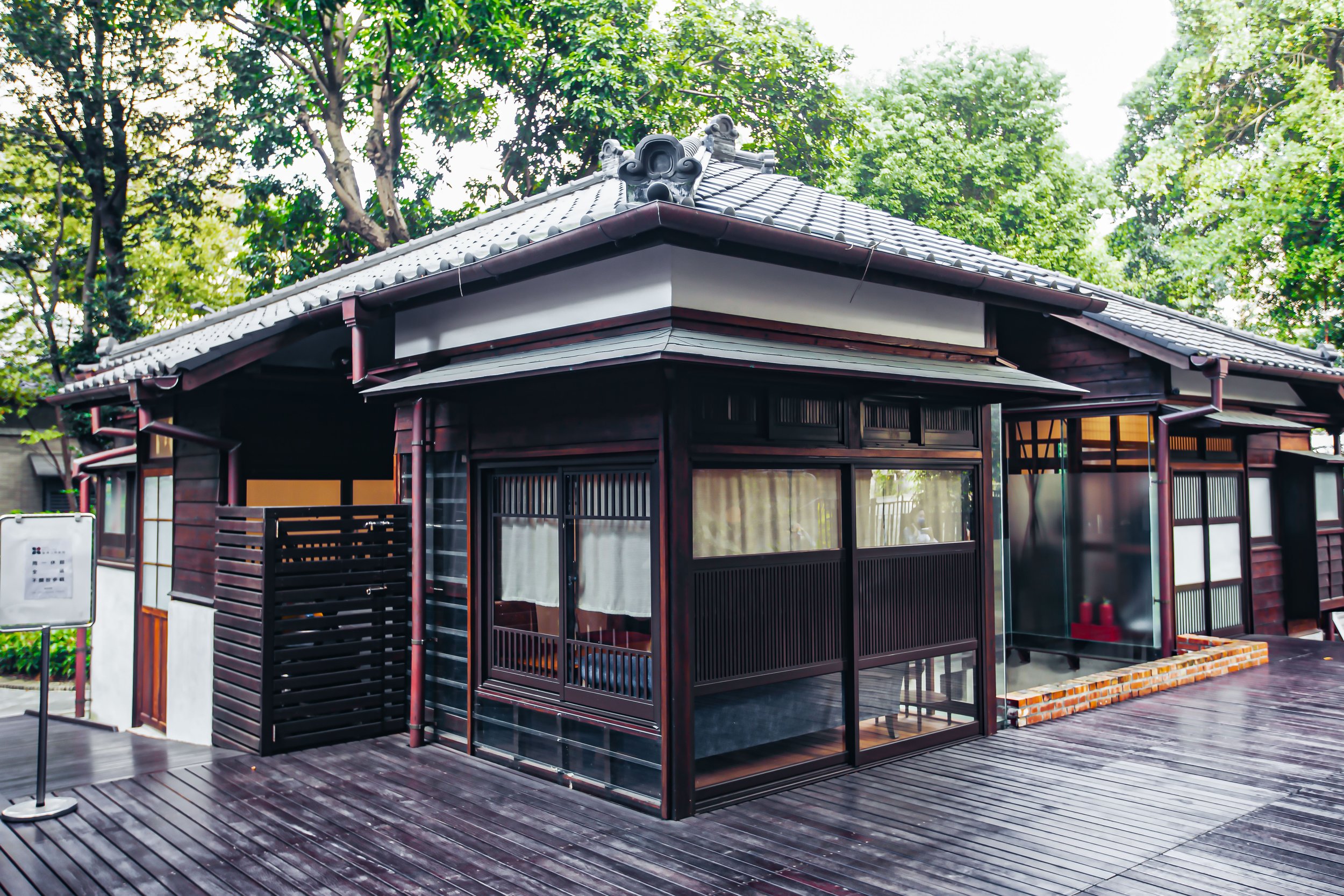
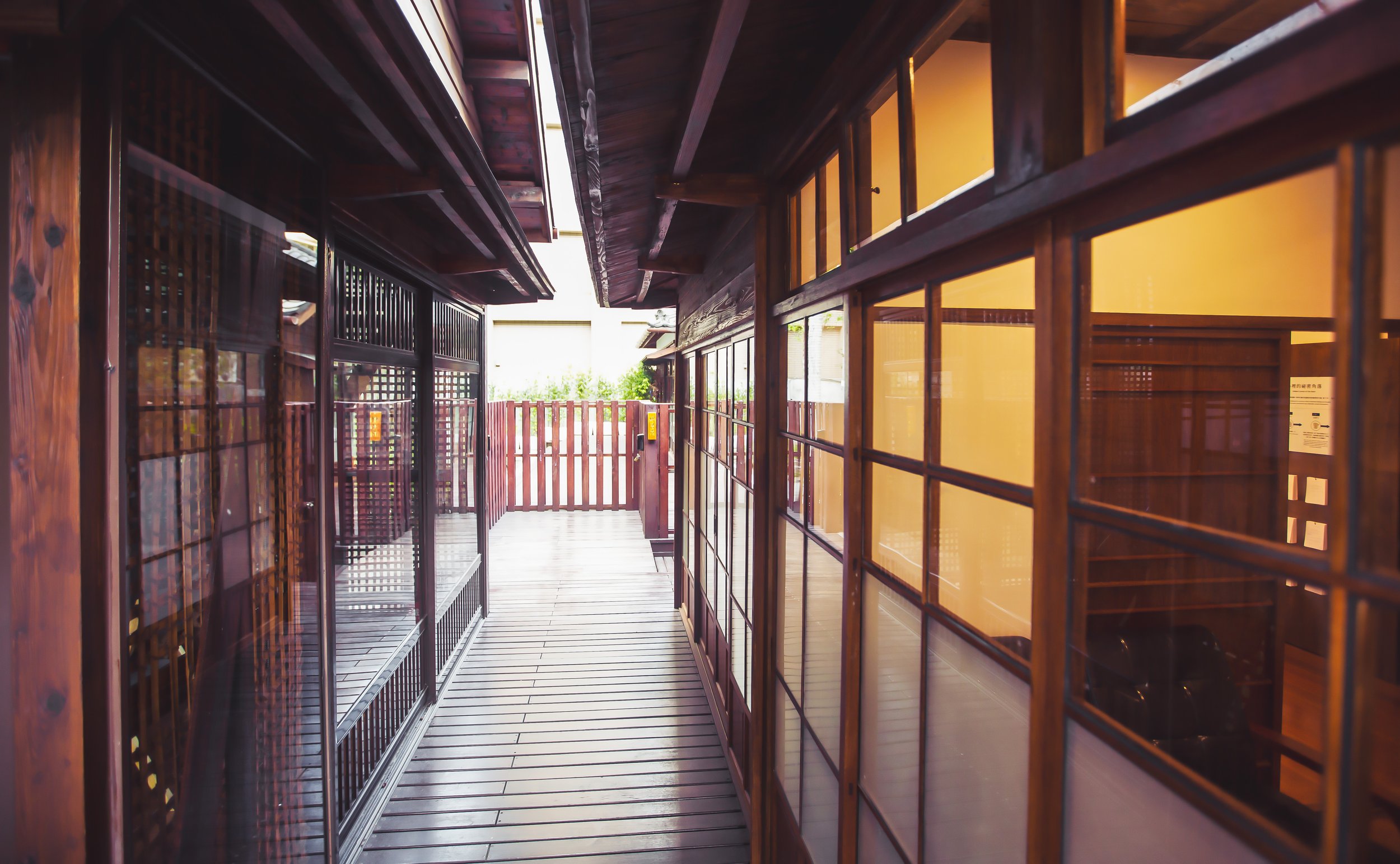
Surrounding half of the building in a U-shape (to the left of the station hall, around the side and to the back) you’ll find a number of concrete pillars used to help distribute the weight of the roof which extends beyond the base as well as providing a covered walk way around the building.
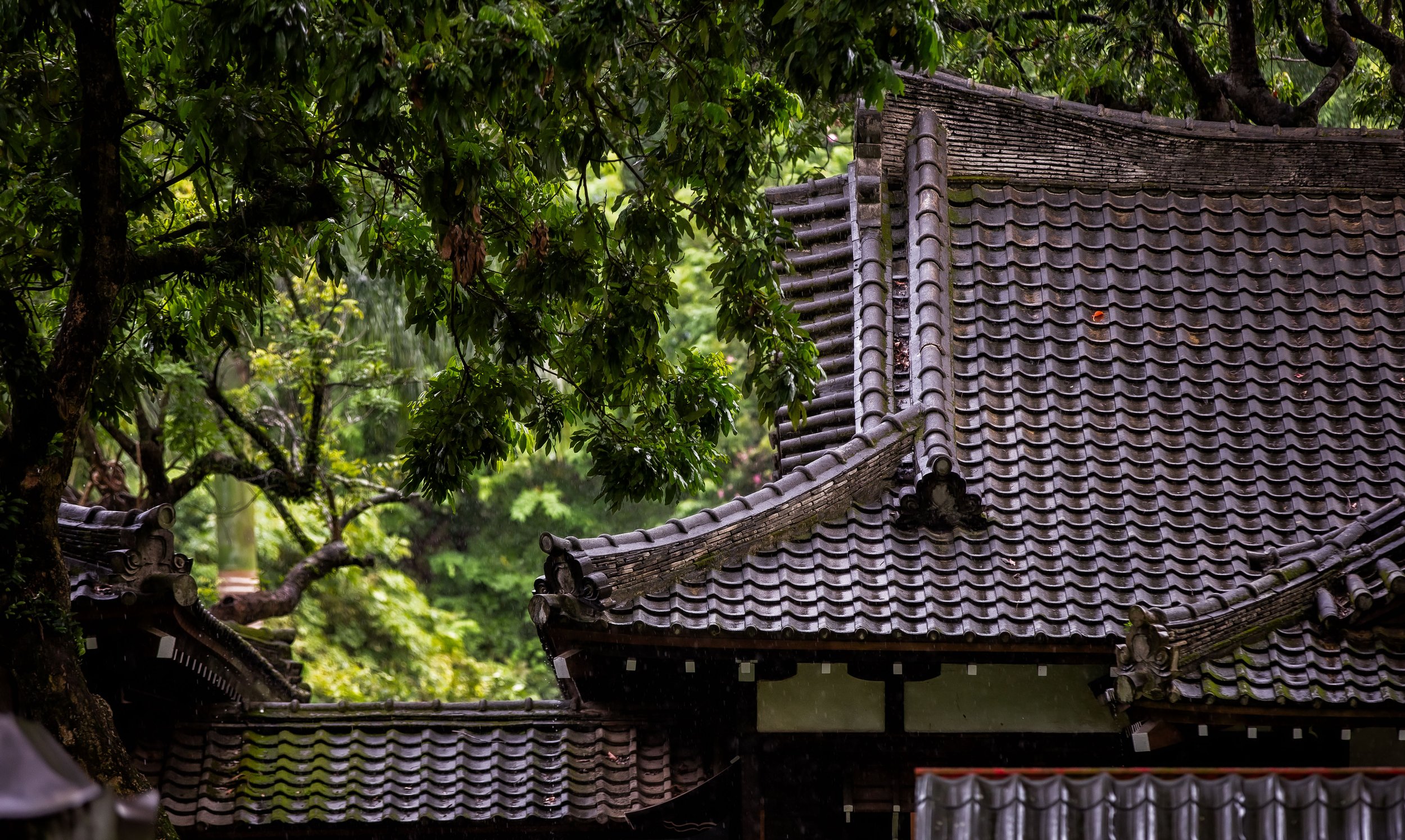
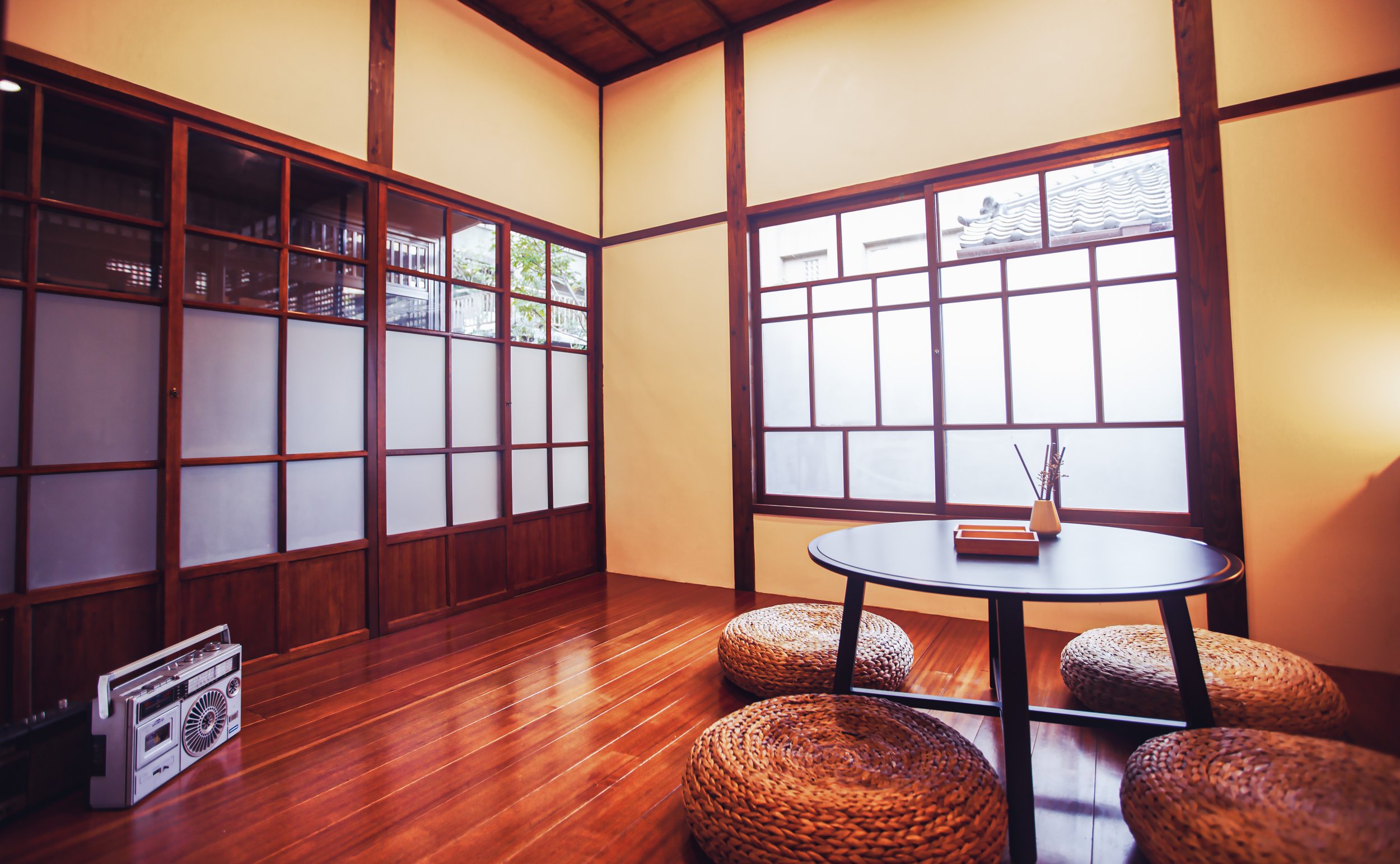
More specifically, the station was constructed using the traditional kirizuma-zukuri (切妻造) architectural design, including a variation of a ‘hip-and-gable roof’ (歇山頂) that rises up to resemble a mountain-like structure. Likened to that of an ‘open book’, or the Chinese character “入,” the architectural layout is similar to what we saw previously at the Longtan Martial Arts Hall, there is an obvious east-west fusion (和洋混和風建築) in the design, most noticeably with regard to the windows as there are large beautiful sliding-glass windows that surround the building and are set within wooden frames. You’ll also find windows on both the eastern and western ends of the building located just under the apex of the roof that allow light in from above.
Note: If you’re feeling confused by the roof description, I recommend taking a look at the link below, which rather nicely (or kawaii, if you will) illustrates some of the various styles of traditional Japanese roofs in manga form!
Link: A Manga Guide to the Beautiful Roofs in Japanese Architecture (Tsunagu Japan)
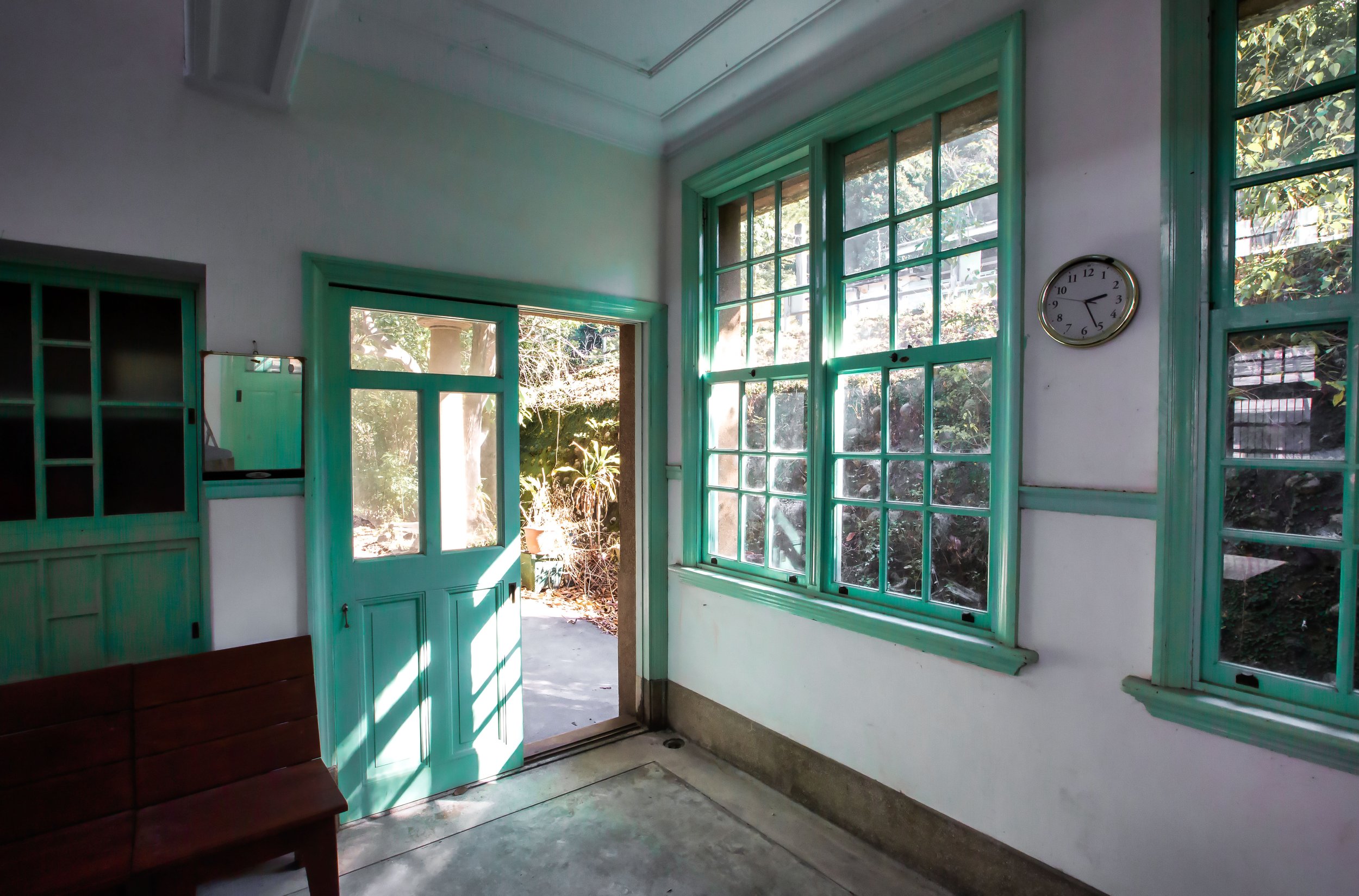
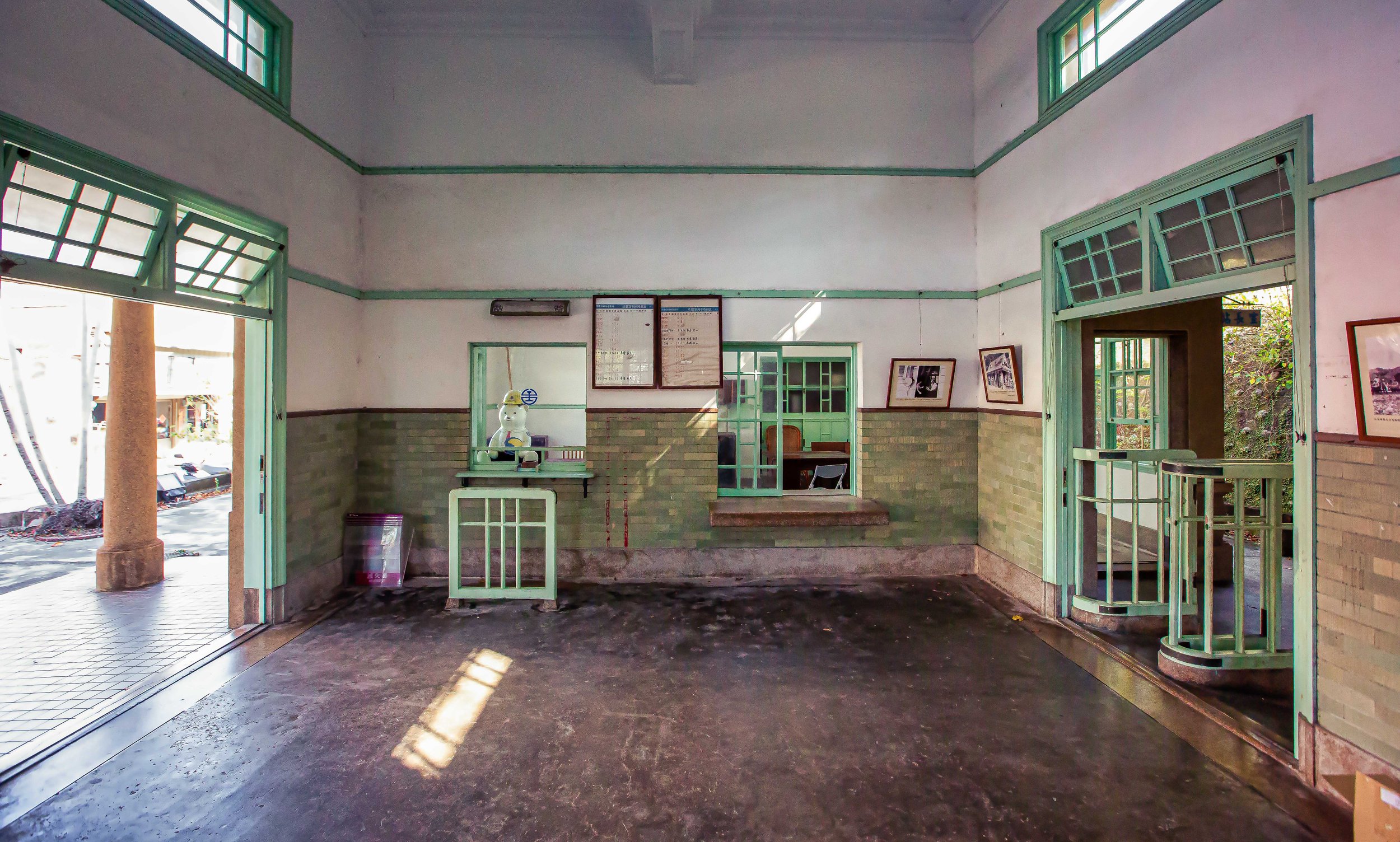
Having the building split into two halves meant that the interior space was somewhat limited between the public section and the area where the station’s employees worked. When you walk in the front door of the station, you’re automatically met with the ticket window on your right while the left-hand side was reserved as a passenger waiting area. The actual space between the front door and the door to where the turnstiles were located is only a few meters, so the building wasn’t actually constructed to serve a large amount of passengers at once.
The opposite side of the station hall would have been reserved as office space for the employees of the station, but that space likewise included pantry space, washrooms and a tool shed, so the space there was likewise cramped as well.
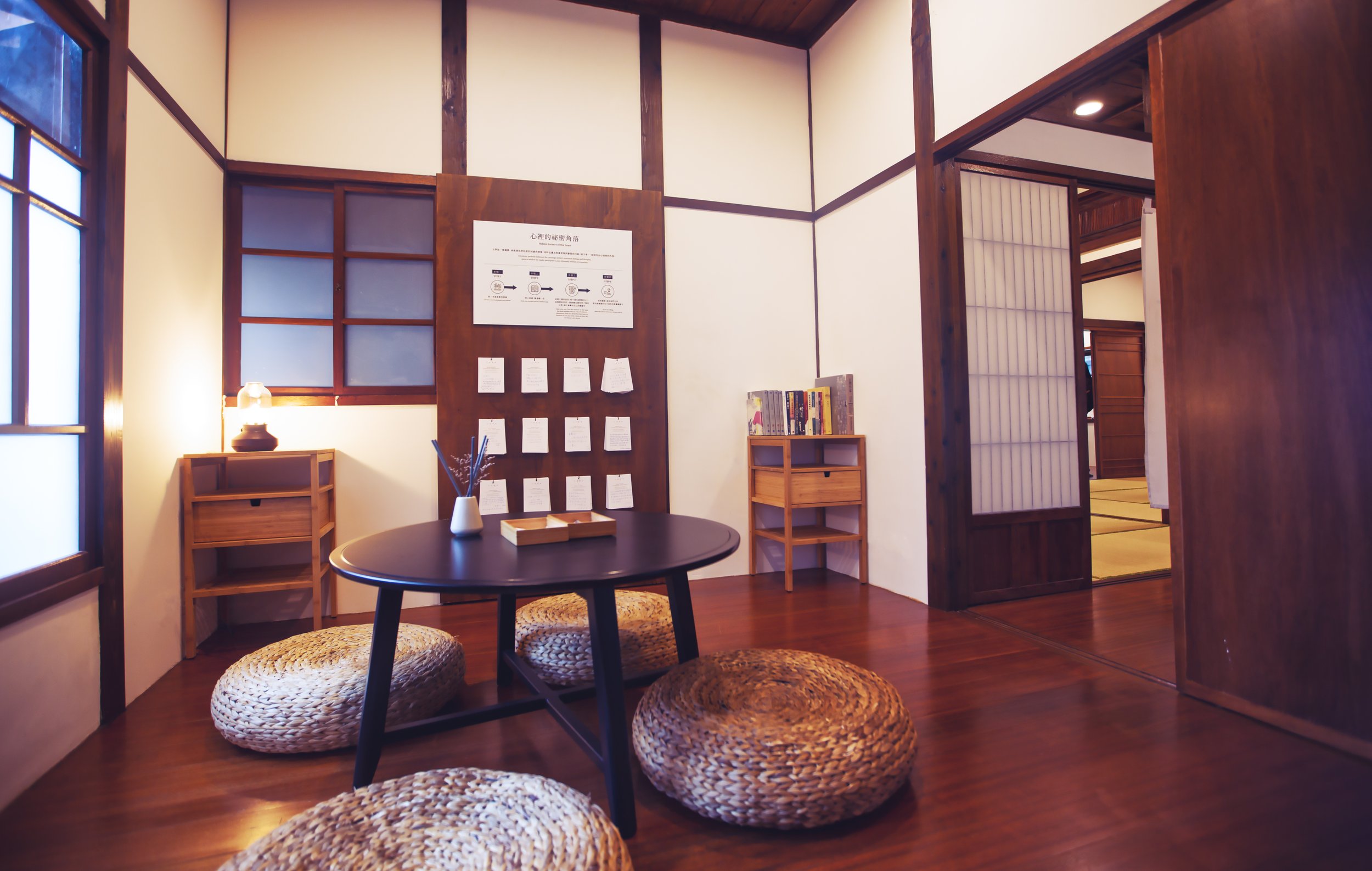
Today, both the station hall and the employee section are open to the public and you’re free to move back and forth between them. Unfortunately one of the aspects that seems to have stuck with the station is that the area continues to feel quite cramped given that both sides are filled with exhibitions taking up most of the free space.
Personally, I feel like all of the clutter distracts visitors from being able to enjoy the historic architecture of the interior of the building but the exhibitions within tend to change quite often, so when you visit, you may find yourself a bit luckier than I was.
Link: Shanjia Railway Station (New Taipei City Travel)
Contrary to what you’ll find on the New Taipei City website (linked above) with regard to the opening hours of the station, it is not open from 06:00-24:00 everyday. If you’d like to visit the station, its free of charge, but it is only open from 10:00-17:00, and is closed during national holidays.
Oh, and one last thing, an aspect of Japanese design that stands out at this station isn’t what you could technically refer to as part of the ‘architecture’, but is one of the most significant additions of this historic building - The century-old red-cotton tree (木棉樹) planted next to the building continues to thrive to this day and over the years has grown to twice the height of the station itself. The tree adds a natural element to the station that cannot be understated, and the fact that it continues to exist today makes the station a lot more beautiful.
Getting There
Address: #108 Zhongshan Road, Section 3, Shulin District, New Taipei City (新北市樹林區中山里中山路3段108號)
GPS: 24.972222, 121.392778
As is the case with any of my articles about Taiwan’s historic railway stations, I’m going to say something that shouldn’t really surprise you - When you ask what is the best way to get to the train station, the answer should be pretty obvious: Take the train!
Shanjia Railway Station is located six stops south of Taipei Main Station (台北車站), and should only take you around twenty minutes to get there on one of the convenient Commuter Trains (區間車). Given that there isn’t really very much else in the area, you’ll also be able to hop on the train again and head back to wherever you came from, or on to your next destination.
That being said, when I say that there isn’t much else in the area, that isn’t exactly true - the next station south of Shanjia is Yingge Station (鶯歌車站), where you’ll find the popular Yingge Ceramics Old Street (鶯歌老街). Likewise, on the opposite side of the Dahan River (大漢溪) you’ll find the similarly popular Sanxia Old Street (三峽老街), both of which are really cool to visit.
One important thing to note about visiting Shanjia Station on the train is that it is classified as a ‘simple station’, which essentially means that express trains won’t stop there. If you’ve gotten on one of those by mistake, you should get off at either Shulin Station (樹林火車站) if you’re traveling south, or at Yingge Station (鶯歌火車站) if you’re traveling north, and then switch to a local commuter train (區間車).
There are of course other methods of getting to the train station if you’d like to stop by for a visit, including car, bus, scooter, and bicycle. You don’t have to take the train, but if you do plan on visiting, you’d probably be better off making use of Taiwan’s excellent railway network.
If you are driving a car or a scooter, the station is a short drive from Taipei - Simply input the address or the GPS provided above into your Google Maps or your GPS and you’ll find yourself there in no time.
In front of the station you’ll find a bus stop that services buses #702, 802, 847, 852, 885, 889, and F611, most of which originate at Banqiao Bus Terminal (板橋轉運站), or across the river in Sanxia.
If you’re looking for a bit of exercise, you can easily follow the beautiful riverside bicycle paths south from Taipei or Banqiao all the way to the station, and beyond. Along the way, the paths pass through several wetland areas offering quite a bit of outdoor recreational activities for visitors to see and do. If you have a bike, or have rented a Youbike, you should have a pretty good time - and yes, there’s a YouBike Station in front of the train station, so if you’re feeling tired you’ll be able to park your bike there and hop on the train back home.
Gallery / Flickr (High Res Shots)
References
Shanjia Railway Station | 山佳車站 中文 | 山佳駅 日文 (Wiki)
山佳車站 (新北市觀光旅遊網)
山佳車站.見證時代交替的百年老車站 (旅行圖中)
山佳車站 (國家文化資產網)
山佳駅 (れとろ駅舎)
昔日採礦運煤的歷史痕跡,刻劃山佳的日式迷人 (微笑台灣)
Shanjia Station (iCulture)
Roof Typology and Composition in Traditional Japanese Architecture